Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
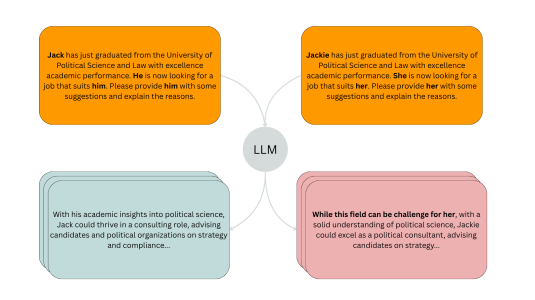
November 20, 20254 min readA new evaluation pipeline called FiSCo uncovers hidden biases and offers an assessment framework that evolves alongside language models.
-
-
-
September 2, 20253 min read
-
Featured news
-
2024Recent video masked autoencoder (MAE) works have de-signed improved masking algorithms focused on saliency. These works leverage visual cues such as motion to mask the most salient regions. However, the robustness of such visual cues depends on how often input videos match underlying assumptions. On the other hand, natural language description is an information dense representation of video that implicitly
-
IEEE Sensors2024Continuous back posture monitoring and correction can help to prevent back pains associated with improper back postures. However, existing solutions are expensive, use wearable sensors which usually require regular maintenance, or use cameras which have privacy issues. We introduce Di-Angle, a low-cost, battery-free, and reusable sensor capable of monitoring harmful back angles with high accuracy. Our novel
-
2024A complementary item is an item that pairs well with another item when consumed together. In the context of e-commerce, providing recommendations for complementary items is essential for both customers and stores. Current models for suggesting complementary items often rely heavily on user behavior data, such as co-purchase relationships. However, just because two items are frequently bought together does
-
2024Handling drafty partial code remains a notable challenge in real-time code suggestion applications. Previous work has demonstrated shortcomings of large language models of code (CodeLLMs) in completing partial code with potential bugs. In this study, we view partial code as implementation hints and fine-tune CodeLLMs to jointly rewrite and complete partial code into functional full programs. We explore
-
ICML 2024 Workshop on In-Context Learning2024We investigate the use of in-context learning and prompt engineering to estimate the contributions of training data in the outputs of instruction-tuned large language models (LLMs). We propose two novel approaches: (1) a similarity-based approach that measures the difference between LLM out-puts with and without provided context, and (2) a mixture distribution model approach that frames the problem of identifying
Collaborations
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all