In a previous article on sustainable buildings, we talked about the approach of “sense, act, and scale” to drive efficiencies in buildings, and provided information using scientific publications. In this article, we will explore how data-driven analysis can help to identify fault detection and drive energy efficiencies for facilities management by providing details on:
- Key challenges for building management and operations;
- Building system design fundamentals;
- Key data points to investigate faults for facilities-level sustainability; and
- Data-driven fault identification on AWS
Global temperatures are on the rise, greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions are the primary contributor, and facilities are among the top contributors to GHG. As stipulated in the Paris Agreement, facilities need to be 30% more energy efficient and net carbon neutral by 2050. Many companies have set new targets to reduce their emissions in recent years. For example, Amazon has set out the mission to be net neutral by 2040 and, in its recent sustainability report, has touched on how the company is using innovative design to build sustainability into physical Amazon campuses.
This article provides information on how companies of all sizes can operate and maintain their existing buildings more efficiently by identifying and fixing faults using data-driven mechanisms. In this vein, Amazon is sponsoring an AI challenge at NeurIPS this year that focuses on building energy management in a smart grid. Bottom line: energy optimization of facilities must be a key component of your organization’s plan to operate more sustainably.
Facility energy optimization provides an organization’s facilities team low-hanging-fruit opportunities for reducing costs and carbon. However, building systems do inherit many complexities that must be addressed.
Some of the key facilities-management challenges are:
- A building’s lifespan is 50+ years, and a facility’s system sensors are typically installed on day one. Many new cloud-native sensor options come to market every year, but building management systems (BMS) aren’t open, making it difficult to modernize data architectures for building infrastructure;
- Across any large real estate portfolio there is a wide range of technology, standards, building types, and designs that are difficult to manage over their lifecycles;
- Building management and automation systems require a third party to own and modify production data, and licensing fees aren’t based on consumption pricing; and
- Facilities teams generally lack the cloud expertise required to design a bespoke management solution, and their IT teams often don’t have product-level experience to provide as an alternative for addressing building-management needs.
Facilities management and sustainability
Facilities management teams have limited options to modify most core BMS functions.
These systems are sometimes referred to as black boxes in that they don’t have the same level of do-it-yourself features that most cloud users have come to expect. There can be contractual challenges, as well, for building tenants who don’t have access to BMS information. This is by design, primarily due to a clear operational argument that safety and security control functions should be limited to key personnel. However, this lack of access to building-performance analytics, required for enterprise-level sustainability transformations, is increasingly considered a blocker by many of our sustainability customers.
Let’s begin our analysis by looking at a building’s biggest consumer of electricity and producer of emissions: the HVAC system.
HVAC units are central to a building and constitute roughly 50% of a building’s energy consumption. As a result, they are well instrumented and generally follow a rules-based approach. The downside: this approach can lead to many false alarms and building managers rely on manual inspection and occupants to communicate important faults that require attention. Building managers and engineers focus significant time and budget on HVAC systems, but nevertheless HVAC system faults still can account for 5% to 20% of energy waste.
The most common example of an HVAC unit with which we are all familiar is an air conditioner. In a BMS, HVAC is comprised of sub-components that provide heating or cooling, ventilation (air handling units, fans) and AC (rooftop units, variable refrigerants) and more.
A building’s data model, and the larger building management schema, are established when the building first opens. Alerts, alarms, and performance data are issued through the BMS and a manager will notify a building services team to take action as needed. However, as the building and infrastructure ages many alarms become endemic and are difficult to remedy. Alarm fatigue is a term often used to describe the resulting BMS operator experience.
Variable air volume (VAV) units are another important asset that help to maintain temperatures by managing local air flow. VAV units help optimize the temperature by modifying air flow as opposed to conventional air volume (CAV) units which provide a constant volume of air that only affects air temperature.
There are often hundreds of VAV units in a larger building and managing them is burdensome. Building engineers have limited time to configure each of them as building demands change and VAV unit configurations are typically left unchanged after the commissioning of the building. The result: many unseen or mysterious building faults, and the hidden loss of energy over the years.
