At this year’s Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Prime Video presented four papers that indicate the broad range of cutting-edge problems we work on.
In one paper, “Movies2Scenes: Using movie metadata to learn scene representation", we present a novel contrastive-learning approach that uses only commonly available movie metadata to learn a general-purpose scene representation. On a diverse set of tasks evaluated using multiple benchmark datasets, models that use our representations consistently outperform models using existing state-of-the-art representations.
Notably, our learned representation offers an average improvement of 7.9% on the seven classification tasks and 9.7% on the two regression tasks in the Long-Form Video Understanding (LVU) dataset. This effort is an important step toward the first foundation model for general-purpose movie understanding.
In another paper, “Selective structured state-spaces for long-form video understanding”, we expand on the recently proposed S4 model that employs a lightweight mask generator to adaptively select informative image tokens, resulting in more efficient and accurate modeling of long-term spatiotemporal dependencies in videos. Our approach is consistently more accurate than the previous state-of-the-art model, by as much as 9.6%, while reducing the memory footprint by 23%.
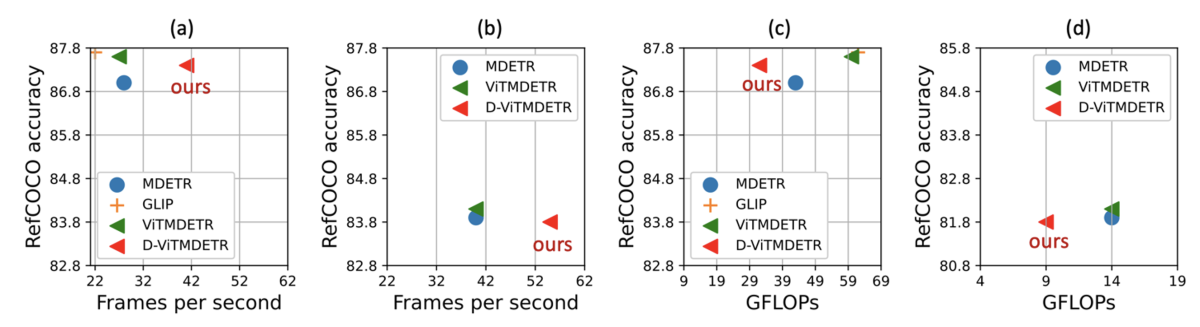
Similarly, our paper "Dynamic inference with grounding based vision and language models" explores the problem of computational redundancy in large vision-and-language models, addressing this challenge by dynamically skipping network layers, dropping input tokens, and fusing multimodal tokens, conditioned on the input image-text pair. Our results show that we can improve the run-time efficiency of the state-of-the-art models by up to 50% on multiple downstream tasks with an accuracy drop of only 0.3%.
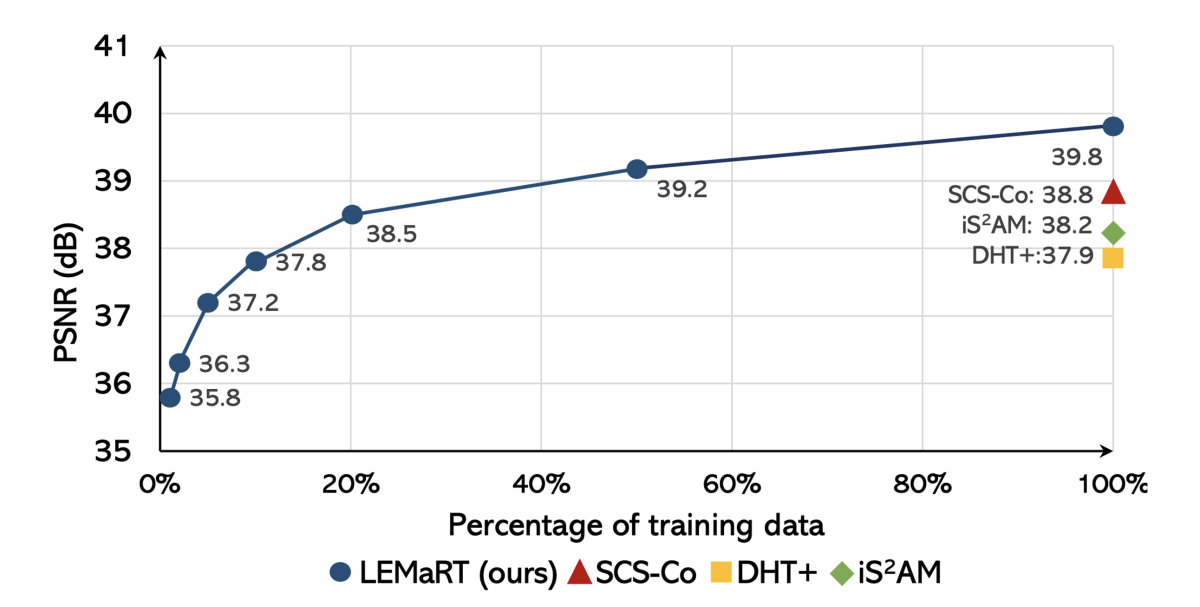
