Time series forecasting and graph representations of data are both major topics of research at Amazon: time series forecasting is crucial to both supply chain optimization and product recommendation, and graph representations help make sense of the large datasets that are common at Amazon’s scale, such as the Amazon product catalogue.
So it’s no surprise that both topics are well represented among the Amazon papers at the 2022 International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), which takes place this week. Another paper also touches on one of Amazon’s core scientific interests, natural-language processing, or computation involving free-form text inputs.
The remaining Amazon papers discuss more general machine learning techniques, such as data augmentation, or automatically selecting or generating training examples that can improve the performance of machine learning models. Another paper looks at dataset optimization more generally, proposing a technique that could be used to evaluate individual examples for inclusion in a dataset or exclusion from it. And two papers from Amazon Web Services’ Causal-Representation Learning team, which includes Amazon vice president and distinguished scientist Bernhard Schölkopf, examine the limitations of existing approaches to machine learning.
Graphs
Graphs represent data as nodes, usually depicted as circles, and edges, usually depicted as line segments connecting nodes. Graph-structured data can make machine learning more efficient, because the graph explicitly encodes relationships that a machine learning model would otherwise have to infer from data correlations.
Graph neural networks (GNNs) are a powerful tool for working with graph-structured data. Like most neural networks, GNNs produce embeddings, or fixed-length vector representations of input data, that are useful for particular computational tasks. In the case of GNNs, the embeddings capture information about both the object associated with a given node and the structure of the graph.
In real-world applications — say, a graph indicating which products tend to be purchased together — some nodes may not be connected to any others, and some connections may be spurious inferences from sparse data. In “Cold Brew: Distilling graph node representations with incomplete or missing neighborhoods”, Amazon scientists present a method for handling nodes whose edge data is absent or erroneous.
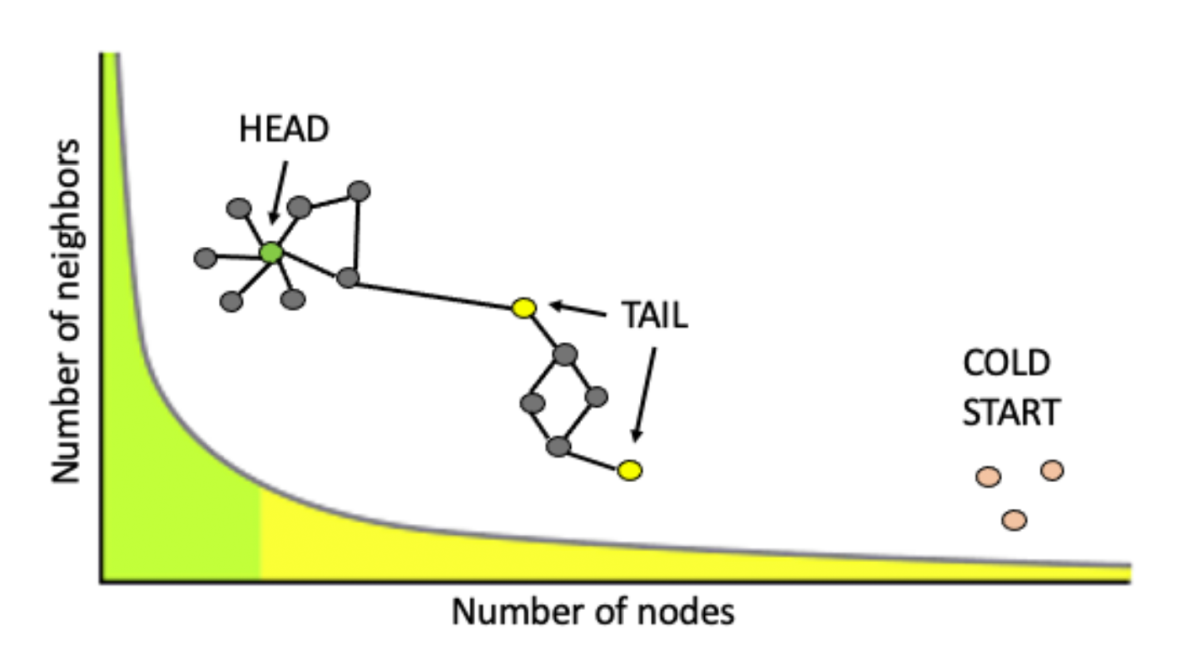
In a variation on knowledge distillation, they use a conventional GNN, which requires that each input node be connected to the rest of the graph, to train a teacher network that can produce embeddings for connected nodes. Then they train a standard multilayer perceptron — a student network — to mimic the teacher’s outputs. Unlike a conventional GNN, the student network doesn’t explicitly use structural data to produce embeddings, so it can also handle unconnected nodes. The method demonstrates significant improvements over existing methods of inferring graph structure on several benchmark datasets.