Many modern buildings are designed to accommodate whatever the building planners know at the time of commissioning. As a result, HVAC system configuration isn’t a data-driven process because operational data doesn’t yet exist. The only real incentives for HVAC system optimization typically result from failures and occupant complaints. To meet future sustainability targets, buildings must be equipped with data-driven smart configurations that can be adjusted automatically.
To achieve this, we must understand the fundamentals of air flow as we need to combine the expertise of building engineers, IoT engineers, and data engineers to resolve some of the complex air-flow challenges. This also requires an understanding of how facilities are generally managed today, which we’ll examine next.
Anatomy of facilities management
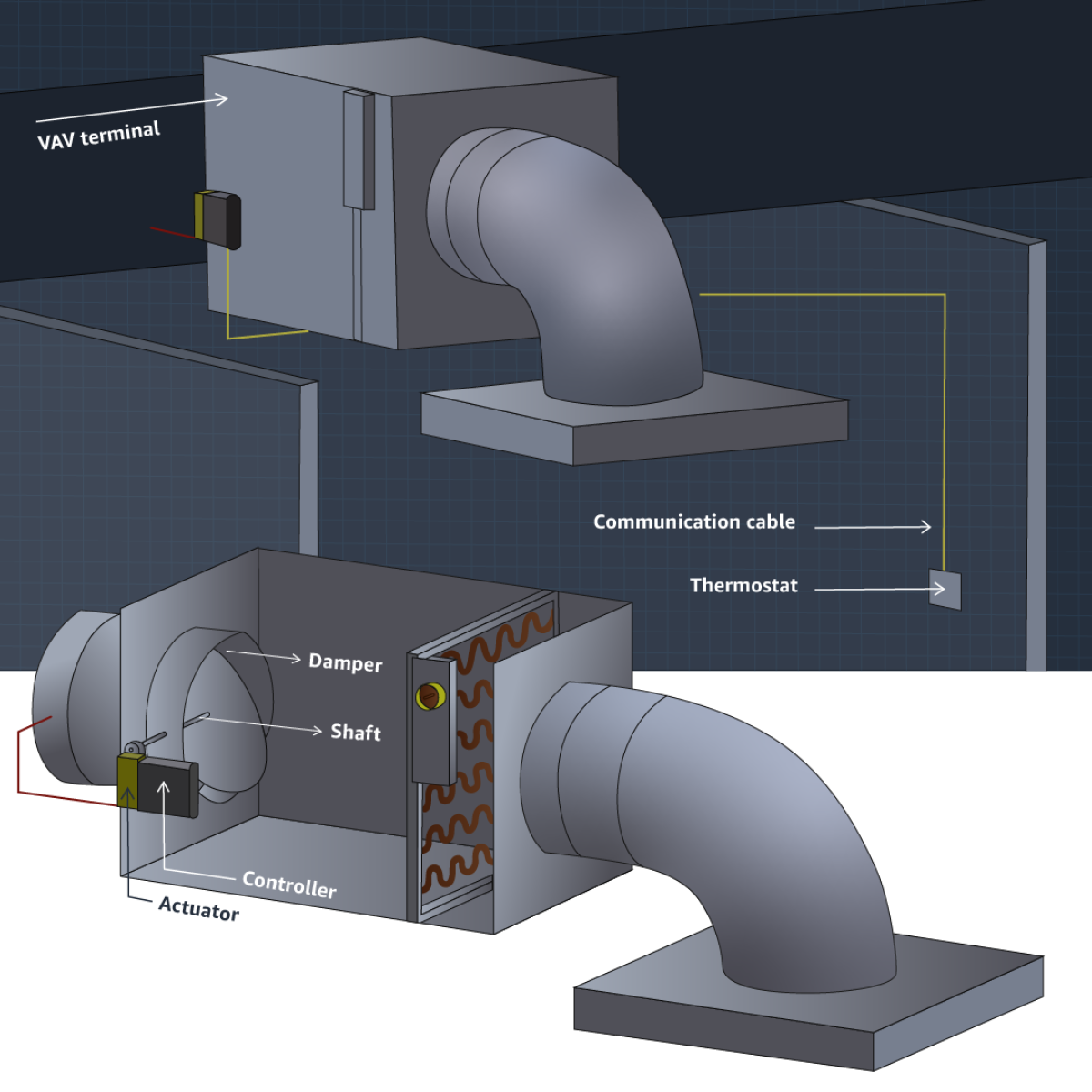
The image below shows how an air-handling unit (AHU) uses fans to distribute air through ducting. These ducts are attached to AHUs (a type of VAV unit), controlling the flow of air to specific rooms.

