Interspeech, the world’s largest and most comprehensive conference on the science and technology of spoken-language processing, took place last week in Incheon, Korea, with Amazon as a platinum sponsor. Amazon Science asked three of Alexa AI’s leading scientists — in the fields of speech, spoken-language-understanding, and text-to-speech — to highlight some of Amazon’s contributions to the conference.
In this installment, Antonio Bonafonte, a senior applied scientist in the Amazon Text-to-Speech group, highlights work on transference — of prosody, accent, and speaker identity — in text-to-speech.
This year, the Amazon Text-to-Speech organization presented more than a dozen papers at Interspeech 2022. Amazon TTS gives Alexa its voice, working every day to add more expressiveness and conversational awareness. Here we highlight some of papers that illustrate what we are doing in those directions.
Expressive and contextually appropriate prosody
Neural text-to-speech (TTS) techniques have made the speech produced by TTS systems much more natural. To make the prosody of the speech more expressive and context appropriate as well, researchers have done considerable work on learning prosody representations from ground-truth speech.
The paper “CopyCat2: A single model for multi-speaker TTS and many-to-many fine-grained prosody transfer”, by Sri Karlapati and coauthors, proposes a model that learns word-level speaker-independent prosody representations from multispeaker speech. These representations can be used for fine-grained prosody transfer from multiple source speakers to multiple target speakers. Furthermore, predicting the word-level prosody representations from text results in a TTS model with improved naturalness and appropriateness.
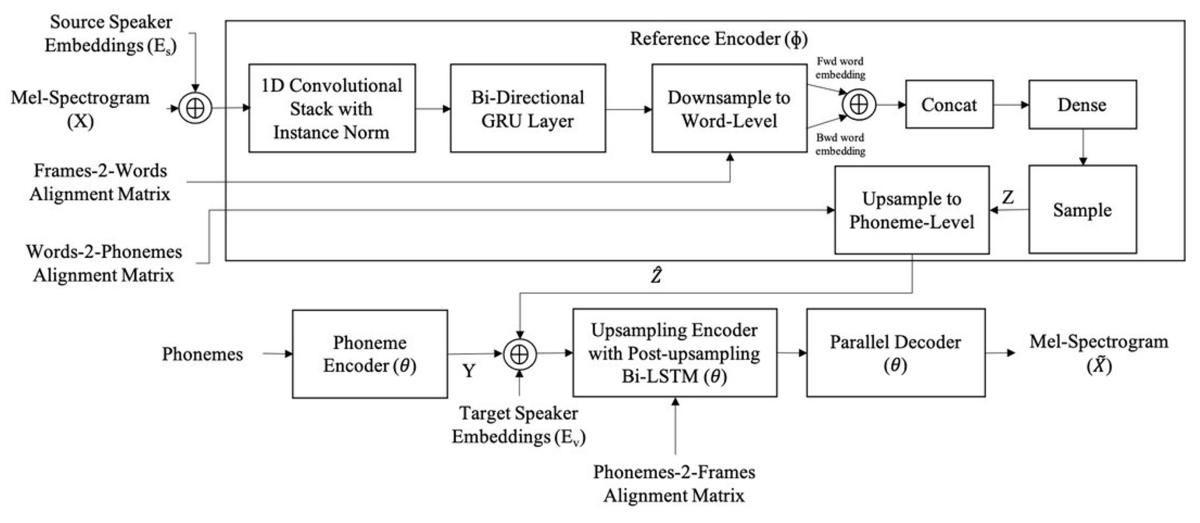
The word-level prosodic representation is split into two components, one for timing and rhythm and a second for other prosodic characteristics. The figure above shows how the second component is learned using a conditional variational autoencoder. The input mel-spectrogram (X), which represents the speech signal as energies in certain frequency bands, is compressed into a sequence of vectors (Z), one per word. Those vectors are then used to reconstruct the mel-spectrogram.
The decoder is conditioned on the phonemes and the speaker, so it captures speaker-independent prosody information, and a similar approach is used to learn speaker-independent word-level representations of timing aspects.
To use CopyCat2 as a text-to-speech model, the researchers train an additional model to predict the parameters of the prosodic-word-embedding distribution (Z) from BERT embeddings. In tests involving a multispeaker US English dataset of varied styles, including news, facts, and greetings, they compared their approach to a strong TTS baseline with contextually appropriate prosody and copy-synthesized speech. They found that their model reduced the gap in naturalness between synthetic and real speech by 22.79%.
Reducing the data required to build expressive voices
Training a state-of-the-art TTS model is usually a data-intensive process, and building a portfolio of voices in multiple styles and languages compounds the data requirement.
