Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
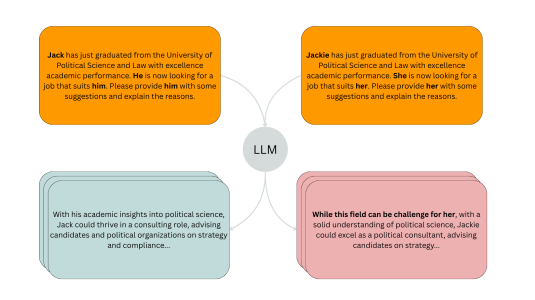
November 20, 20254 min readA new evaluation pipeline called FiSCo uncovers hidden biases and offers an assessment framework that evolves alongside language models.
-
-
-
September 2, 20253 min read
-
Featured news
-
NeurIPS 2023 Workshop on SyntheticData4ML2023We present CALICO, a method to fine-tune Large Language Models (LLMs) to localize conversational agent training data from one language to another. For slots (named entities), CALICO supports three operations: verbatim copy, literal translation, and localization, i.e. generating slot values more appropriate in the target language, such as city and airport names located in countries where the language is
-
NeurIPS 20232023In recent years, multi-objective optimization (MOO) emerges as a foundational problem underpinning many multi-agent multi-task learning applications. However, existing algorithms in MOO literature remain limited to centralized learning settings, which do not satisfy the distributed nature and data privacy needs of such multi-agent multi-task learning applications. This motivates us to propose a new federated
-
IEEE BigData 20232023The global e-commerce store needs to ensure compliance with various regulations at local, national, and international levels. One business use case is to identify face masks to avoid price gouging during times of high demand. In order to keep billions of items safe and legally compliant, it is important to ensure accurate classifications. Classification revisers aim to enhance classification accuracy by
-
EuroSys 20232023Multi-task model training has been adopted to enable a single deep neural network model (often a large language model) to handle multiple tasks (e.g., question answering and text summarization). Multi-task training commonly receives input sequences of highly different lengths due to the diverse contexts of different tasks. Padding (to the same sequence length) or packing (short examples into long sequences
-
CIKM 20232023Change Point Detection (CPD) models are used to identify abrupt changes in the distribution of a data stream and have a widespread practical use. CPD methods generally compare the distribution of data sequences before and after a given time step to infer if there is a shift in distribution at the said time step. Numerous divergence measures, which measure distance between data distributions of sequence
Collaborations
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all