Across disciplines, AI research has recently seen a surge in the popularity of self-supervised learning, in which a machine learning model is first trained on a “proxy task”, which is related to but not identical to the target task, using unlabeled or automatically labeled data. Then the model is fine-tuned on labeled data for the target task.
With GNNs, the proxy tasks generally teach the network only how to represent node data. But in “Node feature extraction by self-supervised multi-scale neighborhood prediction”, Amazon researchers and their colleagues at the University of Illinois and UCLA present a proxy task that teaches the GNN how to represent information about graph structure as well. Their approach is highly scalable, working with graphs with hundreds of millions of nodes, and in experiments, they show that it improves GNN performance on three benchmark datasets, by almost 30% on one of them.
The approach, which builds on Amazon’s XR-Transformer model and is known as GIANT-XRT, has already been widely adopted and is used by the leading teams in several of the public Open Graph Benchmark competitions hosted by Stanford University (leaderboard 1 | leaderboard 2 | leaderboard 3).
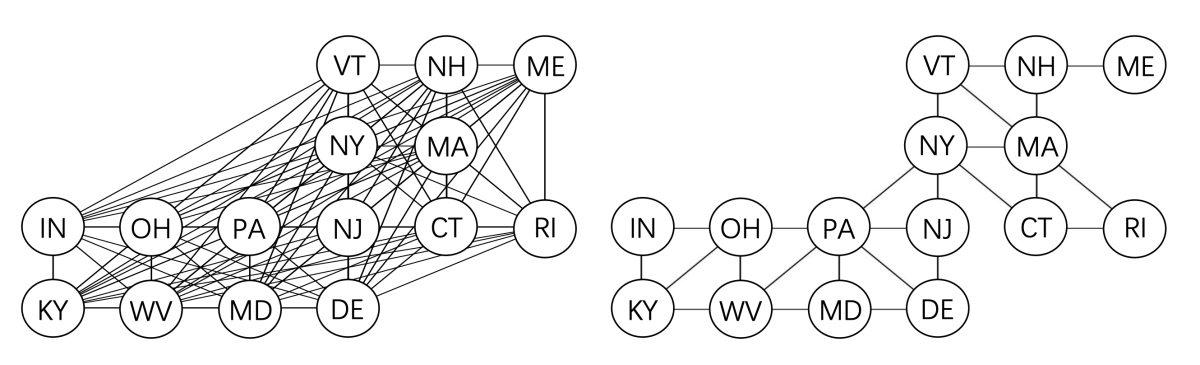
A third paper, “Graph-relational domain adaptation”, applies graphs to the problem of domain adaptation, or optimizing a machine learning model to work on data with a different distribution than the data it was trained on. Conventional domain adaptation techniques treat all target domains the same, but the Amazon researchers and their colleagues at Rutgers and MIT instead use graphs to represent relationships among all source and target domains. For instance, weather patterns in adjacent U.S. states tend to be more similar than the weather patterns in states distant from each other. In experiments, the researchers show that their method improves on existing domain adaptation methods on both synthetic and real-world datasets.
Time series
Time series forecasting is essential to demand prediction, which Amazon uses to manage inventory, and it’s also useful for recommendation, which can be interpreted as continuing a sequence of product (say, music or movie) selections.
In “Bridging recommendation and marketing via recurrent intensity modeling”, Amazon scientists adapt existing mechanisms for making personal recommendations on the basis of time series data (purchase histories) to the problem of identifying the target audience for a new product.
