Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
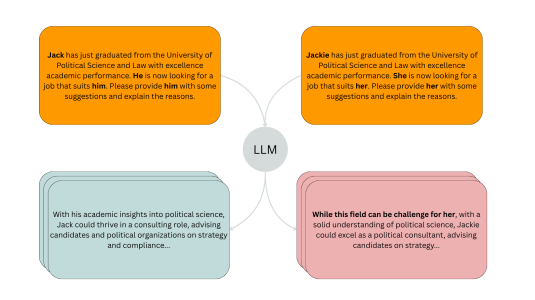
November 20, 20254 min readA new evaluation pipeline called FiSCo uncovers hidden biases and offers an assessment framework that evolves alongside language models.
-
-
-
September 2, 20253 min read
-
Featured news
-
EMNLP 20232023Rich and diverse knowledge-bases (KB) are foundational building blocks for online knowledge-sharing communities such as StackOverflow and Quora and applications such as conversational assistants (aka chatbots). A popular format for knowledge bases is question-answer pairs (or FAQs), where questions are designed to accurately match a multitude of queries. In this paper, we address the problem of automatic
-
EMNLP 20232023We present MultiCoNER V2, a dataset for fine-grained Named Entity Recognition covering 33 entity classes across 12 languages, in both monolingual and multilingual settings. This dataset aims to tackle the following practical challenges in NER: (i) effective handling of fine-grained classes that include complex entities like movie titles, and (ii) performance degradation due to noise generated from typing
-
EMNLP 20232023Personalization of automatic speech recognition (ASR) models is a widely studied topic because of its many practical applications. Most recently, attention-based contextual biasing techniques are used to improve the recognition of rare words and/or domain-specific entities. However, due to performance constraints, the biasing is often limited to a few thousand entities, restricting real-world usability.
-
EMNLP 20232023We propose InsightNet, a novel approach for the automated extraction of structured insights from customer reviews. Our end-to-end machine learning framework is designed to overcome the limitations of current solutions, including the absence of structure for identified topics, non-standard aspect names, and lack of abundant training data. The proposed solution builds a semi-supervised multi-level taxonomy
-
ASRU 20232023We explore the ability of large language models (LLMs) to act as speech recognition post-processors that perform rescoring and error correction. Our first focus is on instruction prompting to let LLMs perform these task without fine-tuning, for which we evaluate different prompting schemes, both zeroand few-shot in-context learning, and a novel “task activation” prompting method that combines causal instructions
Collaborations
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all