Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
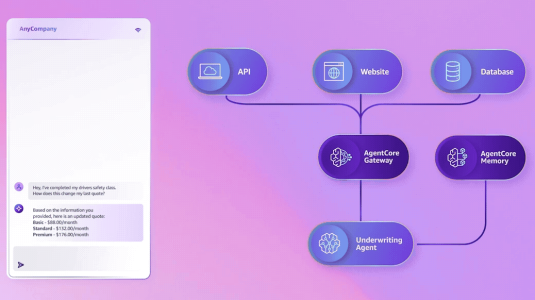
October 16, 2025Amazon vice president and distinguished engineer Marc Brooker explains how agentic systems work under the hood — and how AWS’s new AgentCore framework implements their core components.
Featured news
-
2025Vision Language Models (VLMs) have achieved significant advancements in complex visual understanding tasks. However, VLMs are prone to hallucinations—generating outputs that lack alignment with visual content. This paper addresses hallucination detection in VLMs by leveraging the visual grounding information encoded in transformer attention maps. We identify three primary challenges in this approach: the
-
2025In this paper, we present a novel algorithm for quantifying uncertainty and information gained within 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) through P-Optimality. While 3D-GS has proven to be a useful world model with high-quality rasterizations, it does not natively quantify uncertainty or information, posing a challenge for real-world applications such as 3D-GS SLAM. We propose to quantify information gain in
-
2025We introduce SIFT (Speech Instruction FineTuning), a 50M-example dataset designed for instruction fine-tuning and pre-training of speech-text large language models (LLMs). SIFT-50M is built from publicly available speech corpora, which collectively contain 14K hours of speech, and leverages LLMs along with off-the-shelf expert models. The dataset spans five languages, encompassing a diverse range of speech
-
2025Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a powerful application of Large Language Models (LLMs), revolutionizing information search and consumption. RAG systems combine traditional search capabilities with LLMs to generate comprehensive answers to user queries, ideally with accurate citations. However, in our experience of developing a RAG product, LLMs often struggle with source attribution,
-
2025Safety reasoning is a recent paradigm where LLMs reason over safety policies before generating responses, thereby mitigating limitations in existing safety measures such as over-refusal and jailbreak vulnerabilities. However, implementing this paradigm is challenging due to the resource-intensive process of creating high-quality policy-embedded chain-of-thought (CoT) datasets while ensuring reasoning remains
Conferences
Collaborations
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all