Amazon DynamoDB is one of the most popular NoSQL database offerings on the Internet, designed for simplicity, predictability, scalability, and reliability. To celebrate DynamoDB’s 10th anniversary, the DynamoDB team wrote a paper describing lessons we’d learned in the course of expanding a fully managed cloud-based database system to hundreds of thousands of customers. The paper was presented at this year’s USENIX ATC conference.
The paper captures the following lessons that we have learned over the years:
- Designing systems for predictability over absolute efficiency improves system stability. While components such as caches can improve performance, they should not introduce bimodality, in which the system has two radically different ways of responding to similar requests (e.g., one for cache misses and one for cache hits). Consistent behaviors ensure that the system is always provisioned to handle the unexpected.
- Adapting to customers’ traffic patterns to redistribute data improves customer experience.
- Continuously verifying idle data is a reliable way to protect against both hardware failures and software bugs in order to meet high durability goals.
- Maintaining high availability as a system evolves requires careful operational discipline and tooling. Mechanisms such as formal proofs of complex algorithms, game days (chaos and load tests), upgrade/downgrade tests, and deployment safety provide the freedom to adjust and experiment with the code without the fear of compromising correctness.
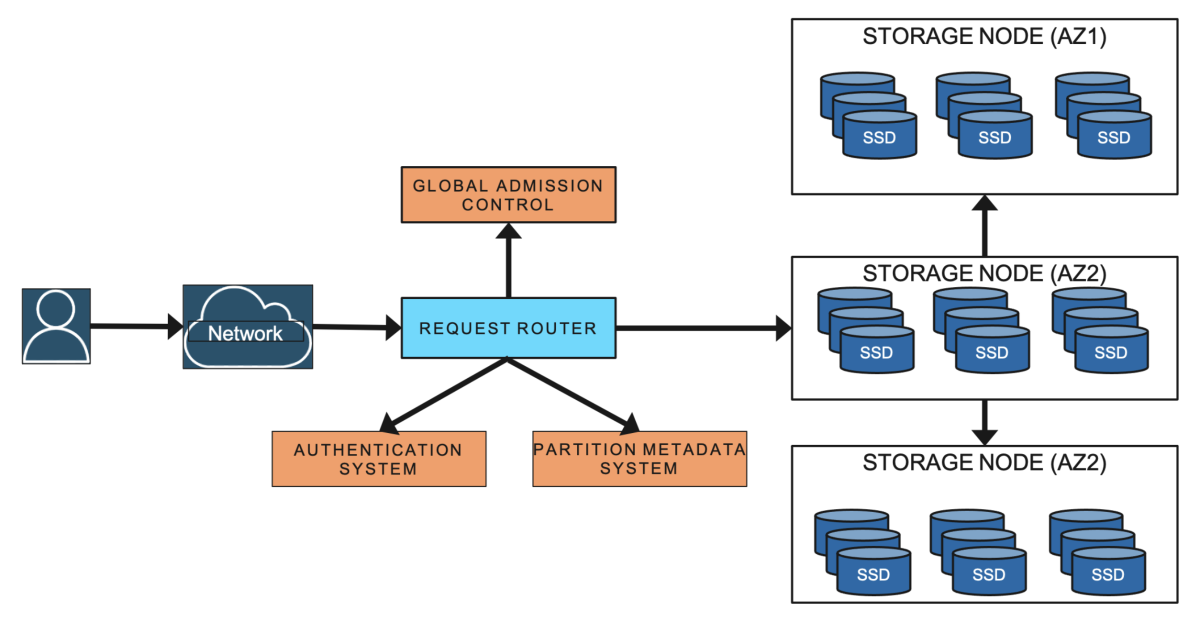
Before we dig deeper into these topics, a little terminology. A DynamoDB table is a collection of items (e.g., products), and each item is a collection of attributes (e.g., name, price, category, etc.). Each item is uniquely identified by its primary key. In DynamoDB, tables are typically partitioned, or divided into smaller sub-tables, which are assigned to nodes. A node is a set of dedicated computational resources — a virtual machine — running on a single server in a datacenter.
DynamoDB stores three copies of each partition, in different availability zones. This makes the partition highly available and durable because the availability zones’ storage resources share nothing and are substantially independent. For instance, we wouldn’t assign a partition and one of its copies to nodes that share a power supply, because a power outage would take both of them offline. The three copies of the same partition are known as a replication group, and there is a leader for the group that is responsible for replicating all the customer mutations and serving strongly consistent reads.
Those definitions in hand, let’s turn to our lessons learned.
