Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
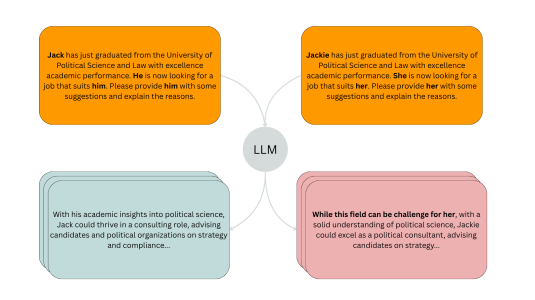
November 20, 20254 min readA new evaluation pipeline called FiSCo uncovers hidden biases and offers an assessment framework that evolves alongside language models.
-
-
-
September 2, 20253 min read
-
Featured news
-
SAT 20242024Quantum Computing (QC) is a new computational paradigm that promises significant speedup over classical computing in various domains. However, near-term QC faces numerous challenges, including limited qubit connectivity and noisy quantum operations. To address the qubit connectivity constraint, circuit mapping is required for executing quantum circuits on quantum computers. This process involves performing
-
2024Speaker Diarization (SD) systems are typically audio-based and operate independently of the ASR system in traditional speech transcription pipelines and can have speaker errors due to SD and/or ASR reconciliation, especially around speaker turns and regions of speech overlap. To reduce these errors, a Lexical Speaker Error Correction (LSEC), in which an external language model provides lexical information
-
NAACL 2024 Workshop on TrustNLP2024Large language models incorporate world knowledge and present breakthrough performances on zero-shot learning. However, these models capture societal bias (e.g., gender or racial bias) due to bias during the training process which raises ethical concerns or can even be potentially harmful. The issue is more pronounced in multi-modal settings, such as image captioning, as images can also add onto biases
-
2024Audio-visual representations leverage information from both modalities to produce joint representations. Such representations have demonstrated their usefulness in a variety of tasks. However, both modalities incorporated in the learned model might not necessarily be present all the time during inference. In this work, we study whether and how we can make exist- ing models, trained under pristine conditions
-
ICML 2024 Workshop on Foundation Models in the Wild2024Extrapolative protein design is a crucial task for automated drug discovery to design proteins with higher fitness than what has been seen in train- ing (eg. higher stability, tighter binding affinity, etc.). The current state-of-the-art methods assume that one can safely steer protein design in the extrapolation region by learning from pairs alone. We hypothesize that (1) noisy pairs do not accurately
Collaborations
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all