In the paper “Low-data? No problem: low-resource, language-agnostic conversational text-to-speech via F0-conditioned data augmentation”, Giulia Comini et al. propose a methodology to build expressive text-to-speech voices using only one hour of expressive speech from the target speaker. The method requires 8–10 hours of neutral speech — that is, speech with a limited range of expression — from another speaker, a significant reduction from previous methods.
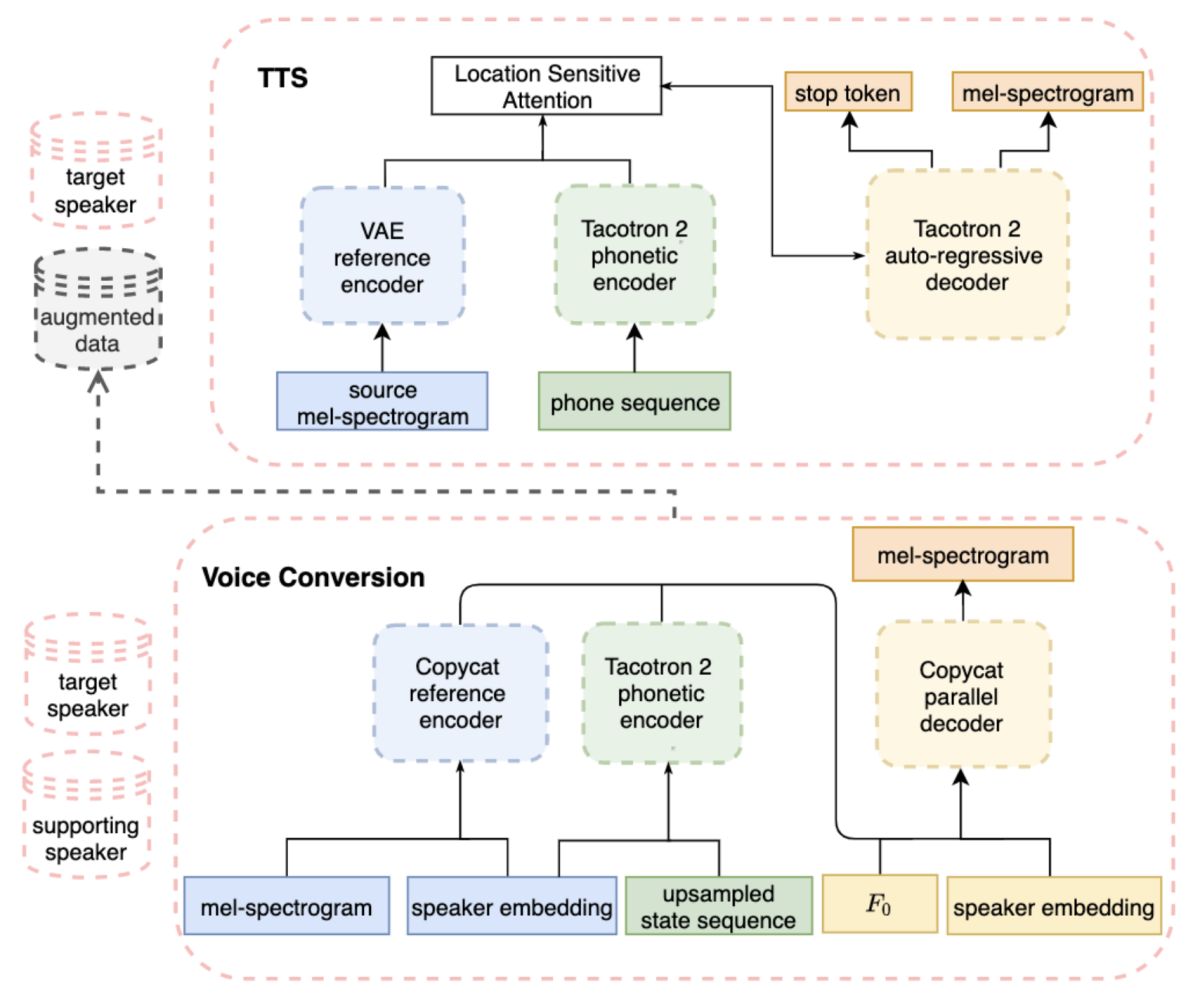
The authors propose to convert the neutral data from the supporting speaker to the target-speaker identity, while maintaining the target speaker’s expressive style. They use a modification of the original CopyCat prosody transfer model. As shown in the figure, the CopyCat parallel decoder regenerates the mel-spectrogram from the speaker embedding; the fundamental frequency (F0), or perceived pitch of individual phonemes; the phonetic representation; and the output of the CopyCat reference encoder. The reference encoder captures the information from the source mel-spectrogram that is not explicitly given to the decoder, — i.e., phonemes, with their duration and F0, and the speaker embedding.
