Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
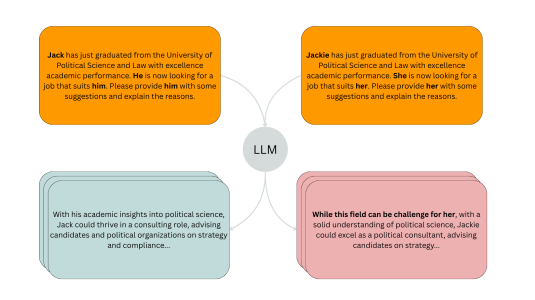
November 20, 20254 min readA new evaluation pipeline called FiSCo uncovers hidden biases and offers an assessment framework that evolves alongside language models.
-
-
-
September 2, 20253 min read
-
Featured news
-
WACV 20242024Lipstick virtual try-on (VTO) experiences have become widespread across the e-commerce sector and assist users in eliminating the guesswork of shopping online. How-ever, such experiences still lack in both realism and accuracy. In this work, we propose LipAT, a neural framework that blends the strengths of Physics-Based Rendering (PBR) and Neural Style Transfer (NST) approaches to directly apply lipstick
-
WACV 20242024Large vision-language representation learning models like CLIP have demonstrated impressive performance for zero-shot transfer to downstream tasks while largely benefiting from inter-modal (image-text) alignment via contrastive objectives. This downstream performance can further be enhanced by full-scale fine-tuning which is often compute intensive, requires large labelled data, and can reduce out-of-distribution
-
WACV 20242024In this paper, we address the detection of co-occurring salient objects (CoSOD) in an image group using frequency statistics in an unsupervised manner, which further enable us to develop a semi-supervised method. While previous works have mostly focused on fully supervised CoSOD, less attention has been allocated to detecting co-salient objects when limited segmentation annotations are available for training
-
WACV 20242024Data augmentation is vital for object detection tasks that require expensive bounding box annotations. Recent successes in diffusion models have inspired the use of diffusion-based synthetic images for data augmentation. However, existing works have primarily focused on image classification, and their applicability to boost object detection’s performance remains unclear. To address this gap, we propose
-
WACV 20242024The asymmetrical retrieval setting is a well suited solution for resource constrained applications such as face recognition and image retrieval. In this setting, a large model is used for indexing the gallery while a lightweight model is used for querying. The key principle in such systems is ensuring that both models share the same embedding space. Most methods in this domain are based on knowledge distillation
Collaborations
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all