Interspeech, the world’s largest and most comprehensive conference on the science and technology of spoken-language processing, took place this week in Incheon, Korea, with Amazon as a platinum sponsor. Amazon Science asked three of Alexa AI’s leading scientists — in the fields of speech, spoken-language-understanding, and text-to-speech — to highlight some of Amazon’s contributions to the conference.
In this installment, senior principal scientist Andreas Stolcke selects papers from Alexa AI’s speech science organization, focusing on two overarching themes in recent research on speech-enabled AI: end-to-end neural speech recognition and fairness.
End-to-end neural speech recognition
Traditionally, speech recognition systems have included components specialized for different aspects of linguistic knowledge: acoustic models to capture the correspondence between speech sounds and acoustic waveforms (phonetics), pronunciation models to map those sounds to words, and language models (LMs) to capture higher-order properties such as syntax, semantics, and dialogue context.
All these models are trained on separate data and combined using graph and search algorithms, to infer the most probable sequence of words corresponding to acoustic input. The latest versions of these systems employ neural networks for individual components, typically in the acoustic and language models, while still relying on non-neural methods for model integration; they are therefore known as “hybrid” automatic-speech-recognition (ASR) systems.
While the hybrid ASR approach is structured and modular, it also makes it hard to model the ways in which acoustic, phonetic, and word-level representations interact and to optimize the recognition system end to end. For these reasons, much recent research in ASR has focused on so-called end-to-end or all-neural recognition systems, which infer a sequence of words directly from acoustic inputs.
End-to-end ASR systems use deep multilayered neural architectures that can be optimized end to end for recognition accuracy. While they do require large amounts of data and computation for training, once trained, they offer a simplified computational architecture for inference, as well as superior performance.
Alexa’s ASR employs end-to-end as its core algorithm, both in the cloud and on-device. Across the industry and in academic research, end-to-end architectures are still being improved to achieve better accuracy, to require less computation and/or latency, or to mitigate the lack of modularity that makes it challenging to inject external (e.g., domain-specific) knowledge at run time.