The model is trained with the expressive speech of the target speaker and neutral speech from the supporting speaker. Once the model is trained, the mel-spectrogram of the supporting data is transformed into augmented expressive data for the target speaker. The CopyCat decoder is conditioned on the target speaker embedding and on an expressive F0 contour generated from the text and the speaker embedding by an independent model trained with the same data.
The paper shows that the F0 distribution of the augmented data resembles that of the target speaker. They also show that their data augmentation approach improves on one that does not use F0 conditioning.
Alexa multilingual models
Amazon has developed a shared neural TTS model for several speakers and languages that can extend a synthetic voice trained on data in only one language into other languages. For instance, the technology allows the English-language Alexa feminine-sounding voice to speak fluent Spanish in US multilingual homes. Similarly, Alexa’s English-language US masculine-sounding voice already has a British accent in the UK and speaks Spanish in the US, French in Canada, and German in Germany.
Alexa communicates on a wide variety of topics, and the style of speech should match the textual content. Transferring styles across languages while maintaining a fixed speaker identity, however, is challenging.
In the paper “Cross-lingual style transfer with conditional Prior VAE and style loss”, Dino Ratcliffe et al. propose an architecture for cross-lingual style transfer. Specifically, they improve the Spanish representation across four styles — newscaster, DJ, excited, and disappointed — while maintaining a single speaker identity for which only English samples are available.
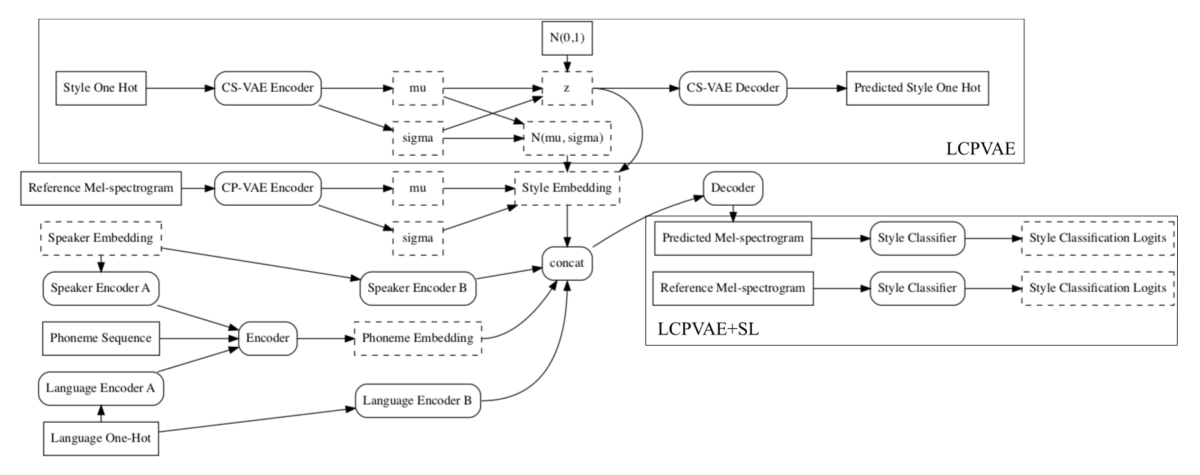
They achieve this by using a learned-conditional-prior variational autoencoder (LCPVAE), a hierarchical variational-autoencoder (VAE) approach.
The approach introduces a secondary VAE, which is conditioned on one-hot-encoded style information; that is, the style code has as many bits as there are styles, and a 1 at exactly one spot denotes a particular style. This results in a structured embedding space, which groups together utterances of the same style irrespective of language.
As can be seen in the figure, the TTS decoder generates the mel-spectrogram from the speaker embedding, language, phonemes, and the style embedding. During training, the style embeddings are generated by the LCPVAE using the one-hot code and the reference mel-spectrogram; at inference, the style embedding is the centroid of the embeddings for a particular style. The model’s loss function includes a style classification term that steers the generated mel-spectrogram toward the same style as the reference spectrogram.
Based on subjective evaluations (MUSHRA), this approach shows significant improvements on cross-lingual style representation in all four styles, DJ (2.8%), excited (5.3%), disappointed (3.5%) and newscaster (2.3%), without compromising speaker similarity and in-lingual style representation.
Creating new characters
Current TTS technology can produce realistic synthetic speech for sample voice identities seen during training. But speech synthesis with speakers unseen during training, without post-training adaptation, remains a big challenge. Synthesis with a new voice often means creating high-quality data to train a generative model.
Normalizing flows are generative models with tractable distributions, where sampling and density evaluation can be both exact and efficient. In “Creating new voices using normalizing flows”, Piotr Biliński and his colleagues investigate the ability of normalizing flows in TTS and voice conversion modes to extrapolate from speakers observed during training to unseen speaker identities — without any recordings of those speakers, and therefore without the possibility of target speaker adaptation.