Lastly, our paper "LEMaRT: Label-efficient masked region transform for image harmonization" addresses the problem of requiring large amounts of labeled data to train image harmonization models, which modify content from different source images so that they blend together better in composite images. To this end, our method automatically generates training data by simulating defects in appearance that image harmonization models are expected to remove. Our method outperforms previous state-of-the-art approaches by a margin of 0.4dB (mean square error improvement = ~9%) when it is fine-tuned on only 50% of the training data from one of the standard benchmarks (iHarmony4) and by 1.0 dB (MSE improvement = ~21%) when it is trained on the full training dataset.
Toward a foundation model for movie understanding
The term “foundation model” generally relates to (i) a single large model that is (ii) trained on large amounts of mostly unlabeled data and can (iii) drive a number of downstream tasks. While several general-purpose visual-and-textual foundation models exist (e.g., BERT, GPT-4, CLIP, DALL-E 2, etc.), no foundation model particularly geared for movie understanding has been proposed before our work.
This is partly because directly applying existing visual or textual foundation models for movie understanding has limited effectiveness, given the large domain gap between cinematic content and the web-crawled images and text used to train those models. Factors such as the inaccessibility of much large-scale cinematic content, the computational resources required to process it, and the lack of benchmark datasets for evaluation on downstream applications add to the challenge of building a foundation model for movie understanding.
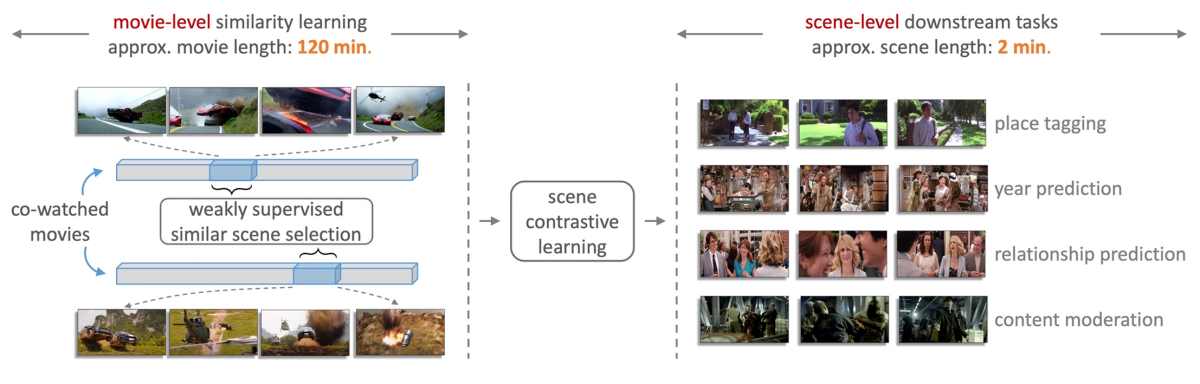
To address these challenges, we proposed a novel model trained on over five million scenes automatically identified from thousands of movies and comprising more than 45 million frames. Our model does not require any manual annotations and relies only on commonly available movie-level information (genre, synopsis, etc.). The scene representations from our model can be applied to improve the performance of a diverse set of downstream tasks, which is a key step toward building a foundation model for movie understanding.
