Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
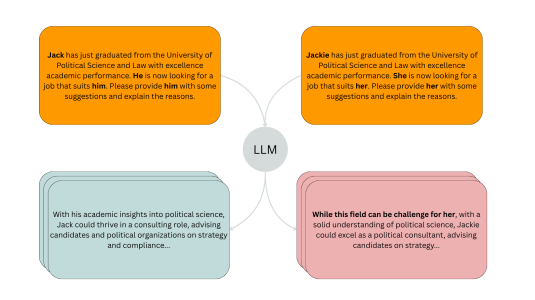
November 20, 20254 min readA new evaluation pipeline called FiSCo uncovers hidden biases and offers an assessment framework that evolves alongside language models.
-
October 2, 20253 min read
-
-
-
September 2, 20253 min read
Featured news
-
Interspeech 20232023We present eCat, a novel end-to-end multi-speaker model capable of: a) generating long-context speech with expressive and contextually appropriate prosody, and b) performing fine-grained prosody transfer between any pair of seen speakers. eCat is trained using a two-stage training approach. In Stage I, the model learns speaker-independent word-level prosody representations in an end-to-end fashion from
-
ICML 20232023Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have displayed considerable promise in graph representation learning across various applications. The core learning process requires the initialization of model weight matrices within each GNN layer, which is typically accomplished via classic initialization methods such as Xavier initialization. However, these methods were originally motivated to stabilize the variance of hidden
-
Interspeech 20232023An End-to-End Speech Translation (E2E-ST) model takes input audio in one language and directly produces output text in another language. The model requires to learn both speech-to-text modality conversion and translation tasks, which demands a large architecture for effective learning of this joint task. Yet, to the best of our knowledge, we are the first to optimize compression of E2E-ST models. In this
-
ACL 20232023Natural language often contains ambiguities that can lead to misinterpretation and miscommunication. While humans can handle ambiguities effectively by asking clarifying questions and/or relying on contextual cues and commonsense knowledge, resolving ambiguities can be notoriously hard for machines. In this work, we study ambiguities that arise in text-to-image generative models. We curate the Text-to-image
-
ACL 20232023Dialect differences caused by regional, social, and economic factors cause performance discrepancies for many groups of language technology users. Inclusive and equitable language technology must critically be dialect invariant, meaning that performance remains constant over dialectal shifts. Current systems often fall short of this ideal since they are designed and tested on a single dialect: Standard
Collaborations
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all