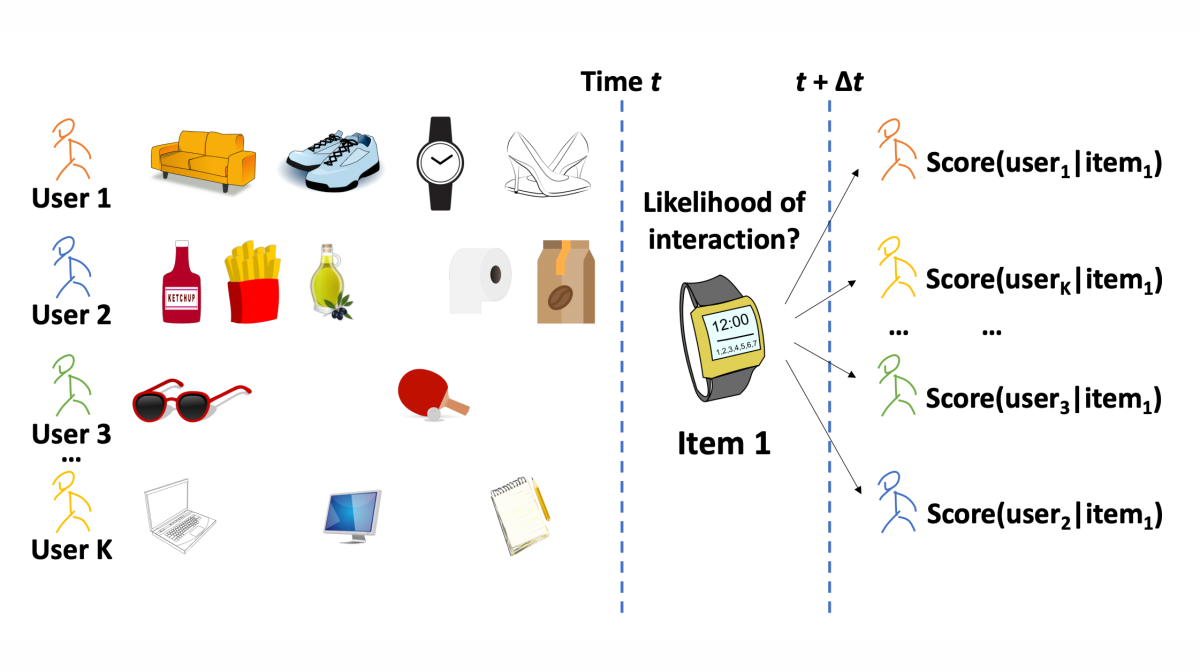
Where methods for identifying a product’s potential customers tend to treat customers as atemporal collections of purchase decisions, the Amazon researchers instead frame the problem as optimizing both the product’s relevance to the customer and the customer’s activity level, or likelihood of buying any product in a given time span. In experiments, this improved the accuracy of a prediction model on several datasets.
One obstacle to the development of machine learning models that base predictions on time series data is the availability of training examples. In “PSA-GAN: Progressive self attention GANs for synthetic time series”, Amazon researchers propose a method for using generative adversarial networks (GANs) to artificially produce time series training data.
GANs pit generators, which produce synthetic data, against discriminators, which try to distinguish synthetic data from real. The two are trained together, each improving the performance of the other.
The Amazon researchers show how to synthesize plausible time series data by progressively growing — or adding network layers to — both the generator and the discriminator. This enables the generator to first learn general characteristics that the time series as a whole should have, then learn how to produce series that exhibit those characteristics.
Data augmentation
In addition to the paper on synthetic time series, one of Amazon’s other papers at ICLR, “Deep AutoAugment”, also focuses on data augmentation.
It’s become standard practice to augment the datasets used to train machine learning models by subjecting real data to sequences of transformations. For instance, a training image for a computer vision task might be flipped, stretched, rotated or cropped, or its color or contrast might be modified. Typically, the first few transformations are selected automatically, based on experiments in which a model is trained and retrained, and then domain experts add a few additional transformations to try to make the modified data look like real data.
In “Deep AutoAugment”, former Amazon senior applied scientist Zhi Zhang and colleagues at Michigan State University propose a method for fully automating the construction of a data augmentation pipeline. The goal is to continuously add transformations that steer the feature distribution of the synthetic data toward that of the real data. To do that, the researchers use gradient matching, or identifying training data whose sequential updates to the model parameters look like those of the real data. In tests, this approach improved on 10 other data augmentation techniques across four sets of real data.
