Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
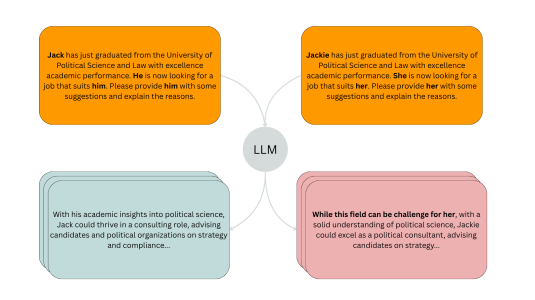
November 20, 20254 min readA new evaluation pipeline called FiSCo uncovers hidden biases and offers an assessment framework that evolves alongside language models.
-
-
-
September 2, 20253 min read
-
Featured news
-
2024Dialog systems, such as voice assistants, are expected to engage with users in complex, evolving conversations. Unfortunately, traditional automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems deployed in such applications are usually trained to recognize each turn independently and lack the ability to adapt to the conversational context or incorporate user feedback. In this work, we introduce a general framework
-
2024Recent advances in retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) have initiated a new era in repository-level code completion. However, the invariable use of retrieval in existing methods exposes issues in both efficiency and robustness, with a large proportion of the retrieved contexts proving unhelpful or harmful to code language models (code LMs). In this paper, we propose a selective RAG framework to avoid retrieval
-
Finite-time convergence and sample complexity of actor-critic multi-objective reinforcement learning2024Reinforcement learning with multiple, potentially conflicting objectives is pervasive in real-world applications, while this problem remains theoretically under-explored. This paper tackles the multi-objective reinforcement learning (MORL) problem and introduces an innovative actor-critic algorithm named MOAC which finds a policy by iteratively making trade-offs among conflicting reward signals. Notably
-
2024Existing Large Language Models (LLMs) usually remain static after deployment, which might make it hard to inject new knowledge into the model. We aim to build models containing a considerable portion of self-updatable parameters, enabling the model to integrate new knowledge effectively and efficiently. To this end, we introduce MemoryLLM, a model that comprises a transformer and a fixed-size memory pool
-
2024This paper proposes the use of “multicalibration” to yield interpretable and reliable confidence scores for outputs generated by large language models (LLMs). Multicalibration asks for calibration not just marginally, but simultaneously across various intersecting groupings of the data. We show how to form groupings for prompt/completion pairs that are correlated with the probability of correctness via
Collaborations
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all