Alexa AI papers at Interspeech address several open problems in end-to-end ASR, and we summarize a few of those papers here.
In “ConvRNN-T: Convolutional augmented recurrent neural network transducers for streaming speech recognition”, Martin Radfar and coauthors propose a new variant of the popular recurrent-neural-network-transducer (RNN-T) end-to-neural architecture. One of their goals is to preserve the property of causal processing, meaning that the model output depends only on past and current (but not future) inputs, which enables streaming ASR. At the same time, they want to improve the model’s ability to capture long-term contextual information.
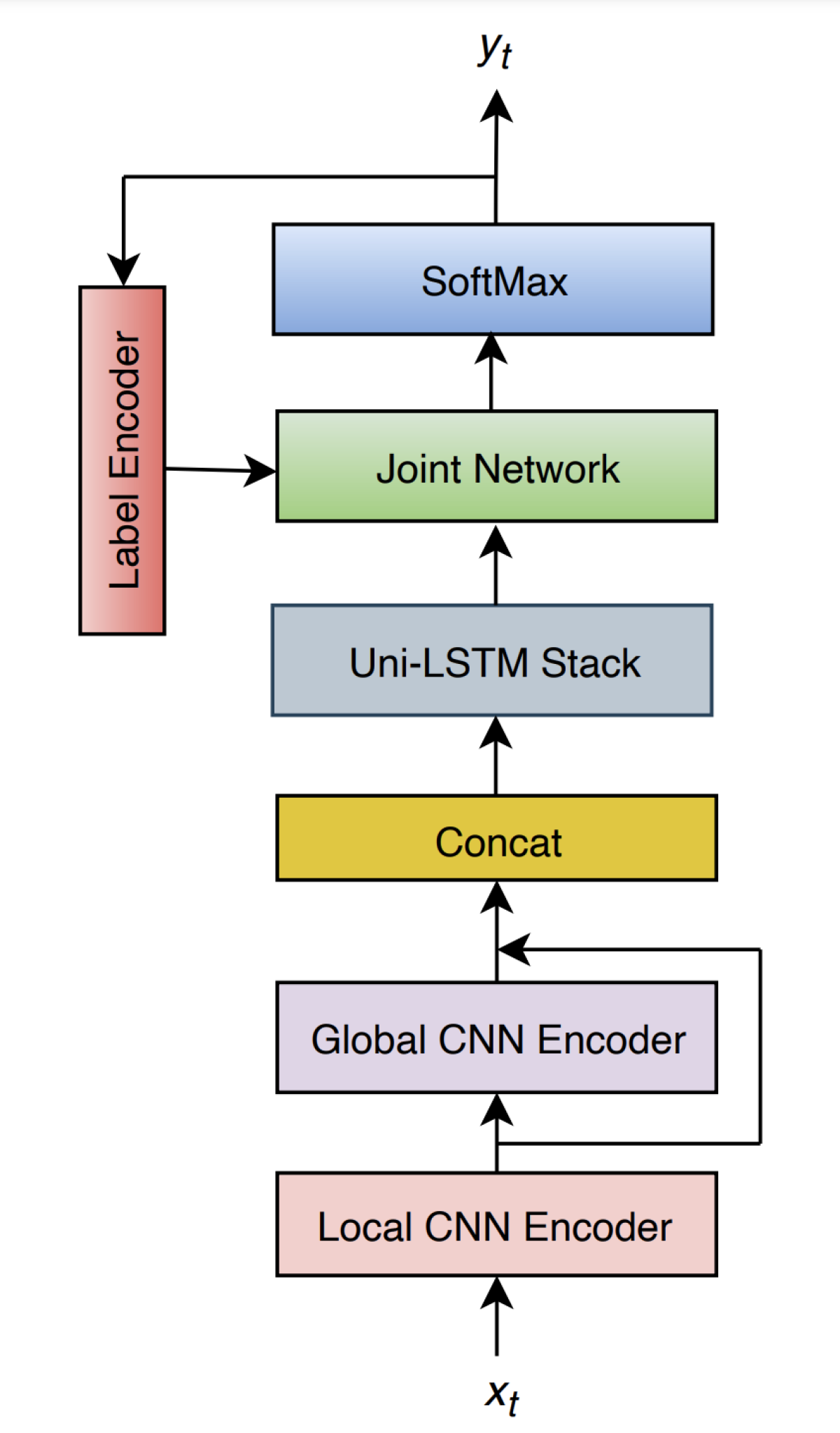
To achieve both goals, they augment the vanilla RNN-T with two distinct convolutional (CNN) front ends: a standard one for encoding correlations localized in time and a novel “global CNN” encoder that is designed to capture long-term correlations by summarizing activations over the entire utterance up to the current time step (while processing utterances incrementally through time).
The authors show that the resulting ConvRNN-T gives superior accuracy compared to other proposed neural streaming ASR architectures, such as the basic RNN-T, Conformer, and ContextNet.
Another concern with end-to-end ASR models is computational efficiency, especially since the unified neural architecture makes these models very attractive for on-device deployment, where compute cycles and (for mobile devices) power are at a premium.
In their paper “Compute cost amortized Transformer for streaming ASR”, Yi Xie and colleagues exploit the intuitive observation that the amount of computation a model performs should vary as a function of the difficulty of the task; for instance, input in which noise or an accent causes ambiguity may require more computation than a clean input with a mainstream accent. (We may think of this as the ASR model “thinking harder” in places where the words are more difficult to discern.)
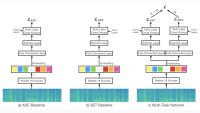
The researchers achieve this with a very elegant method that leverages the integrated neural structure of the model. Their starting point is a Transformer-based ASR system, consisting of multiple stacked layers of multiheaded self-attention (MHA) and feed-forward neural blocks. In addition, they train “arbitrator” networks that look at the acoustic input (and, optionally, also at intermediate block outputs) to toggle individual components on or off.