To change the temperature of a given zone (often representing a physical room), a sensor will send a notification through a building gateway and controller. This device serves as an intermediary between the BMS server and a given HVAC unit.
There is some automation built into these HVAC systems in the form of thermostats. The automation comes in the form of a given cooling unit responding to a temperature reading, calculated by the thermostat. These setpoints provide a temperature range that, when followed, provide the best performance of the system.
Setpoint typically refers to the point at which a building system is set to activate or deactivate, eg a heating system might be set to switch on if the internal temperature falls below 20°C.
AHU and VAV unit control points are managed by BMS software. This software is vendor managed and the configuration of the control system is determined at building inception. The configurations can be established based on several factors: room capacity and occupancy, room location, room cooling requirement, zone requirement, and more.
To illustrate a data model that reflects the operation of the HVAC system, let’s look at the VAVs that help distribute the air and the fault-driven alerts apparent in most aging systems. It is difficult to personalize these configurations as they are not data driven and do not update automatically. Let's use the flow of air through a given building as a use case and assume its operation will have a sizable impact on the building's overall energy usage.

There will often be multiple zone-specific faults, such as temperature or flow failures, issues with dampers or fans, software configuration errors that can lead to short-cycling of the unit(s), and communication or controller problems, which make it difficult to even identify the problem remotely. These factors all result in a low-efficiency cooling system that increases emissions, wasting energy and money.
What faults can tell you about sustainable building performance
Faults can be neglected for long periods of time, leaking invisible energy in the process.
Researchers from UC San Diego conducted a detailed data analysis (Bharathan was a co-author) of a 145,000-square-foot building. They identified 88 faults after building engineers fixed all the issues they could find. The paper estimates that fixing these faults could save 410.3 megawatt hours per year and, at a typical electrical cost of 12 cents per kilowatt hour, achieve a $492,360 savings in the first year.
According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s Greenhouse Gas Equivalencies Calculator, that’s the equivalent of 38,244 passenger car trips abated. Cisco offers another example. The company achieved a 28% reduction in electrical usage in their buildings worldwide by using an IP-Enabled Energy Management solution.
Traditional fault fixing focuses on the centralized HVAC subsystems such as AHU. Here we focus on the VAV units that are often ignored. Some of the key issues in VAV units are: air supply flow, temperature setpoints, thermostat adjustments, inappropriate cooling or stuck dampers.
To identify these faults, you can perform data analysis with key data attributes including temperature, heating, and cooling setpoints; upper- and lower- limit changes based on day of week; re-heat coil (on or off); occupancy sensor and settings (occupied, standby or unoccupied); damper sensor and damper settings; and pressure flow.
Using these parameters, we can define informative models. For example, you can create setpoints informed by seasonal weather data, in addition to room thermostats. You also can perform temperature data analysis against known occupancy times.
Data analysis isn’t easy at first; it’s generally not in a state where it can be readily loaded into a graph store. Oftentimes there is a lot of data transformation and IoT work required to get the data to a place where it can be analyzed by data scientists. To solve this challenge, you will need data experts, FM domain experts, cloud engineers, and someone who can bring them together to drive the right focus.