Predictability over absolute efficiency
DynamoDB employs a lot of metadata caches in order to reduce latency. One of those caches stores the routing metadata for data requests. This cache is deployed on a fleet of thousands of request routers, DynamoDB’s front-end service.
In the original implementation, when the request router received the first request for a table, it downloaded the routing information for the entire table and cached it locally. Since the configuration information about partition replicas rarely changed, the cache hit rate was approximately 99.75%.
This was an amazing hit rate. However, on the flip side, the fallback mechanism for this cache was to hit the metadata table directly. When the cache becomes ineffective, the metadata table needs to instantaneously scale from handling 0.25% of requests to 100%. The sudden increase in traffic can cause the metadata table to fail, causing cascading failure in other parts of the system. To mitigate against such failures, we redesigned our caches to behave predictably.
First, we built an in-memory datastore called MemDS, which significantly reduced request routers’ and other metadata clients’ reliance on local caches. MemDS stores all the routing metadata in a highly compressed manner and replicates it across a fleet of servers. MemDS scales horizontally to handle all incoming requests to DynamoDB.
Second, we deployed a new local cache that avoids the bimodality of the original cache. All requests, even if satisfied by the local cache, are asynchronously sent to the MemDS. This ensures that the MemDS fleet is always serving a constant volume of traffic, regardless of cache hit or miss. The regular exercise of the fallback code helps prevent surprises during fallback.
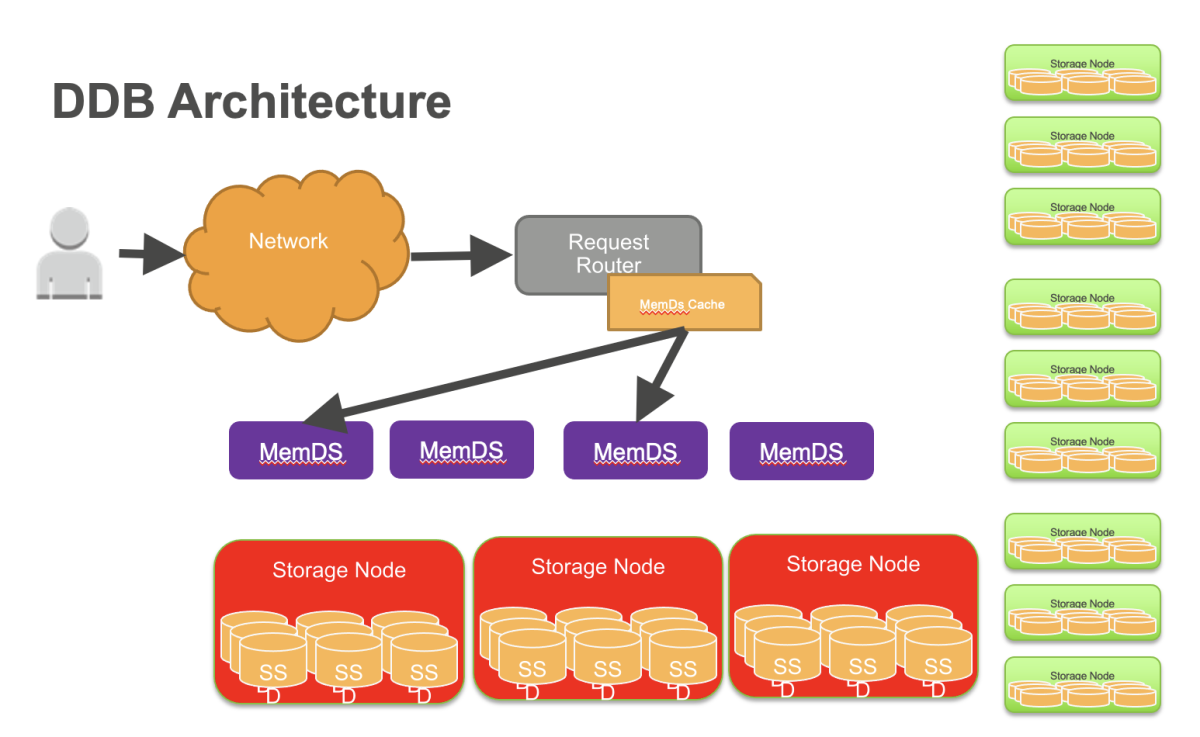
Unlike conventional local caches, MemDS sees traffic that is proportional to the customer traffic seen by the service; thus, during cache failures, it does not see a sudden amplification of traffic. Doing constant work removed the need for complex logic to handle edge cases around cache misses and reduced the reliance on local caches, improving system stability.