Because these component blocks have “skip connections” that combine their outputs with the outputs of earlier layers, they are effectively optional for the overall computation to proceed. A block that is toggled off for a given input frame saves all the computation normally carried out by that block, producing a zero vector output. The following diagram shows the structure of both the elementary Transformer building block and the arbitrator that controls it:
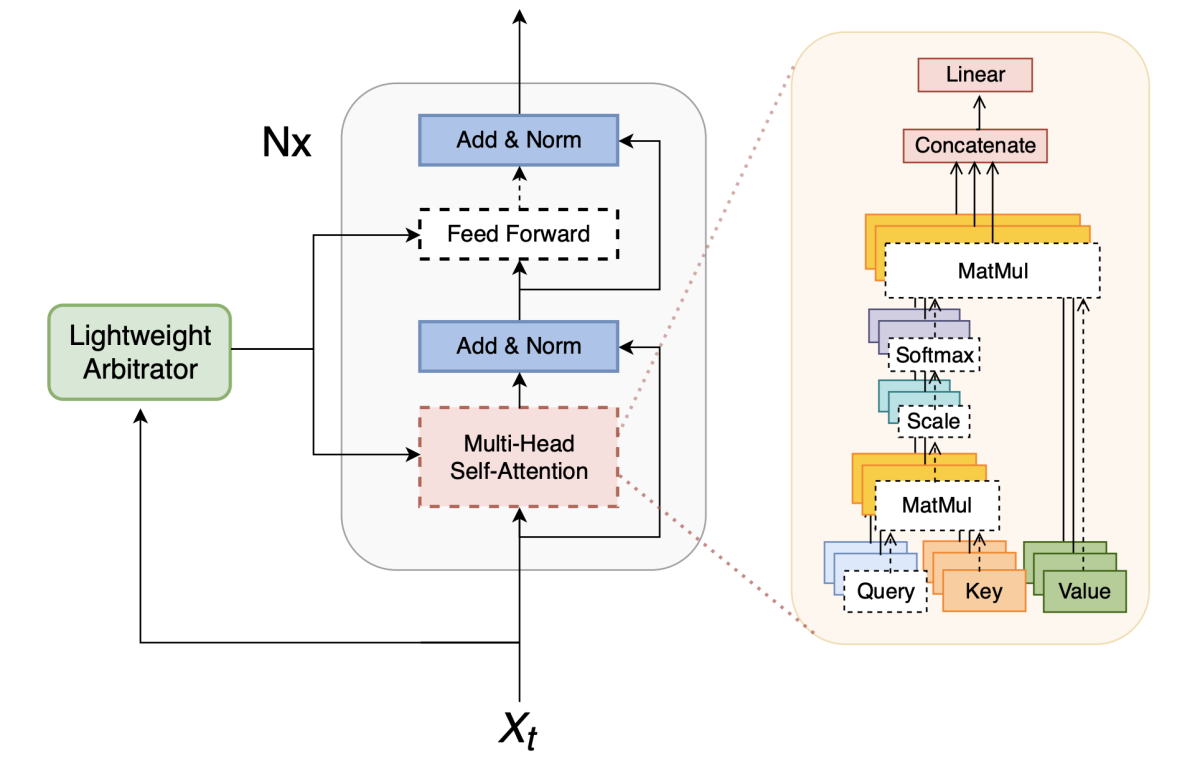
The arbitrator networks themselves are small enough that they do not contribute significant additional computation. What makes this scheme workable and effective, however, is that both the Transformer assemblies and the arbitrators that control them can be trained jointly, with dual goals: to perform accurate ASR and to minimize the overall amount of computation. The latter is achieved by adding a term to the training objective function that rewards reducing computation. Dialing a hyperparameter up or down selects the desired balance between accuracy and computation.
The authors show that their method can achieve a 60% reduction in computation with only a minor (3%) increase in ASR error. Their cost-amortized Transformer proves much more effective than a benchmark method that constrains the model to attend only to sliding windows over the input, which yields only 13% savings and an error increase of almost three times as much.
Finally, in this short review of end-to-end neural ASR advances, we look at ways to recognize speech from more than one speaker, while keeping track of who said what (also known as speaker-attributed ASR).
This has traditionally been done with modular systems that perform ASR and, separately, perform speaker diarization, i.e., labeling stretches of audio according to who is speaking. However, here, too, neural models have recently brought advances and simplification, by integrating these two tasks in a single end-to-end neural model.
