Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
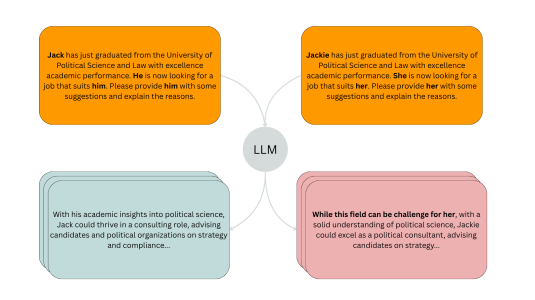
November 20, 20254 min readA new evaluation pipeline called FiSCo uncovers hidden biases and offers an assessment framework that evolves alongside language models.
-
October 20, 20254 min read
-
October 14, 20257 min read
-
October 2, 20253 min read
-
Featured news
-
ICASSP 20232023GAN vocoders are currently one of the state-of-the-art methods for building high-quality neural waveform generative models. However, most of their architectures require dozens of billion floating-point operations per second (GFLOPS) to generate speech waveforms in samplewise manner. This makes GAN vocoders still challenging to run on normal CPUs without accelerators or parallel computers. In this work,
-
ICLR 20232023In this paper, we study how to use masked signal modeling in vision and language (V+L) representation learning. Instead of developing masked language modeling (MLM) and masked image modeling (MIM) independently, we propose to build joint masked vision and language modeling, where the masked signal of one modality is reconstructed with the help from another modality. This is motivated by the nature of image-text
-
ICLR 20232023Anomaly detection in time-series has a wide range of practical applications. While numerous anomaly detection methods have been proposed in the literature, a recent survey concluded that no single method is the most accurate across various datasets. To make matters worse, anomaly labels are scarce and rarely available in practice. The practical problem of selecting the most accurate model for a given dataset
-
EACL 20232023Aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA) has attracted broad attention due to its commercial value. Natural Language Generation-based (NLG) approaches dominate the recent advance in ABSA tasks. However, current NLG practices are inefficient because most of them directly employ an autoregressive generation framework that cannot efficiently generate location information and semantic representations of ABSA
-
ICLR 20232023Empirical studies suggest that machine learning models trained with empirical risk minimization (ERM) often rely on attributes that may be spuriously correlated with the class labels. Such models typically lead to poor performance during inference for data lacking such correlations. In this work, we explicitly consider a situation where potential spurious correlations are present in the majority of training
Collaborations
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all