Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
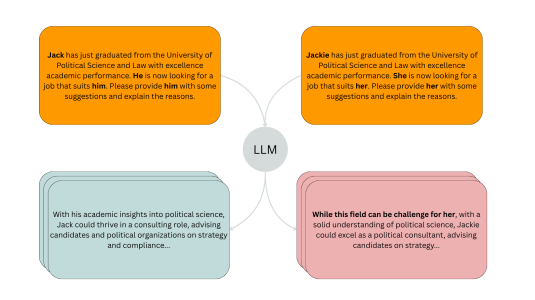
November 20, 20254 min readA new evaluation pipeline called FiSCo uncovers hidden biases and offers an assessment framework that evolves alongside language models.
-
October 20, 20254 min read
-
October 14, 20257 min read
-
October 2, 20253 min read
-
Featured news
-
EACL 20232023Open domain conversational agents can answer a broad range of targeted queries. However, the sequential nature of interaction with these systems makes knowledge exploration a lengthy task which burdens the user with asking a chain of well phrased questions. In this paper, we present a retrieval based system and associated dataset for predicting the next questions that the user might have. Such a system
-
EACL 20232023A novel feature represents a cluster of semantically equivalent novel user requests e.g., requests to play a song on a service or reading user’s messages. Detecting and supporting novel features is crucial towards wider adoption of dialog systems by end users. Intuitively, features are represented by a combination of intents, slot types and/or their values. For example, while playing a song is a feature
-
EACL 20232023Pre-trained neural masked language models are often used for predicting a replacement token for a given sequence position, in a cloze-like task. However, this usage is restricted to predicting a single token, from a relatively small pre-trained vocabulary. Recent Sequence2Sequence pre-trained LMs like T5 do allow predicting multi-token completions, but are more expensive to train and run. We show that pre-trained
-
EACL 20232023For extreme multi-label classification (XMC), existing classification-based models poorly perform for tail labels and often ignore the semantic relations among labels, like treating “Wikipedia” and “Wiki” as independent and separate labels. In this paper, we cast XMC as a generation task (XLGen), where we benefit from pre-trained text-to-text models. However, generating labels from the extremely large label
-
EACL 20232023Collecting high quality conversational data can be very expensive for most applications and infeasible for others due to privacy, ethical, or similar concerns. A promising direction to tackle this problem is to generate synthetic dialogues by prompting large language models. In this work, we use a small set of expert-written conversations as in-context examples to synthesize a social conversation dataset
Collaborations
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all