Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
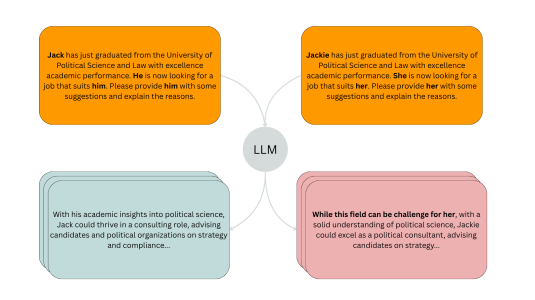
November 20, 20254 min readA new evaluation pipeline called FiSCo uncovers hidden biases and offers an assessment framework that evolves alongside language models.
-
-
-
September 2, 20253 min read
-
Featured news
-
NeurIPS 2023 Workshop on SyntheticData4ML2023Recently, diffusion models have demonstrated great potential for image synthesis due to their ability to generate high-quality synthetic data. However, when applied to sensitive data, privacy concerns have been raised about these models. In this paper, we evaluate the privacy risks of diffusion models through a membership inference (MI) attack, which aims to identify whether a target example is in the training
-
NeurIPS 20232023We derive the first finite-time logarithmic Bayes regret upper bounds for Bayesian bandits. In Gaussian bandits, we obtain O(cΔ log n) and O(ch log2n) bounds for an upper confidence bound algorithm, where ch and cΔ are constants depending on the prior distribution and the gaps of random bandit instances sampled from it, respectively. The latter bound asymptotically matches the lower bound of Lai (1987).
-
NeurIPS 20232023Membership inference attacks are designed to determine, using black-box access to trained models, whether a particular example was used in training or not. Membership inference can be formalized as a hypothesis-testing problem. The most effective existing attacks estimate the distribution of some test statistic (usually the model’s confidence on the true label) on points that were (and were not) used in
-
NeurIPS 20232023We focus on the task of approximating the optimal value function in deep reinforcement learning. This iterative process is comprised of solving a sequence of optimization problems where the loss function changes per iteration. The common approach to solving this sequence of problems is to employ modern variants of the stochastic gradient descent algorithm such as Adam. These optimizers maintain their own
-
Robotic Computing 20232023Home robots operate in diverse and dynamic environments, delivering a range of functions that enhance utility. Many of these functions span extended periods, from weeks to months, typically improving through observations and interactions. Efficient development and validation of these functions necessitate simulations that can run faster than real time. However, many current robot simulators focus on high-fidelity
Collaborations
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all