Natural-language processing
Many natural-language-processing tasks involve pairwise comparison of sentences. Cross-encoders, which map pairs of sentences against each other, yield the most accurate comparison, but they’re computationally intensive, as they need to compute new mappings for every sentence pair. Moreover, converting a pretrained language model into a cross-encoder requires fine-tuning it on labeled data, which is resource intensive to acquire.
Bi-encoders, on the other hand, embed sentences in a common representational space and measure the distances between them. This is efficient but less accurate.
In “Trans-encoder: Unsupervised sentence-pair modelling through self- and mutual-distillations”, Amazon researchers, together with a former intern, propose a model that is trained in an entirely unsupervised way — that is, without unlabeled examples — and captures advantages of both approaches.
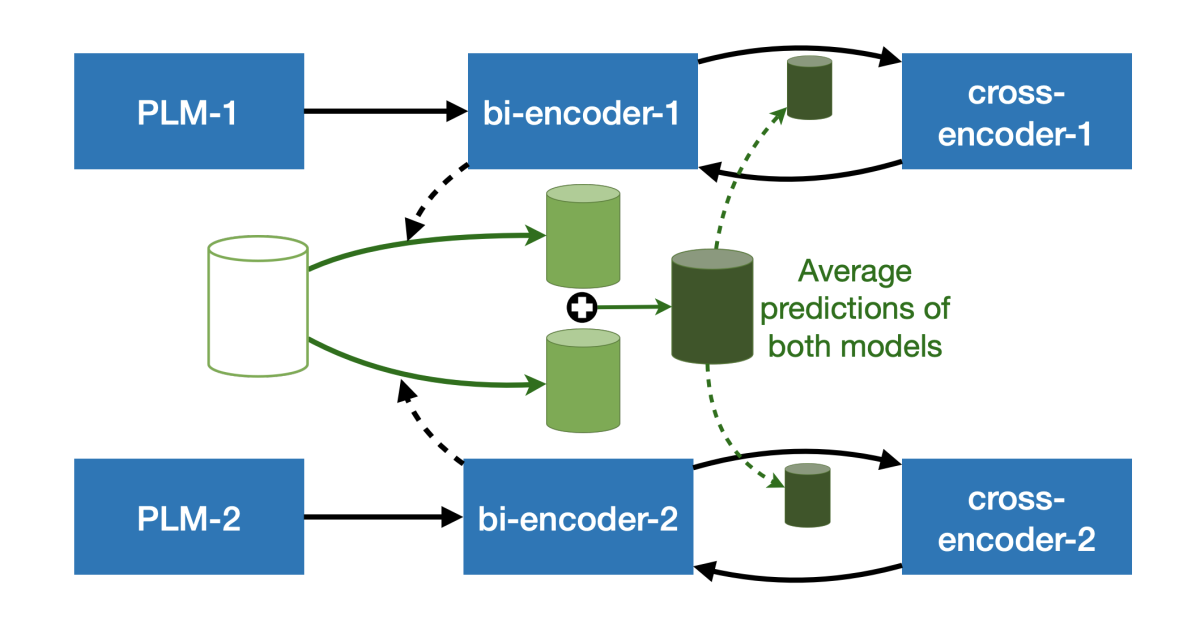
The researchers begin with a pretrained language model, fine-tune it in an unsupervised manner using bi-encoding, then use the fine-tuned model to generate training targets for cross-encoding. They then use the outputs of the cross-encoding model to fine-tune the bi-encoder, iterating back and forth between the two approaches until training converges. In experiments, their model outperformed multiple state-of-the-art unsupervised sentence encoders on several benchmark tasks, with improvements of up to 5% over the best-performing prior models.
Dataset optimization
Weeding errors out of a dataset, selecting new training examples to augment a dataset, and determining how to weight the data in a dataset to better match a target distribution are all examples of dataset optimization. Assessing individual training examples’ contribution to the accuracy of a model, however, is difficult: retraining the model on a dataset with and without every single example is hardly practical.