To begin, the best approach is setting up a meeting between your facilities and IT teams to start examining your building data. Some teams may grant you read-only access to the system. Otherwise, from a .CSV download of the last two to three years of building data, you can perform your analysis.
For data- driven fault identification within your facilities data, you can get started by using the Model, Cluster, and Compare (MCC approach). The primary objective of MCC is to determine clusters of zones within a building, and then use these clusters to automatically determine misconfigured, anomalous, or faulty zone controller configuration.
MCC approach to data-driven analysis
We will use a university-building example to explain the benefits of the MCC approach. The university building comprised personal offices, shared offices, kitchens, and restrooms.
In a typical room, the HVAC provides cold air during the summer. The supplied air flow is modulated to maintain the required temperature during day time, and falls back to a minimum during the night.
In the graph below, we show a room where the opposite happens because of a misconfiguration fault.
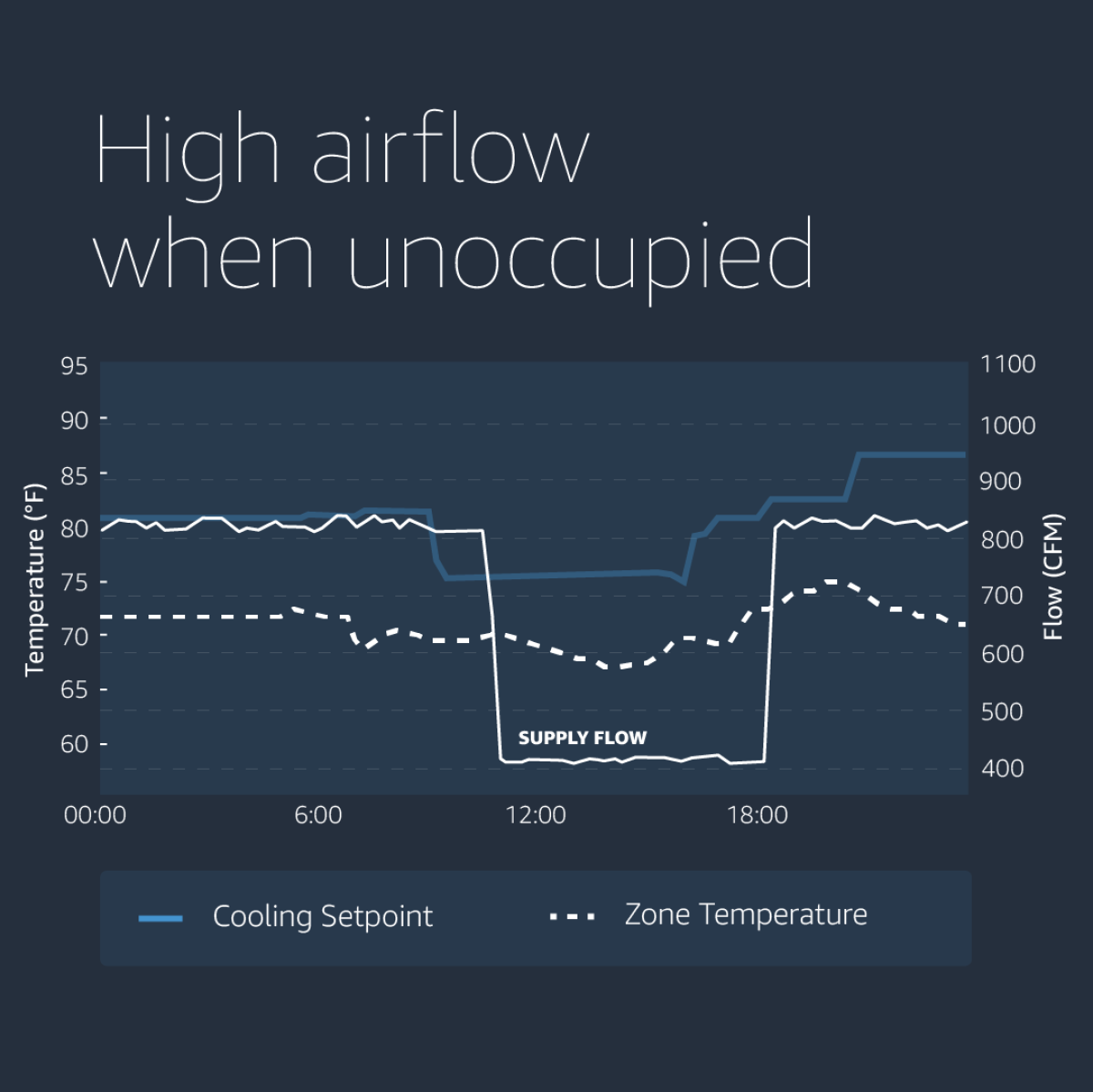
The building management contractor surmised these errors were caused due to a misunderstanding at the time of initial building commissioning. This fault was hidden within the system for years, and was identified while doing an MCC analysis.