We use movie metadata to define a measure of movie similarity and use that similarity measure to identify data pairs for contrastive learning. In contrastive learning, a model is trained on both positive pairs — examples that are similar in the relevant way — and negative pairs. During training, the model learns to produce data representations that pull positive pairs together and push negative pairs apart.
Often, the positive pairs are created by augmenting existing examples — say, re-cropping them, reversing them, or re-coloring them. By instead using movies that are considered similar to each other (see below), we ensure that our positive scene-pairs are not only visually similar but also semantically coherent, providing us with a much richer set of geometric and thematic data augmentations that enhance the training objective beyond traditional augmentation approaches.
As can be seen in the video below, our learned scene representation is able to effectively put thematically similar scenes close to each other.
In the examples below, we compare our representation with the commonly used CLIP visual representation for scene retrieval using place-labeled scenes in the Long-Form Video Understanding (LVU) dataset. Given a query scene, our representation can capture appearance as well as semantic concepts to retrieve similar scenes more effectively, while CLIP can capture only local appearance-based patterns. For overall retrieval precision on six categories of places, our representation offers a 22.7% improvement over CLIP.

Quantitatively, our learned representation exhibits an average improvement of 7.9% and 9.7% on the seven classification tasks and two regression tasks of the LVU dataset, respectively. Furthermore, using our newly collected MCD dataset in Prime Video, we compare our learned scene representation with state-of-the-art models pretrained on action recognition and image classification datasets. Our scene representation outperforms the alternatives by margins ranging from 3.8% to 50.9% across different models and tasks.
Reducing model complexity for long-form-video understanding
At Prime Video, we’re developing state-of-the-art AI models for cinematic-content understanding to facilitate a variety of downstream use cases. One of the key technical problems to this end is effective modeling of complex spatiotemporal dependencies, particularly in long-form videos such as movies and TV episodes.
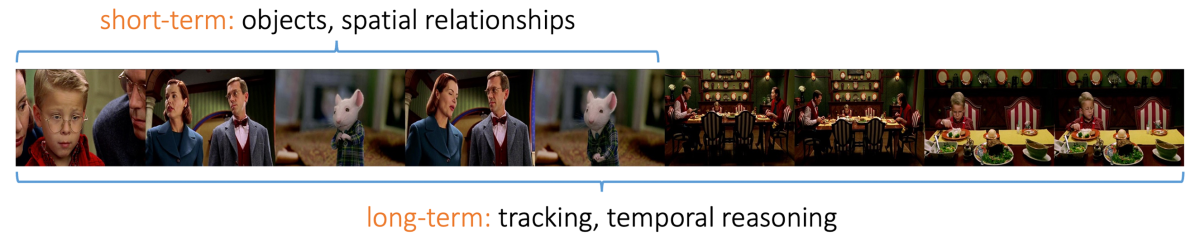
Previously proposed convolutional and recurrent neural networks struggle to learn long-term dependencies. In part this is because of exploding or vanishing gradients — where cascading adjustments to model weights grow too small or too large — as information is incorporated over long durations. Vision transformers can use self-attention to address this challenge, attending to particular, prior frames of video when interpreting the current frame. But this is computationally expensive, as it requires pairwise computations between the current frame and its predecessors.
The recently proposed structured-state-space-sequence (S4) model, with its linear complexity, offers a promising direction in this space; however, we empirically demonstrate that treating all image tokens equally, as the S4 model does, can adversely affect a model’s efficiency and accuracy.
To address this challenge, we present a novel selective S4 (i.e., S5) model that employs a lightweight mask generator to adaptively select informative image tokens, resulting in more efficient and accurate modeling of long-term spatiotemporal dependencies in videos. Unlike previous methods, which used mask-based token reduction in transformers, our S5 model avoids the dense self-attention calculation by following the guidance of the momentum-updated S4 model. This enables our model to efficiently discard less informative tokens and adapt to various long-form-video-understanding tasks more effectively.
