Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
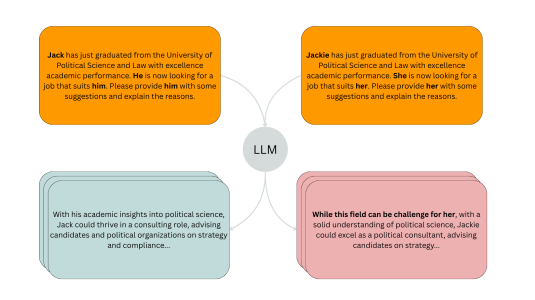
November 20, 20254 min readA new evaluation pipeline called FiSCo uncovers hidden biases and offers an assessment framework that evolves alongside language models.
-
-
-
September 2, 20253 min read
-
Featured news
-
2024Conversational systems often rely on embedding models for intent classification and intent clustering tasks. The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs), which enable instructional embeddings allowing one to adjust semantics over the embedding space using prompts, are being viewed as a panacea for these downstream conversational tasks. However, traditional evaluation benchmarks rely solely on task metrics
-
ICML 2024, TPDP 20242024Recently, diffusion models have become popular tools for image synthesis due to their high-quality outputs. However, like other large models, they may leak private information about their training data. Here, we demonstrate a privacy vulnerability of diffusion models through a membership inference (MI) attack, which aims to identify whether a target example belongs to the training set when given the trained
-
2024A large branch of explainable machine learning is grounded in cooperative game theory. However, research indicates that game-theoretic explanations may mislead or be hard to interpret. We argue that often there is a critical mismatch between what one wishes to explain (e.g. the output of a classifier) and what current methods such as SHAP explain (e.g. the scalar probability of a class). This paper addresses
-
FaCT 20242024Updates to Machine Learning as a Service (MLaaS) APIs may affect downstream systems that depend on their predictions. However, performance changes introduced by these updates are poorly documented by providers and seldom studied in the literature. As a result, API producers and consumers are left wondering: do model updates introduce performance changes that could adversely affect users’ system? Ideally
-
2024Quantifying the degree of similarity between images is a key copyright issue for image-based machine learning. In legal doctrine however, determining the degree of similarity between works requires subjective analysis, and fact-finders (judges and juries) can demonstrate considerable variability in these subjective judgement calls. Images that are structurally similar can be deemed dissimilar, whereas images
Collaborations
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all