Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
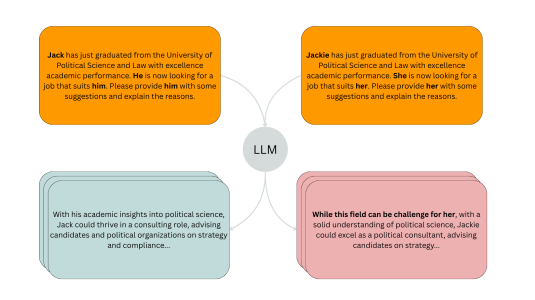
November 20, 20254 min readA new evaluation pipeline called FiSCo uncovers hidden biases and offers an assessment framework that evolves alongside language models.
-
October 2, 20253 min read
-
-
-
September 2, 20253 min read
Featured news
-
SIGDIAL 20232023Dialogue act annotations are important to improve response generation quality in taskoriented dialogue systems. However, it can be challenging to use dialogue acts to control response generation in a generalizable way because different datasets and tasks may have incompatible annotations. While alternative methods that utilize latent action spaces or reinforcement learning do not require explicit annotations
-
Interspeech 20232023To translate speech for automatic dubbing, machine translation needs to be isochronous, i.e. translated speech needs to be aligned with the source in terms of speech durations. We introduce target factors in a transformer model to predict durations jointly with target language phoneme sequences. We also introduce auxiliary counters to help the decoder to keep track of the timing information while generating
-
ACL Findings 20232023Knowledge graph embeddings (KGE) have been extensively studied to embed large-scale relational data for many real-world applications. Existing methods have long ignored the fact many KGs contain two fundamentally different views: high-level ontology-view concepts and fine-grained instance-view entities. They usually embed all nodes as vectors in one latent space. However, a single geometric representation
-
SC232023Memory-based Temporal Graph Neural Networks are powerful tools in dynamic graph representation learning and have demonstrated superior performance in many real-world applications. However, their node memory favors smaller batch sizes to capture more dependencies in graph events and needs to be maintained synchronously across all trainers. As a result, existing frameworks suffer from accuracy loss when scaling
-
ICCV 20232023Unsupervised object-centric learning methods allow the partitioning of scenes into entities without additional localization information and are excellent candidates for reducing the annotation burden of multiple-object tracking (MOT) pipelines. Unfortunately, they lack two key properties: objects are often split into parts and are not consistently tracked over time. In fact, state-of-the-art models achieve
Collaborations
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all