Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
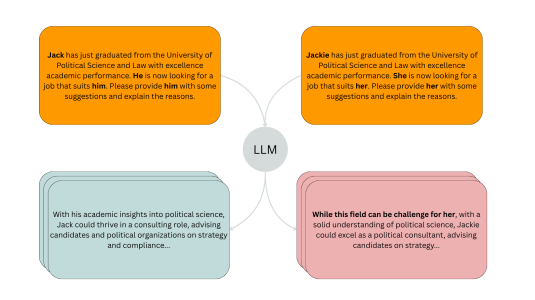
November 20, 20254 min readA new evaluation pipeline called FiSCo uncovers hidden biases and offers an assessment framework that evolves alongside language models.
-
-
-
September 2, 20253 min read
-
Featured news
-
2024Existing dense retrieval systems utilize the same model architecture for encoding both the passages and the queries, even though queries are much shorter and simpler than passages. This leads to high latency of the query encoding, which is performed online and therefore might impact user experience. We show that combining a standard large passage encoder with a small efficient query encoder can provide
-
2024We investigate the problem of synthesizing relevant visual imagery from generic long-form text, leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) and Text-to-Image Models (TIMs). Current Text-to-Image models require short prompts that describe the image content and style explicitly. Unlike image prompts, generation of images from general long-form text requires the image synthesis system to derive the visual content
-
2024In deep metric learning for visual recognition, the calibration of distance thresholds is crucial for achieving desired model performance in the true positive rates (TPR) or true negative rates (TNR). However, calibrating this threshold presents challenges in open-world scenarios, where the test classes can be entirely disjoint from those encountered during training. We define the problem of finding distance
-
2024Single document news summarization has seen substantial progress on faithfulness in recent years, driven by research on the evaluation of factual consistency, or hallucinations. We ask whether these advances carry over to other text summarization domains. We propose a new evaluation benchmark on topic-focused dialogue summarization, generated by LLMs of varying sizes. We provide binary sentence-level human
-
2024Pre-trained masked language models, such as BERT, perform strongly on a wide variety of NLP tasks and have become ubiquitous in recent years. The typical way to use such models is to fine-tune them on downstream data. In this work, we aim to study how the difference in domains between the pre-trained model and the task effects its final performance. We first devise a simple mechanism to quantify the domain
Collaborations
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all