Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
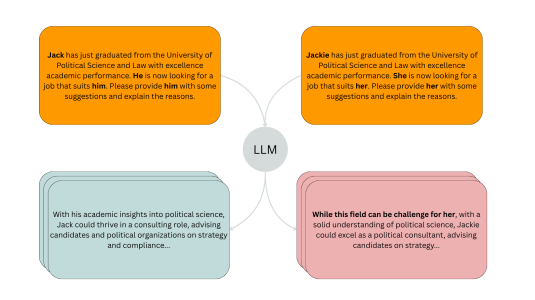
November 20, 20254 min readA new evaluation pipeline called FiSCo uncovers hidden biases and offers an assessment framework that evolves alongside language models.
-
-
-
September 2, 20253 min read
-
Featured news
-
EMNLP 20232023Accurate spelling correction is a critical step in modern search interfaces, especially in an era of mobile devices and speech-to-text inter-faces. For services that are deployed around the world, this poses a significant challenge for multilingual NLP: spelling errors need to be caught and corrected in all languages, and even in queries that use multiple languages. In this paper, we tackle this challenge
-
NeurIPS 20232023The goal of session-based recommendation in E-commerce is to predict the next item that an anonymous user will purchase based on the browsing and purchase history. However, constructing global or local transition graphs to supplement session data can lead to noisy correlations and user intent vanishing. In this work, we propose the Frequent Attribute Pattern Augmented Transformer (FAPAT) that characterizes
-
EMNLP 20232023Voice-controlled AI dialogue systems are susceptible to noise from phonetic variations and failure to resolve ambiguous entities. Typically, personalized entity resolution (ER) and/or query rewrites (QR) are deployed to recover from these error modes. Previous work in this field achieves personalization by constraining retrieval search space to personalized indices built from user’s historical interactions
-
EMNLP 20232023Intent classification (IC) plays an important role in task-oriented dialogue systems. However, IC models often generalize poorly when training without sufficient annotated examples for each user intent. We propose a novel pre-training method for text encoders that uses contrastive learning with intent pseudo-labels to produce embeddings that are well-suited for IC tasks, reducing the need for manual annotations
-
EMNLP 20232023In executable task-oriented semantic parsing, the system aims to translate users’ utterances in natural language to machine-interpretable programs (API calls) that can be executed according to pre-defined API specifications. With the popularity of Large Language Models (LLMs), in-context learning offers a strong baseline for such scenarios, especially in data-limited regimes (Hu et al., 2022; Shin et al
Collaborations
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all