Model
When we try to identify faults with raw sensor data, it often leads to misleading results. For example, a simple fault detection rule may generate an alarm if the temperature of a room goes beyond a threshold. The alarm may be false for any number of reasons: it could be a particularly hot day, or an event is occurring in the room. We need to look for faults that are consistent, and require human attention. Given the large number of alarms that are triggered with simple rules, such faults get overlooked.
Our MCC algorithm looks for rooms that behave differently from others over a long time-span. To compare different rooms, we create a model that captures the generic patterns of usage over months or years. Then we can compare and cluster rooms to weed out the faults.
In our algorithm, we use the measured room temperature and air flow from the HVAC to create a room energy model. The energy spent by the HVAC system on a room is proportional to the product of its temperature and airflow supplied as per the laws of thermodynamics. We use the product of two sensor measurements as the parameter to model the room because it indicates the generic patterns of use. If we find rooms whose energy patterns are substantially different, we can inspect them further.
Cluster
Room temperatures can fluctuate for natural reasons, and our fault-detection algorithm should not flag them.
The MCC algorithm clusters rooms that are similar to each other with the KMeans algorithm. The clusters naturally align rooms that are similar, for example, west-facing rooms, east-facing rooms, kitchenettes, and conference rooms. We can create these clusters manually, based on domain knowledge and usage type, or the clustering algorithm can automate this process.
Compare
Having defined configurations per cluster, the MCC algorithm then compares rooms to identify anomalies. This step ensures that natural fluctuations are ignored, and only the egregious rooms are highlighted, reducing the number of false alarms.
Intelligent rules
