Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
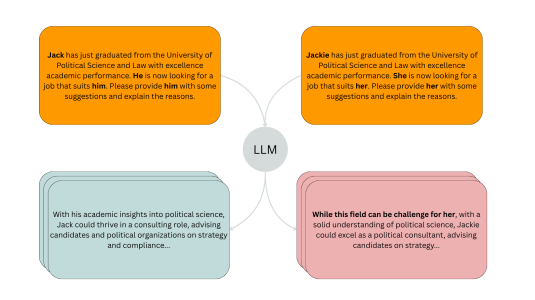
November 20, 20254 min readA new evaluation pipeline called FiSCo uncovers hidden biases and offers an assessment framework that evolves alongside language models.
-
-
-
September 2, 20253 min read
-
Featured news
-
2024We propose Strongly Supervised pre-training with ScreenShots (S4) - a novel pre-training paradigm for Vision-Language Models using data from large-scale web screenshot rendering. Using web screenshots unlocks a treasure trove of visual and textual cues that are not present in using image-text pairs. In S4, we leverage the inherent tree-structured hierarchy of HTML elements and the spatial localization to
-
Journal of Business Research2024Sellers on online marketplaces such as Amazon.com use a variety of retail and retail media advertising services to improve their brand performance, including awareness, consideration, and revenue. But how can they measure their progress and drive these metrics? For 122,000 brands, we measure Amazon shoppers’ brand awareness, consideration, and purchases and test how they change with ad and retail actions
-
2024Given a node-attributed graph, and a graph task (link prediction or node classification), can we tell if a graph neural network (GNN) will perform well? More specifically, do the graph structure and the node features carry enough usable information for the task? Our goals are (1) to develop a fast tool to measure how much information is in the graph structure and in the node features, and (2) to exploit
-
MSR 20242024Data-driven program translation has been recently the focus of sev- eral lines of research. A common and robust strategy is supervised learning. However, there is typically a lack of parallel training data, i.e., pairs of code snippets in source and target language. While many data augmentation techniques exist in the domain of natural language processing, they cannot be easily adapted to tackle code translation
-
ICRA 20242024In this paper, we present a probabilistic and unconstrained model predictive control formulation for robot navigation under uncertainty. We present (1) a closed-form approximation of the probability of collision that naturally models the propagation of uncertainty over the planning horizon and is computationally cheap to evaluate, and (2) a collision-cost formulation which provably preserves forward invariance
Collaborations
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all