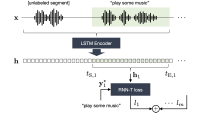
In their paper “Separator-transducer-segmenter: Streaming recognition and segmentation of multi-party speech”, Ilya Sklyar and colleagues not only integrate ASR and segmentation-by-speaker but do so while processing inputs incrementally. Streaming multispeaker ASR with low latency is a key technology to enable voice assistants to interact with customers in collaborative settings. Sklyar’s system does this with a generalization of the RNN-T architecture that keeps track of turn-taking between multiple speakers, up to two of whom can be active simultaneously. The researchers’ separator-transducer-segmenter model is depicted below:
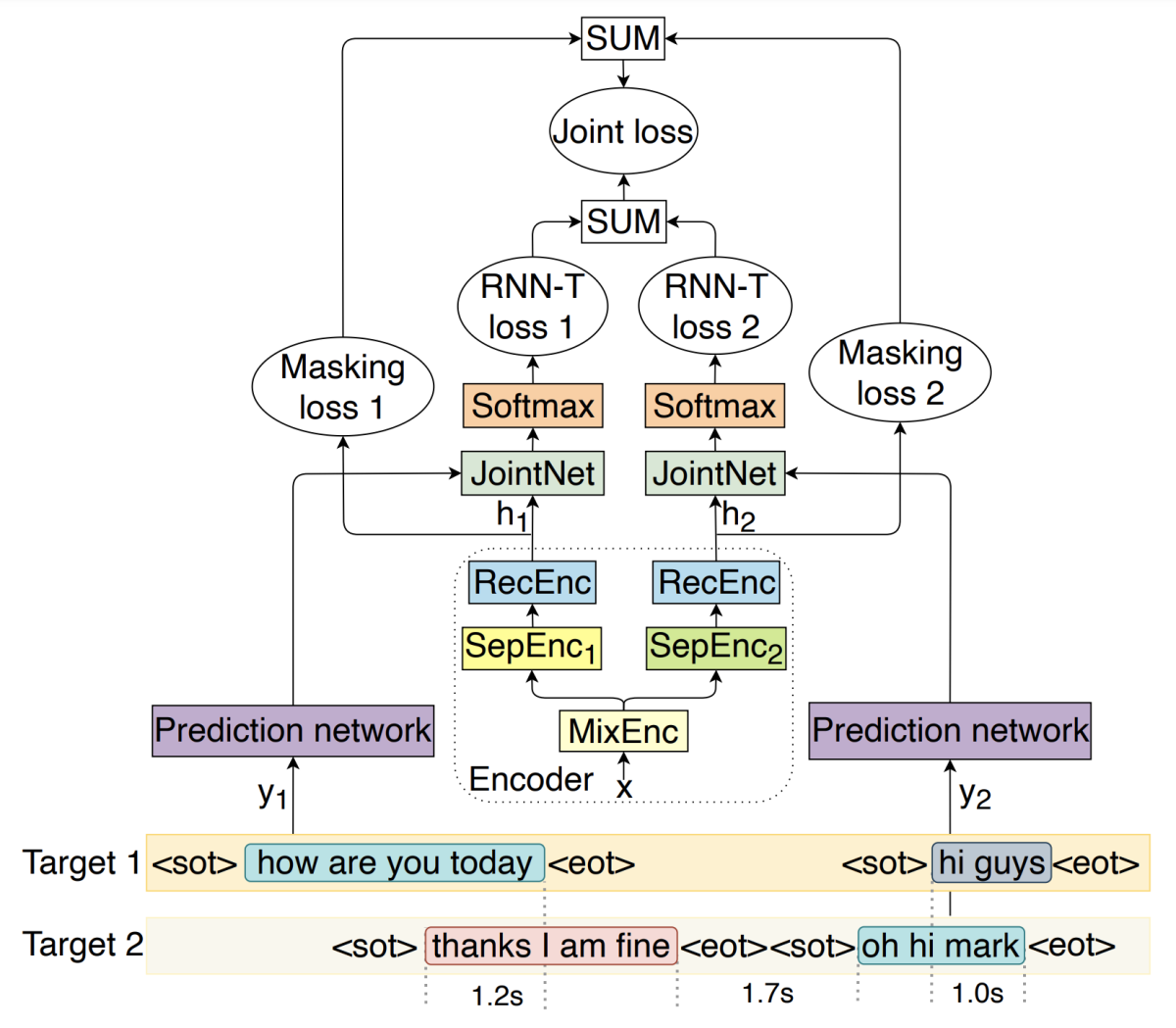
A key element that yields improvements over an earlier approach is the use of dedicated tokens to recognize both starts and ends of speaker turns, for what the authors call “start-pointing” and “end-pointing”. (End-pointing is a standard feature of many interactive ASR systems necessary to predict when a talker is done.) Beyond representing the turn-taking structure in this symbolic way, the model is also penalized during training for taking too long to output these markers, in order to improve the latency and temporal accuracy of the outputs.