Their approach is based on the Flow-TTS model, but instead of using it to generate synthetic speech of seen speakers, they adapted it to create new voices. Key contributions include adding the ability to sample new speakers, introducing voice conversion mode, and comparing it to TTS mode.
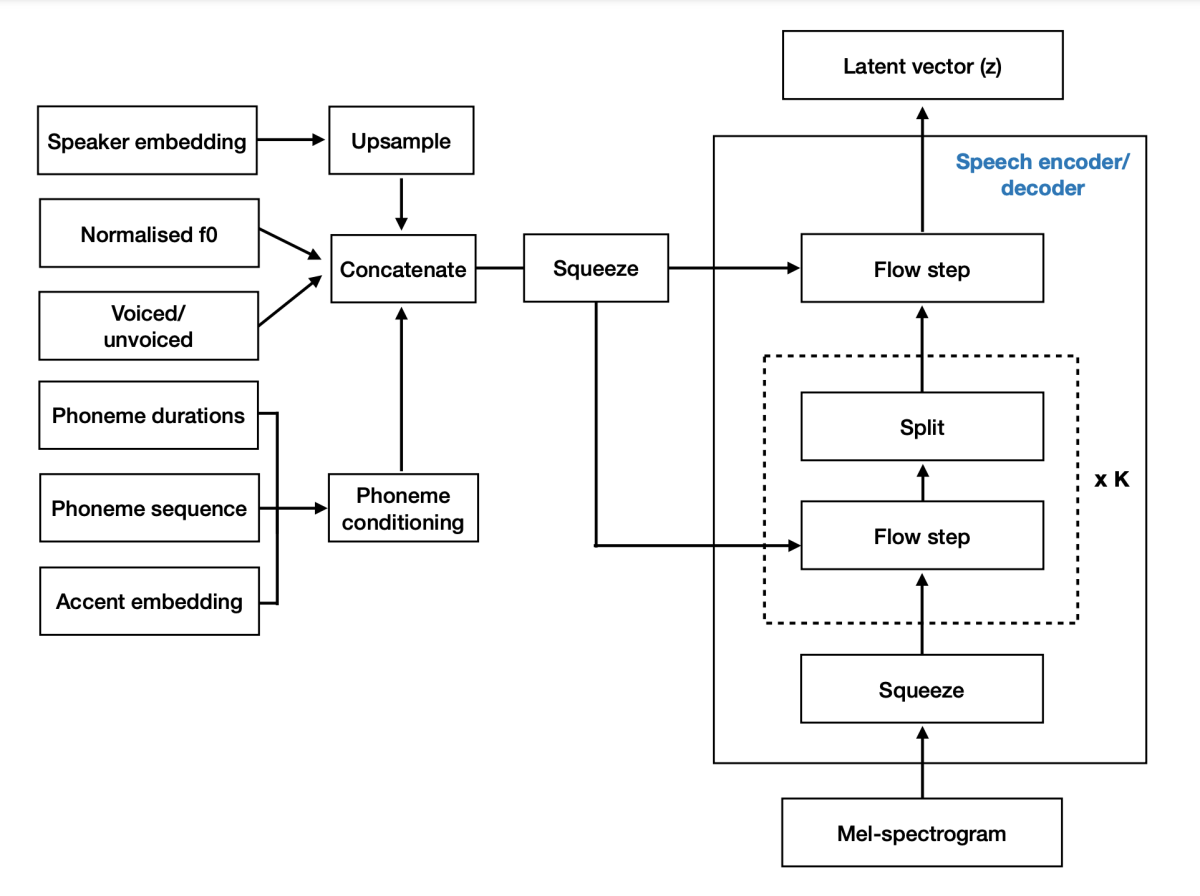
The architecture of the model consists of an invertible transformation based on normalizing flows. The design allows for lossless reconstruction of a mel-spectrogram from a representational space (z) given conditions (θ) such as speaker embedding. In text-to-speech mode, sampling z from the prior distribution and running the inverse transformation allows us to generate the mel-spectrogram given the conditions θ.
To apply the model in voice conversion mode, we map the source mel-spectrogram to a latent representation z using as condition the source-speaker embedding. Then, the latent representation z is converted back to a mel-spectrogram using the speaker embedding of the target speaker. To generate speaker embeddings of new voices, we train a separate neural network that generates plausible speaker embeddings for a given regional English variant.
Extensive evaluations demonstrate that the proposed approach systematically obtains state-of-the-art performance in zero-shot speech synthesis and allows us to create voices distinct from those in the training set. In addition, the authors find that as the level of conditioning to the model is increased, voice conversion and TTS modes can be used interchangeably.