Reshaping partitioning based on traffic
Partitions offer a way to dynamically scale both the capacity and performance of tables. In the original DynamoDB release, customers explicitly specified the throughput that a table required in terms of read capacity units (RCUs) and write capacity units (WCUs). The original system assigned partitions to nodes based on both available space and computational capacity.
As the demands on a table changed (because it grew in size or because the load increased), partitions could be further split to allow the table to scale elastically. Partition abstraction proved really valuable and continues to be central to the design of DynamoDB.
However, the early version of DynamoDB assigned both space and capacity to individual partitions on the basis of size, evenly distributing computational resources across table entries. This led to challenges of “hot partitions” and throughput dilution.
Hot partitions happened because customer workloads were not uniformly distributed and kept hitting a subset of items. Throughput dilution happened when partitions that had been split to handle increased load ended up with so few keys that they could quickly max out their meager allocated capacity.
Our initial response to these challenges was to add bursting and adaptive capacity (along with other features such as split for consumption) to DynamoDB. This line of work also led to the launch of on-demand tables.
Bursting is a way to absorb temporal spikes in workloads at a partition level. It’s based on the observation that not all partitions hosted by a storage node use their allocated throughput simultaneously.
The idea is to let applications tap into unused capacity at a partition level on a best-effort basis to absorb short-lived spikes. DynamoDB still maintains workload isolation by ensuring that a partition can burst only if there is unused throughput at the node level.
DynamoDB also launched adaptive capacity to handle long-lived spikes that cannot be absorbed by the burst capacity. Adaptive capacity monitors traffic patterns and repartitions tables so that heavily accessed items reside on different nodes.
Both bursting and adaptive capacity had limitations, however. Bursting was helpful only for short-lived spikes in traffic, and it was dependent on nodes’ having enough throughput to support it. Adaptive capacity was reactive and kicked in only after transmission rates had been throttled down to avoid overloads.
To address these limitations, the DynamoDB team replaced adaptive capacity with global admission control (GAC). GAC builds on the idea of token buckets, in which bandwidth is allocated to network nodes as tokens, and the nodes “cash in” tokens in order to transmit data. Each request router maintains a local token bucket and communicates with GAC to replenish tokens at regular intervals (on the order of every few seconds). For an extra layer of defense, DynamoDB also uses token buckets at the partition level.
Continuous verification
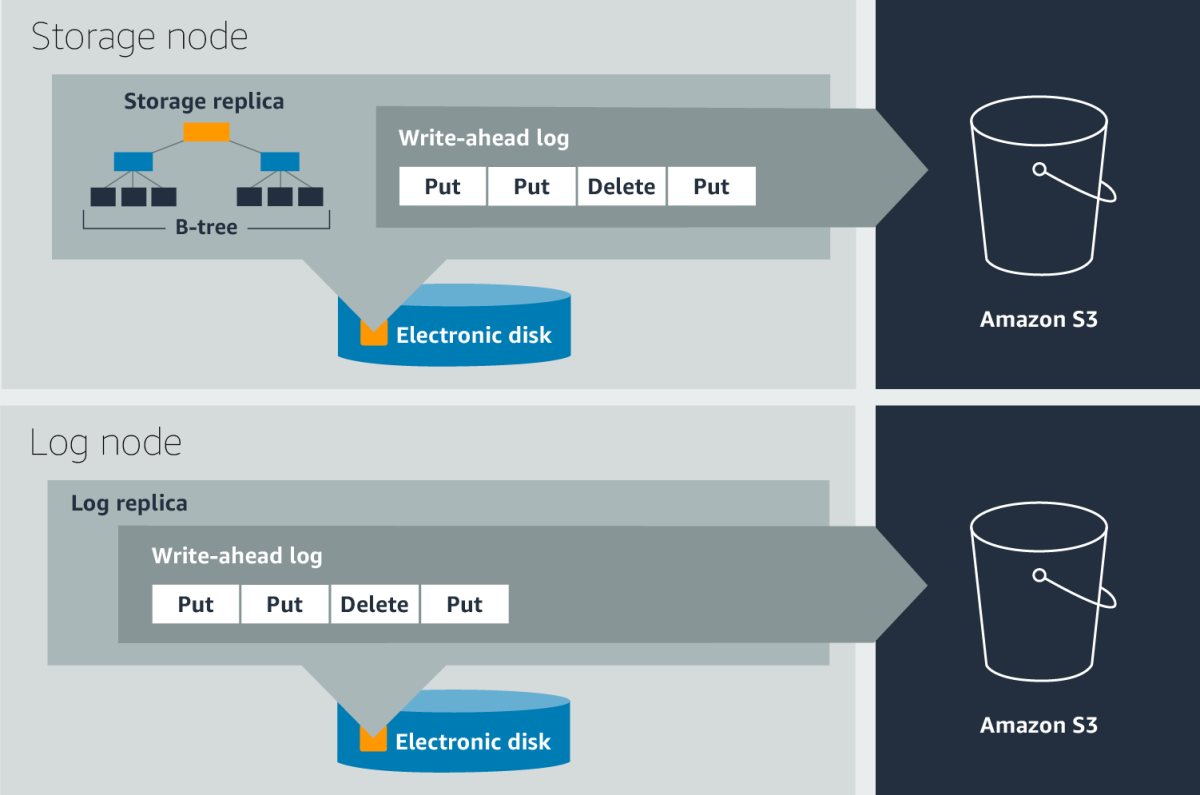
To provide durability and crash recovery, DynamoDB uses write-ahead logs, which record data writes before they occur. In the event of a crash, DynamoDB can use the write-ahead logs to reconstruct lost data writes, bringing partitions up to date.