Fairness in the performance of speech-enabled AI
The second theme we’d like to highlight, and one that is receiving increasing attention in speech and other areas of AI, is performance fairness: the desire to avert large differences in accuracy across different cohorts of users or on content associated with protected groups. As an example, concerns about this type of fairness gained prominence with demonstrations that certain computer vision algorithms performed poorly for certain skin tones, in part due to underrepresentation in the training data.
There’s a similar concern about speech-based AI, with speech properties varying widely as a function of speaker background and environment. A balanced representation in training sets is hard to achieve, since the speakers using commercial products are largely self-selected, and speaker attributes are often unavailable for many reasons, privacy among them. This topic is also the subject of a special session at Interspeech, Inclusive and Fair Speech Technologies, which several Alexa AI scientists are involved in as co-organizers and presenters.
One of the special-session papers, “Reducing geographic disparities in automatic speech recognition via elastic weight consolidation”, by Viet Anh Trinh and colleagues, looks at how geographic location within the U.S. affects ASR accuracy and how models can be adapted to narrow the gap for the worst-performing regions. Here and elsewhere, a two-step approach is used: first, subsets of speakers with higher-than-average error rates are identified; then a mitigation step attempts to improve performance for those cohorts. Trinh et al.’s method identifies the cohorts by partitioning the speakers according to their geographic longitude and latitude, using a decision-tree-like algorithm that maximizes the word-error-rate (WER) differences between resulting regions:
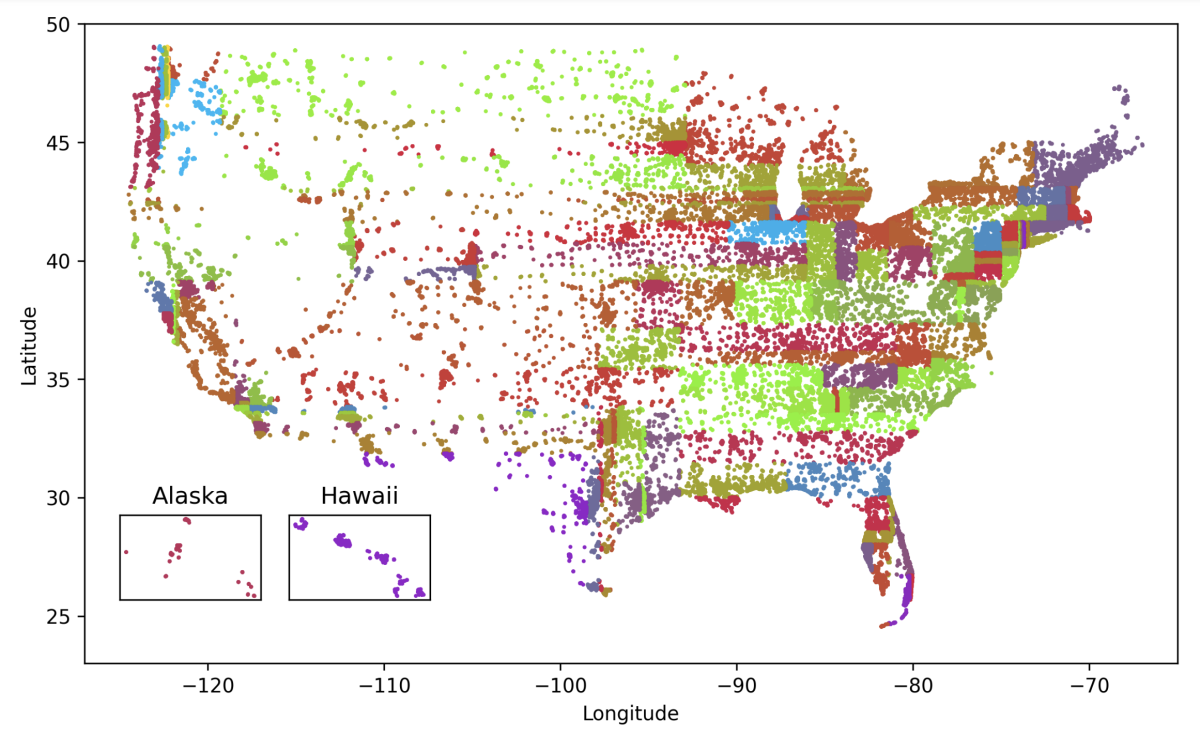
Next, the regions are ranked by their average WERs; data from the highest-error regions is identified for performance improvement. To achieve that, the researchers use fine-tuning to optimize the model parameters for the targeted regions, while also employing a technique called elastic weight consolidation (EWC) to minimize performance degradation on the remaining regions.