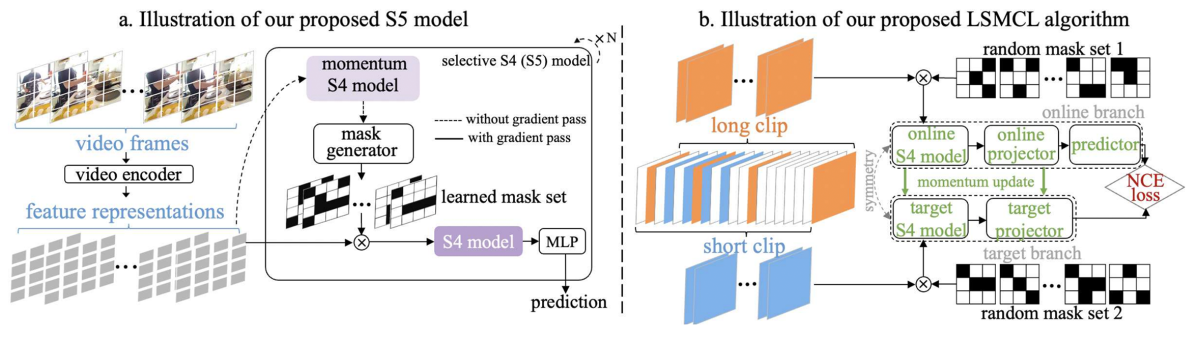
However, as is the case with most token reduction methods, the informative image tokens may be dropped incorrectly. To improve the robustness and the temporal horizon of our model, we propose a novel long-short masked contrastive-learning (LSMCL) approach that enables our model to predict longer temporal contexts using shorter input videos.
We present extensive comparative results using three challenging long-form video-understanding datasets (LVU, COIN, and Breakfast), demonstrating that our approach is consistently more accurate than the previous state-of-the-art S4 model, by as much as 9.6% on one dataset, with a memory footprint that’s 23% smaller.
Dynamic inference of multimodal models using reinforcement learning
The availability of transformer models operating over multiple data modalities as well as large-scale pretraining approaches has led to significant progress on joint image-and-language models. However, these models impose high computational costs and therefore offer low run-time efficiency, making them difficult to apply to Prime Video’s large catalogue.
Although approaches such as pruning, knowledge distillation, and quantization can help address this challenge, they can incur significant drops in accuracy (e.g., ≥ 1% at ≥ 50% model compression rates), as they are primarily designed for model-parameter reduction, not improving run-time efficiency.
To address this challenge, we propose a model that saves computation by dynamically skipping layers of a multimodal network; pruning input tokens from either the language backbone, the image backbone, or both; and fusing tokens from the separate backbones, conditioned on the input image-text pair.
Most multimodal transformer models include multihead self-attention and feed-forward network layers, which can be skipped for some inputs. Additionally, we remove redundant tokens at different levels of the backbones and fuse the image tokens with the language tokens in an adaptive manner. To learn policies for dynamic inference, we train agents using reinforcement learning.
Our results demonstrate that we can improve the run-time efficiency of the state-of-the-art models MDETR and GLIP by up to 50% on the tasks of referring-expression comprehension, segmentation, and visual question-answering, with a maximum accuracy drop of only 0.3%.
Improving label efficiency of image harmonization models
Image harmonization is an important component of the broader problem of image composition, where new images are created by extracting foreground regions from one image and transferring them to another image in a photorealistic manner.
The main technical challenge for image harmonization is the appearance mismatch between the foreground extracted from the source image and the background of the destination image. Image harmonization aims to adjust the appearance of the foreground to make it compatible with the background. However, training traditional models for image harmonization requires a large amount of labeled data, which is costly and time-consuming to obtain.
