Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
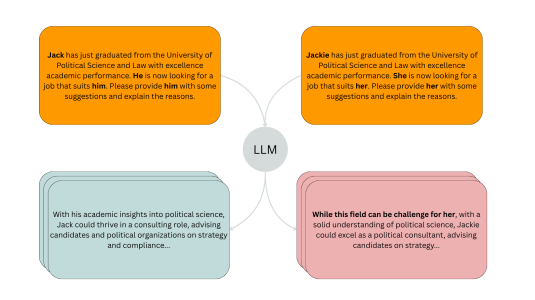
November 20, 20254 min readA new evaluation pipeline called FiSCo uncovers hidden biases and offers an assessment framework that evolves alongside language models.
-
-
-
September 2, 20253 min read
-
Featured news
-
2024The increasing use of transformer-based large language models brings forward the challenge of processing long sequences. In document visual question answering (DocVQA), leading methods focus on the single-page setting, while documents can span hundreds of pages. We present GRAM, a method that seamlessly extends pre-trained single-page models to the multi-page setting, with-out requiring computationally-heavy
-
2024Synthesizing novel views for dynamic scenes from a collection of RGB inputs poses significant challenges due to the inherent under-constrained nature of the problem. To mitigate this ill-posedness, practitioners in the field of neural radiance fields (NeRF) often resort to the adoption of intricate geometric regularization techniques, including scene flow, depth estimation, or learned perceptual similarity
-
EACL 2024 Workshop on Natural Language Processing for Human Resources2024Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have been reshaping Natural Language Processing (NLP) task in several domains. Their use in the field of Human Resources (HR) has still room for expansions and could be beneficial for several time consuming tasks. Examples such as time-off submissions, medical claims filing, and access requests are noteworthy, but they are by no means the sole instances
-
WSDM 2024 Workshop on Interactive and Scalable Information Retrieval Methods for E-Commerce2024Query Autocomplete (QAC) systems predict the best query suggestions based on customer typed prefix and other contextual signals. Conventional techniques employ the Most Popular Completion (MPC) method, where query suggestions that are popular and begin with the prefix (prefix aware) are retrieved from a pre-computed index. To account for contextual signals like past search activity of the user in the session
-
EACL 20242024In this work, We present Unified Embeddings for Multimodal Retrieval (UNIMUR), a simple but effective approach that embeds multimodal inputs and retrieves visual and textual outputs via frozen Large Language Models (LLMs). Specifically, UNIMUR jointly retrieves multimodal outputs via unified multimodal embedding and applies dual alignment training to account for both visual and textual semantics. Thus,
Collaborations
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all