This is important to prevent a phenomenon known as “catastrophic forgetting”, in which neural models degrade substantially on prior training data during fine-tuning. The idea is to quantify the influence that different dimensions of the parameter space have on the overall performance and then avoid large variations along those dimensions when adapting to a data subset. This approach decreases the WER mean, maximum, and variance across regions and even the overall WER (including the regions not fine-tuned on), beating out several baseline methods for model adaptation.
Pranav Dheram et al., in their paper “Toward fairness in speech recognition: Discovery and mitigation of performance disparities”, look at alternative methods for identifying underperforming speaker cohorts. One approach is to use human-defined geographic regions as given by postal (a.k.a. zip) codes, in combination with demographic information from U.S. census data, to partition U.S. geography.
Zip codes are sorted into binary partitions by majority demographic attributes, so as to maximize WER discrepancies. The partition with higher WER is then targeted for mitigations, an approach similar to that adopted in the Trinh et al. paper. However, this approach is imprecise (since it lumps together speakers by zip code) and limited to available demographic data, so it generalizes poorly to other geographies.
Alternatively, Dheram et al. use speech characteristics learned by a neural speaker identification model to group speakers. These “speaker embedding vectors” are clustered, reflecting the intuition that speakers who sound similar will tend to have similar ASR difficulty.
Subsequently, these virtual speaker regions (not individual identities) can be ranked by difficulty and targeted for mitigation, without relying on human labeling, grouping, or self-identification of speakers or attributes. As shown in the table below, the automatic approach identifies a larger gap in ASR accuracy than the “geo-demographic” approach, while at the same time targeting a larger share of speakers for performance mitigation:
Cohort discovery |
WER gap (%) |
Bottom-cohort share (%) |
Geodemographic Automatic |
41.7 65.0 |
0.8 10.0 |
The final fairness-themed paper we highlight explores yet another approach to avoiding performance disparities, known as adversarial reweighting (ARW). Instead of relying on explicit partitioning of the input space, this approach assigns continuous weights to the training instances (as a function of input features), with the idea that harder examples get higher weights and thereby exert more influence on the performance optimization.
Secondly, ARW more tightly interleaves, and iterates, the (now weighted) cohort identification and mitigation steps. Mathematically, this is formalized as a min-max optimization algorithm that alternates between maximizing the error by changing the sample weights (hence “adversarial”) and minimizing the weighted verification error by adjusting the target model parameters.
ARW was designed for group fairness in classification and regression tasks that take individual data points as inputs. “Adversarial reweighting for speaker verification fairness”, by Minho Jin et al., looks at how the concept can be applied to a classification task that depends on pairs of input samples, i.e., checking whether two speech samples come from the same speaker. Solving this problem could help make a voice-based assistant more reliable at personalization and other functions that require knowing who is speaking.
The authors look at several ways to adapt ARW to learning similarity among speaker embeddings. The method that ultimately worked best assigns each pair of input samples an adversarial weight that is the sum of individual sample weights (thereby reducing the dimensionality of the weight prediction). The individual sample weights are also informed by which region of the speaker embedding space a sample falls into (as determined by unsupervised k-means clustering, the same technique used in Dheram et al.’s automatic cohort-identification method).