In “DIVA: Dataset derivative of a learning task”, Amazon researchers show how to compute the dataset derivative: a function that can be used to assess a given training example’s utility relative to a particular neural-network model. During training, the model learns not only the weights of network parameters but also weights for individual training examples. The researchers show that, using a linearization technique, they can derive a closed-form equation for the dataset derivative, allowing them to assess the utility of a given training example without retraining the network.

Limitations
“Machine learning ultimately is based on statistical dependencies,” Bernhard Schölkopf recently told Amazon Science. “Oftentimes, it's enough if we work at the surface and just learn from these dependencies. But it turns out that it's only enough as long as we're in this setting where nothing changes.”
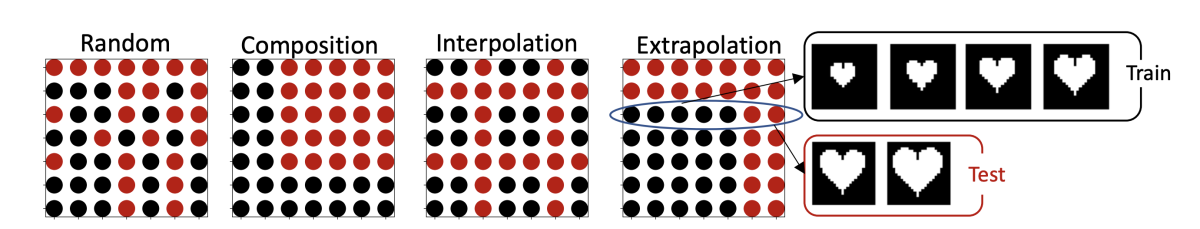
The two ICLR papers from the Causal Representation Learning team explore contexts in which learning statistical dependencies is not enough. “Visual representation learning does not generalize strongly within the same domain” describes experiments with image datasets in which each image is defined by specific values of a set of variables — say, different shapes of different sizes and colors, or faces that are either smiling or not and differ in hair color or age.
The researchers test 17 machine learning models and show that, if certain combinations of variables or specific variable values are held out of the training data, all 17 have trouble recognizing them in the test data. For instance, a model trained to recognize small hearts and large squares has trouble recognizing large hearts and small squares. This suggests that we need revised training techniques or model designs to ensure that machine learning systems are really learning what they’re supposed to.
Similarly, in “You mostly walk alone: Analyzing feature attribution in trajectory prediction”, members of the team consider the problem of predicting the trajectories of moving objects as they interact with other objects, an essential capacity for self-driving cars and other AI systems. For instance, if a person is walking down the street, and a ball bounces into her path, it could be useful to know that the person might deviate from her trajectory to retrieve the ball.
Adapting the game-theoretical concept of Shapley values, which enable the isolation of different variables’ contributions to an outcome, the researchers examine the best-performing recent models for predicting trajectories in interactive contexts and show that, for the most part, their predictions are based on past trajectories; they pay little attention to the influence of interactions.
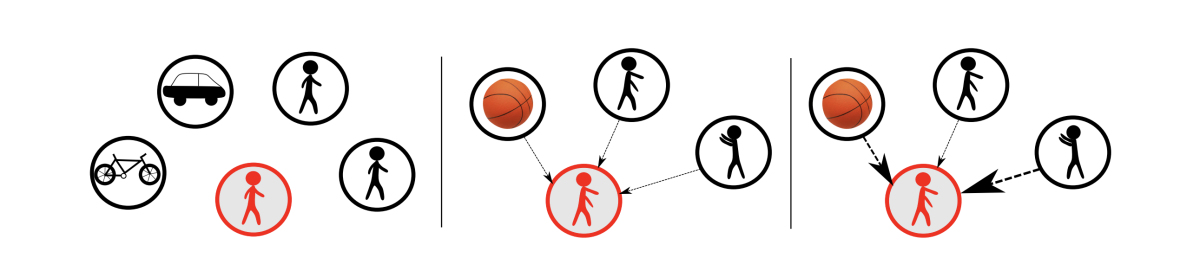
The one exception is a models trained on a dataset of basketball video, where all the players’ movements are constantly coordinated. There, existing models do indeed learn to recognize the influence of interaction. This suggests that careful curation of training data could enable existing models to account for interactions when predicting trajectories.




