The MCC study created rules to detect new faults after analyzing the anomalies manually. Rules are a natural way to integrate with an existing system, and to catch similar faults that occur in the future. Rules are also interpretable by domain experts, enabling further tuning.
An interesting example of an identified fault is shown below:
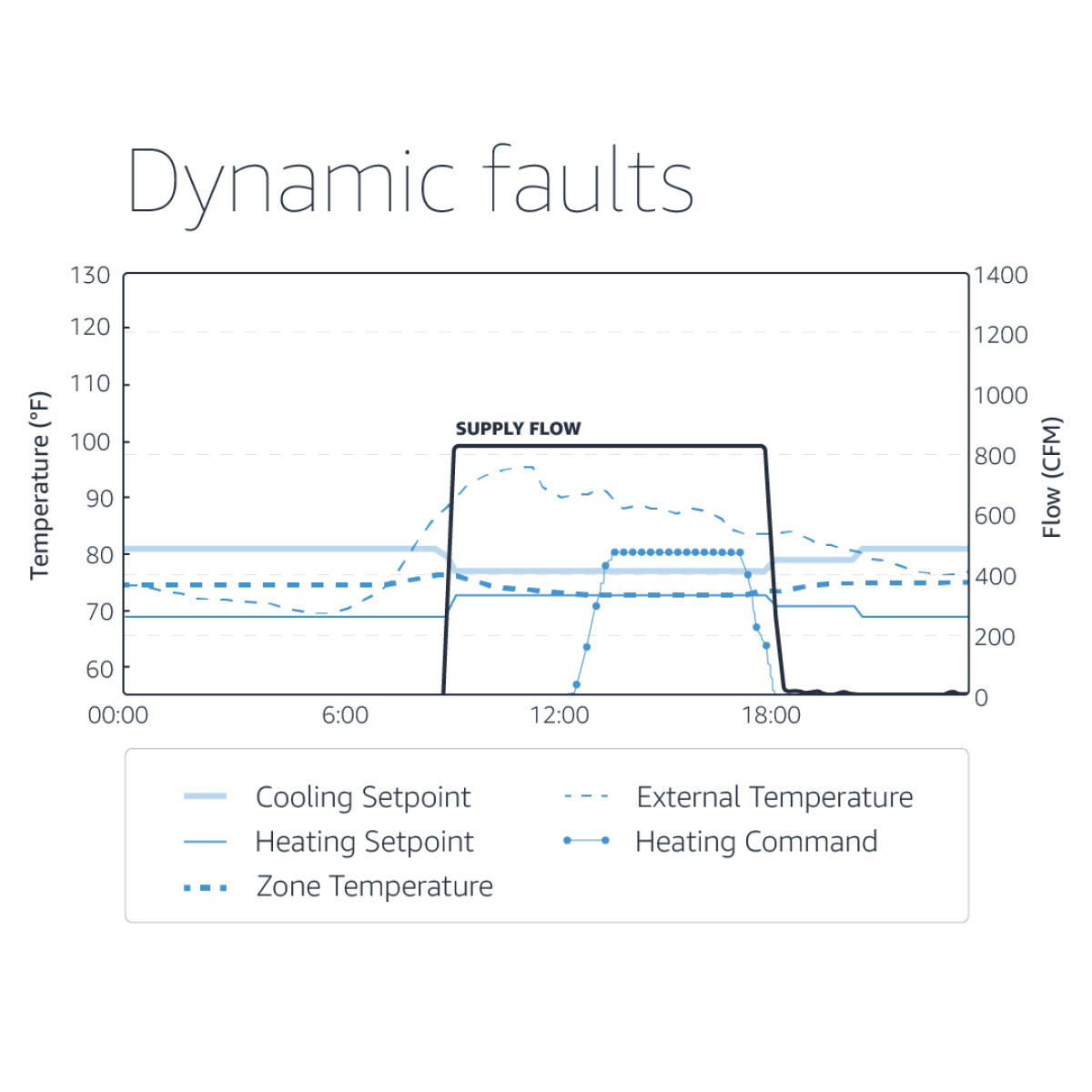
There were five rooms with similar issues on the same floor and 15 overall within the building. The cause of the fault: the designed air flow specifications were based on maximum occupancy. Issues such as these cause enormous energy waste, and they often go unnoticed for years.
A path forward
In this post we’ve provided some foundational concepts to consider in how you can better use data to improve both facility performance and availability.
Whether your goal is to improve building performance in support of sustainability transformation or to improve fault detection, the path starts with modernizing the data models that support your facilities. Following a data modernization path will illustrate where the building architecture that provides the data is not meeting expectations.
As a next step, facilities and IT managers can get started by:
- Performing a basic audit of their buildings and look for options to gather key parameter data outlined above.
- Consolidating data from the relevant sources, applying data standardization, and making use of the fault-detection approach outlined above.
- Making use of AWS Data Analytics and AWS AI/ML services to perform data analysis and apply machine learning algorithms to identify data anomalies. Amazon uses these services to manage the thousands of world-class facilities that serve our employees, customers, and communities. Learn more about our sustainable building initiatives.
These steps will help identify energy hot spots and hidden faults in your facilities; facilities managers can then make use of this information to fix the relevant faults and drive facility sustainability. Finally, consider making sustainability data easily accessible to executive teams to help drive discussions and decisions on impactful carbon-abatement initiatives.





