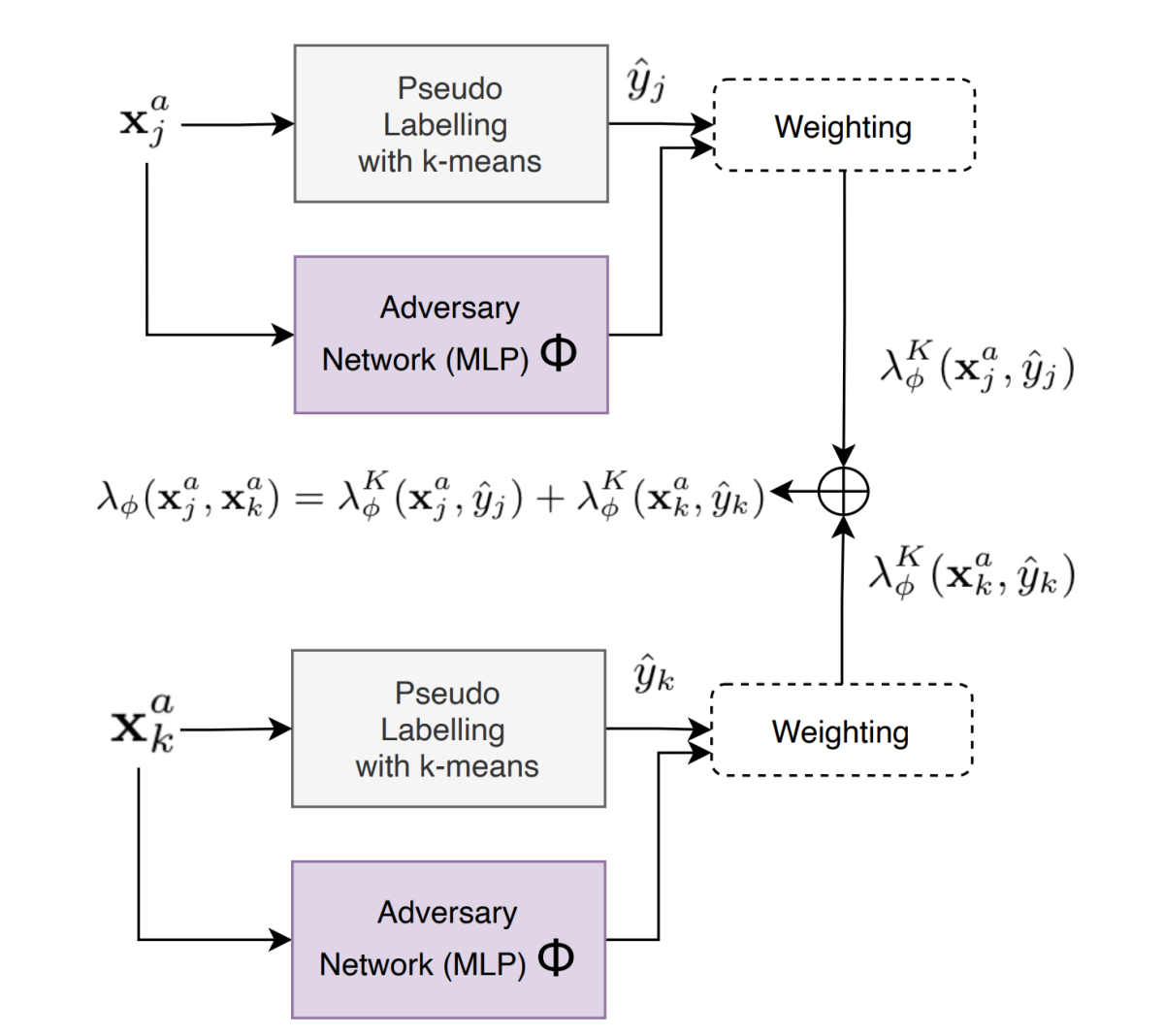
I omit the details, but once the pairwise (PW) adversarial weights are formalized in this way, we can insert them into the loss function for metric learning, which is the basis of training a speaker verification model. Min-max optimization can then take turns training the adversary network that predicts the weights and optimizing the speaker embedding extractor that learns speaker similarity.
On a public speaker verification corpus, the resulting system reduced overall equal-error rate by 7.6%, while also reducing the gap between genders by 17%. It also reduced the error variability across different countries of origin, by nearly 10%. Note that, as in the case of the Trinh et al. ASR fairness paper, fairness mitigation improves both performance disparities and overall accuracy.
This concludes our thematic highlights of Alexa Speech Interspeech papers. Note that Interspeech covers much more than speech and speaker recognition. Please check out companion pieces that feature additional work, drawn from technical areas that are no less essential for a functioning speech-enabled AI assistant: natural-language understanding and speech synthesis.