Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
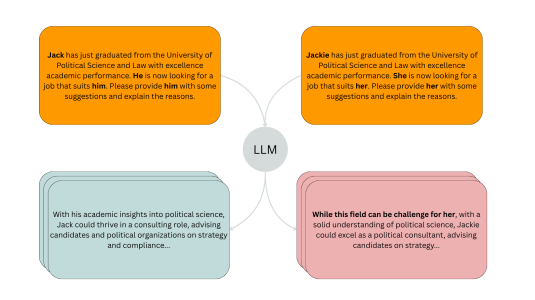
November 20, 20254 min readA new evaluation pipeline called FiSCo uncovers hidden biases and offers an assessment framework that evolves alongside language models.
-
-
-
September 2, 20253 min read
-
Featured news
-
WACV 20242024Vision-language models have been widely explored across a wide range of tasks and achieve satisfactory performance. However, it’s under-explored how to consolidate entity understanding through a varying number of images and to align it with the pre-trained language models for generative tasks. In this paper, we propose MIVC, a general multiple instance visual component to bridge the gap between various
-
AAAI 20242024We propose DocFormerv2, a multi-modal transformer for Visual Document Understanding (VDU). The VDU domain entails understanding documents (beyond mere OCR predictions) e.g., extracting information from a form, VQA for documents and other tasks. VDU is challenging as it needs a model to make sense of multiple modalities (visual, language and spatial) to make a prediction. Our approach, termed DocFormerv2
-
ICDE 20242023Search tasks require finding items similar to a given query, making it a crucial aspect of various applications. However, storing and computing similarity for millions or billions of item representations can be computationally expensive. To address this, quantization-based hash methods present memory and inference-efficient solutions by converting continuous representations into non-negative integer codes
-
The 2023 International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (ASONAM 2023)2023In online businesses, personalization of site content is crucial for providing a better user experience and increasing customer engagement. Machine learning algorithms are often used to analyze customer data such as browsing behavior, purchase history to tailor the website content to each individual customer’s preferences and needs. However, measuring the success of these personalized experiences can be
-
NeurIPS 20232023Transformers are central in modern natural language processing and computer vision applications. Despite recent works devoted to reducing the quadratic cost of such models (as a function of the sequence length), dealing with ultra long sequences (e.g., with more than 16K tokens) remains challenging. Applications such as answering questions based on a book or summarizing a scientific article are inefficient
Collaborations
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all