Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
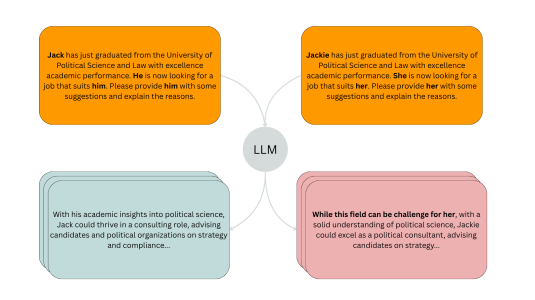
November 20, 20254 min readA new evaluation pipeline called FiSCo uncovers hidden biases and offers an assessment framework that evolves alongside language models.
-
October 2, 20253 min read
-
-
-
September 2, 20253 min read
Featured news
-
ACL Findings 20232023Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are becoming integral components of real world services relied upon by millions of users. Unfortunately, architects of these systems can find it difficult to ensure reliable performance as irrelevant details like random initialization can unexpectedly change the outputs of a trained system with potentially disastrous consequences. We formulate the model stability problem by studying
-
ACL Findings 20232023Open-domain question answering (ODQA) is a crucial task in natural language processing. A typical ODQA system relies on a retriever module to select relevant contexts from a large corpus for a downstream reading comprehension model. Existing ODQA datasets consist mainly of Wikipedia corpus, and are insufficient to study models’ generalizability across diverse domains, as models are trained and evaluated
-
ACL Findings 20232023Retrieval accuracy is crucial to the performance of open-domain question answering (ODQA) systems. Recent work has demonstrated that dense hierarchical retrieval (DHR), which retrieves document candidates first and then relevant passages from the refined document set, can significantly outperform the single stage dense passage retriever (DPR). While effective, this approach requires document structure information
-
ACL 20232023Large language models (LMs) beyond a certain scale, demonstrate the emergent capability of generating free-text rationales for their predictions via chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting. While CoT can yield dramatically improved performance, such gains are only observed for sufficiently large LMs. Even more concerning, there is little guarantee that the generated rationales are consistent with LM’s predictions
-
Interspeech 20232023Natural Language Understanding (NLU) systems such as chatbots or virtual assistants have seen a significant rise in popularity in recent times, thanks to availability of large volumes of user data. However, typical user data collected for training such models may suffer from sampling biases due to a variety of factors. In this paper, we study the impact of bias in the training data for intent classification
Collaborations
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all