Write-ahead logs are stored in all three replicas of a partition. For higher durability, the write-ahead logs are periodically archived to S3, an object store that is designed for more than 99.99% (in fact, 11 nines) durability. Each replica contains the most recent write-ahead logs, which are usually waiting to be archived. The unarchived logs are typically a few hundred megabytes in size.
DynamoDB continuously verifies data at rest. Our goal is to detect any silent data errors or “bit rot” — bit errors caused by degradation of the storage medium. An example of continuous verification is the scrub process.
The scrub process verifies two things: that all three copies in a replication group have the same data and that the live replicas match a reference replica built offline using the archived write-ahead-log entries.
The verification is done by computing the checksum of the live replica and matching that with a snapshot of the reference replica. A similar technique is used to verify replicas of global tables. Over the years, we have learned that continuous verification of data at rest is the most reliable method of protecting against hardware failures, silent data corruption, and even software bugs.
Availability
DynamoDB regularly tests its resilience to node, rack, and availability zone (AZ) failures. For example, to test the availability and durability of the overall service, DynamoDB performs power-off tests. Using realistic simulated traffic, a job scheduler powers off random nodes. At the end of all the power-off tests, the test tools verify that the data stored in the database is logically valid and not corrupted.
The first point about availability is that it needs to be measurable. DynamoDB is designed for 99.999% availability for global tables and 99.99% availability for regional tables. To ensure that these goals are being met, DynamoDB continuously monitors availability at the service and table levels. The tracked availability data is used to estimate customer-perceived availability trends and trigger alarms if the number of errors that customers see crosses a certain threshold.
These alarms are called customer-facing alarms (CFAs). The goal of these alarms is to report any availability-related problems and proactively mitigate them either automatically or through operator intervention. The key point to note here is that availability is measured not only on the server side but on the client side.
We also use two sets of clients to measure the user-perceived availability. The first set of clients is internal Amazon services using DynamoDB as the data store. These services share the availability metrics for DynamoDB API calls as observed by their software.
The second set of clients is our DynamoDB canary applications. These applications are run from every AZ in the region, and they talk to DynamoDB through every public endpoint. Real application traffic allows us to reason about DynamoDB availability and latencies as seen by our customers. The canary applications offer a good representation of what our customers might be experiencing both long and short term.
The second point is that read and write availability need to be handled differently. A partition’s write availability depends on the health of its leader and of its write quorum, meaning two out of the three replicas from different AZs. A partition remains available as long as there are enough healthy replicas for a write quorum and a leader.
In a large service, hardware failures such as memory and disk failures are common. When a node fails, all replication groups hosted on the node are down to two copies. The process of healing a storage replica can take several minutes because the repair process involves copying the B-tree — a data structure that maps partitions to storage locations — and write-ahead logs.
Upon detecting an unhealthy storage replica, the leader of a replication group adds a log replica to ensure there is no impact on durability. Adding a log replica takes only a few seconds, because the system has to copy only the most recent write-ahead logs from a healthy replica; reconstructing the more memory-intensive B-tree can wait. Quick healing of affected replication groups using log replicas thus ensures the high durability of the most recent writes. Adding a log replica is the fastest way to ensure that the write quorum of the group is always met. This minimizes disruption to write availability due to an unhealthy write quorum. The leader replica serves consistent reads.
Introducing log replicas was a big change to the system, but the Paxos consensus protocol, which is formally provable, gave us the confidence to safely tweak and experiment with the system to achieve higher availability. We have been able to run millions of Paxos groups in a region with log replicas. Eventually, consistent reads can be served by any of the replicas. In case a leader fails, other replicas detect its failure and elect a new leader to minimize disruptions to the availability of consistent reads.