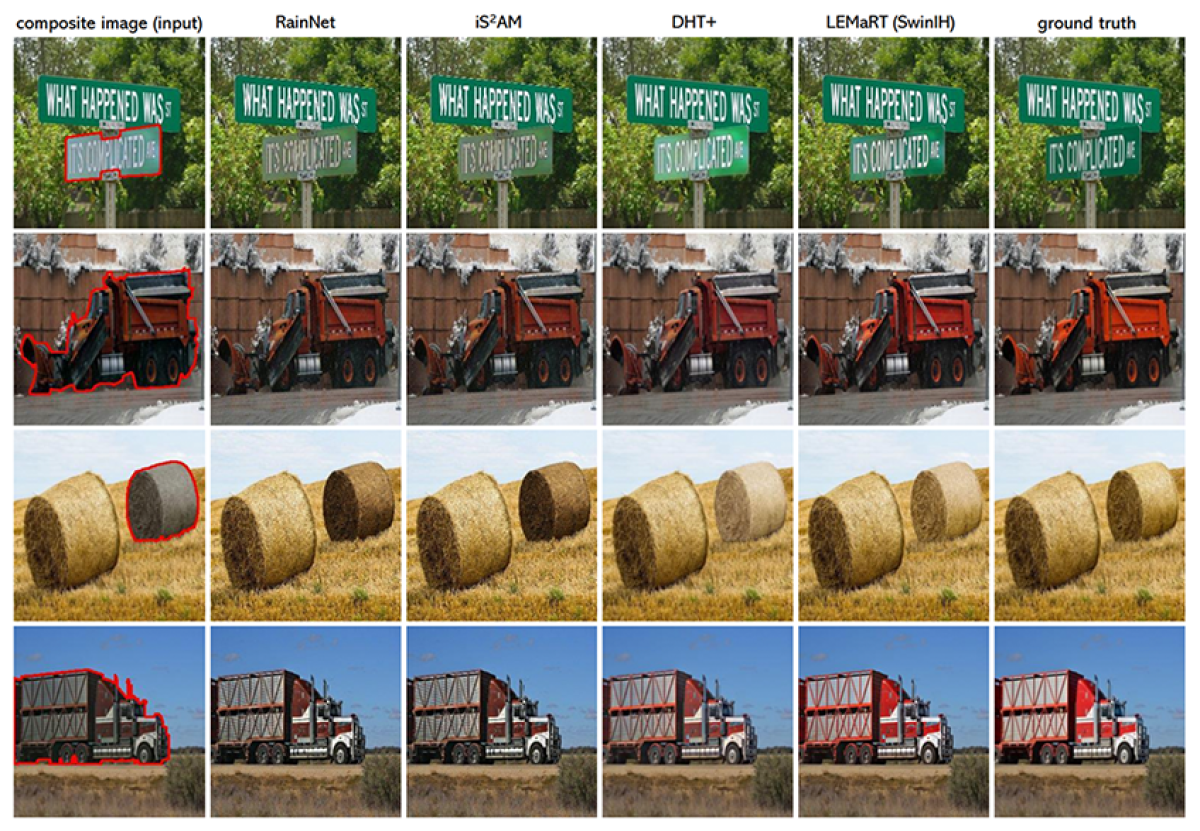
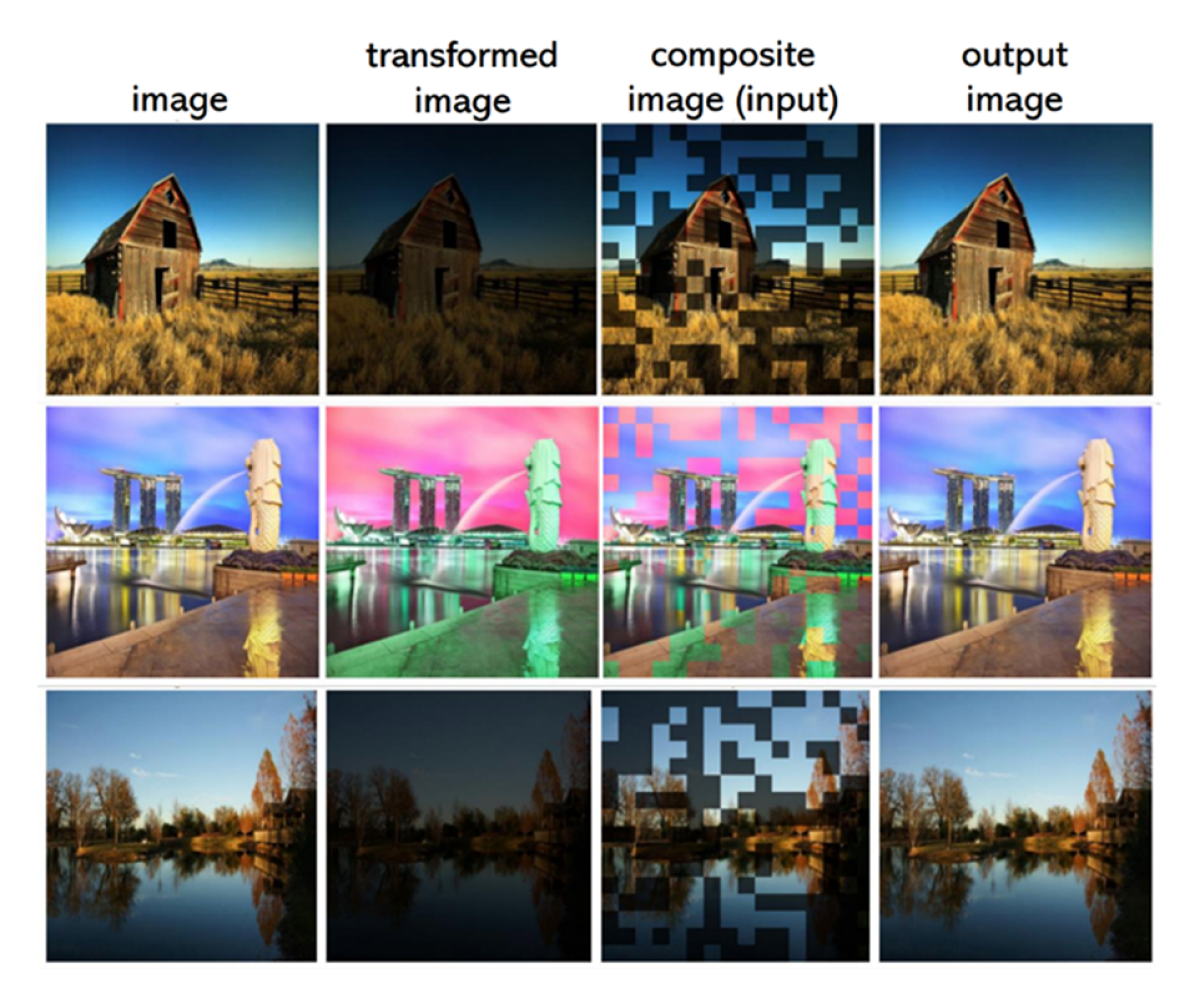
To address this challenge, we introduce a novel approach to pretraining image harmonization models, LEMaRT, which automatically generates training data by simulating the types of defects that image harmonization models are expected to remove. LEMaRT takes an image as input, selects a region in that image, and applies a set of appearance transformations to it. We use these modified images, along with the original images, to pretrain our image harmonization model. Furthermore, we introduce an image harmonization model, SwinIH, by retrofitting the previously proposed Swin Transformer with a combination of local and global self-attention mechanisms.

Pretraining our SwinIH model with our LEMaRT approach results in a new state of the art for image harmonization, while being label-efficient, i.e., consuming less annotated data for fine-tuning than existing methods. Notably, on the iHarmony4 dataset, SwinIH outperforms the state of the art, i.e., SCS-Co by a margin of 0.4 dB when it is fine-tuned on only 50% of the training data and by 1.0 dB when it is trained on the full training dataset.
Qualitative comparisons suggest that LEMaRT is better at color correction than prior methods, thanks to the pretraining process, during which LEMaRT learns the distribution of photorealistic images.