Cryptographic algorithms are essential to online security, and at Amazon Web Services (AWS), we implement cryptographic algorithms in our open-source cryptographic library, AWS LibCrypto (AWS-LC), based on code from Google’s BoringSSL project. AWS-LC offers AWS customers implementations of cryptographic algorithms that are secure and optimized for AWS hardware.
Two cryptographic algorithms that have become increasingly popular are x25519 and Ed25519, both based on an elliptic curve known as curve25519. To improve the customer experience when using these algorithms, we recently took a deeper look at their implementations in AWS-LC. Henceforth, we use x/Ed25519 as shorthand for “x25519 and Ed25519”.
In 2023, AWS released multiple assembly-level implementations of x/Ed25519 in AWS-LC. By combining automated reasoning and state-of-the-art optimization techniques, these implementations improved performance over the existing AWS-LC implementations and also increased assurance of their correctness.
In particular, we prove functional correctness using automated reasoning and employ optimizations targeted to specific CPU microarchitectures for the instruction set architectures x86_64 and Arm64. We also do our best to execute the algorithms in constant time, to thwart side-channel attacks that infer secret information from the durations of computations.
In this post, we explore different aspects of our work, including the process for proving correctness via automated reasoning, microarchitecture (μarch) optimization techniques, the special considerations for constant-time code, and the quantification of performance gains.
Elliptic-curve cryptography
Elliptic-curve cryptography is a method for doing public-key cryptography, which uses a pair of keys, one public and one private. One of the best-known public-key cryptographic schemes is RSA, in which the public key is a very large integer, and the corresponding private key is prime factors of the integer. The RSA scheme can be used both to encrypt/decrypt data and also to sign/verify data. (Members of our team recently blogged on Amazon Science about how we used automated reasoning to make the RSA implementation on Amazon’s Graviton2 chips faster and easier to deploy.)
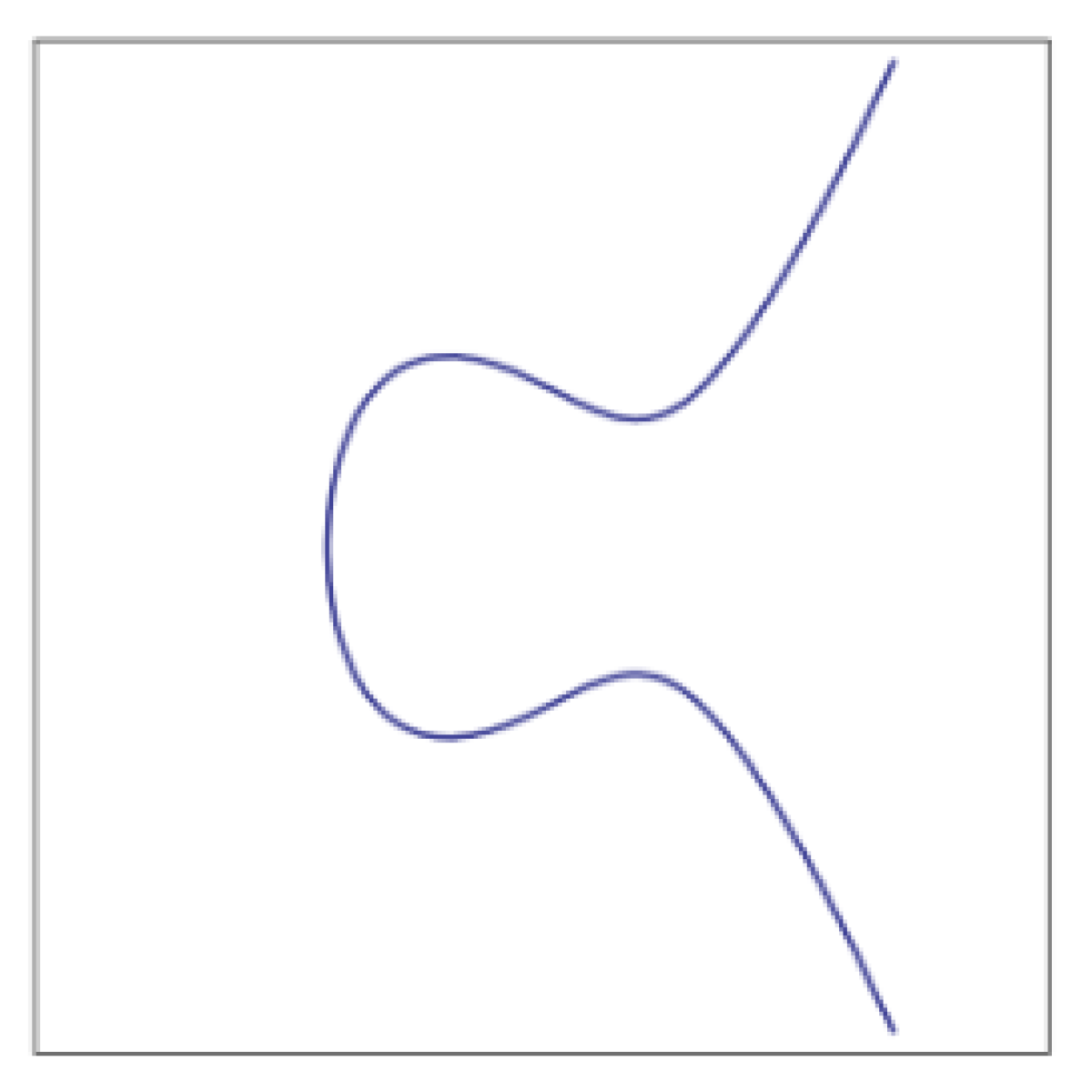
Elliptic curves offer an alternate way to mathematically relate public and private keys; sometimes, this means we can implement schemes more efficiently. While the mathematical theory of elliptic curves is both broad and deep, the elliptic curves used in cryptography are typically defined by an equation of the form y2 = x3 + ax2 + bx + c, where a, b, and c are constants. You can plot the points that satisfy the equation on a 2-D graph.
An elliptic curve has the property that a line that intersects it at two points intersects it at at most one other point. This property is used to define operations on the curve. For instance, the addition of two points on the curve can be defined not, indeed, as the third point on the curve collinear with the first two but as that third point’s reflection around the axis of symmetry.
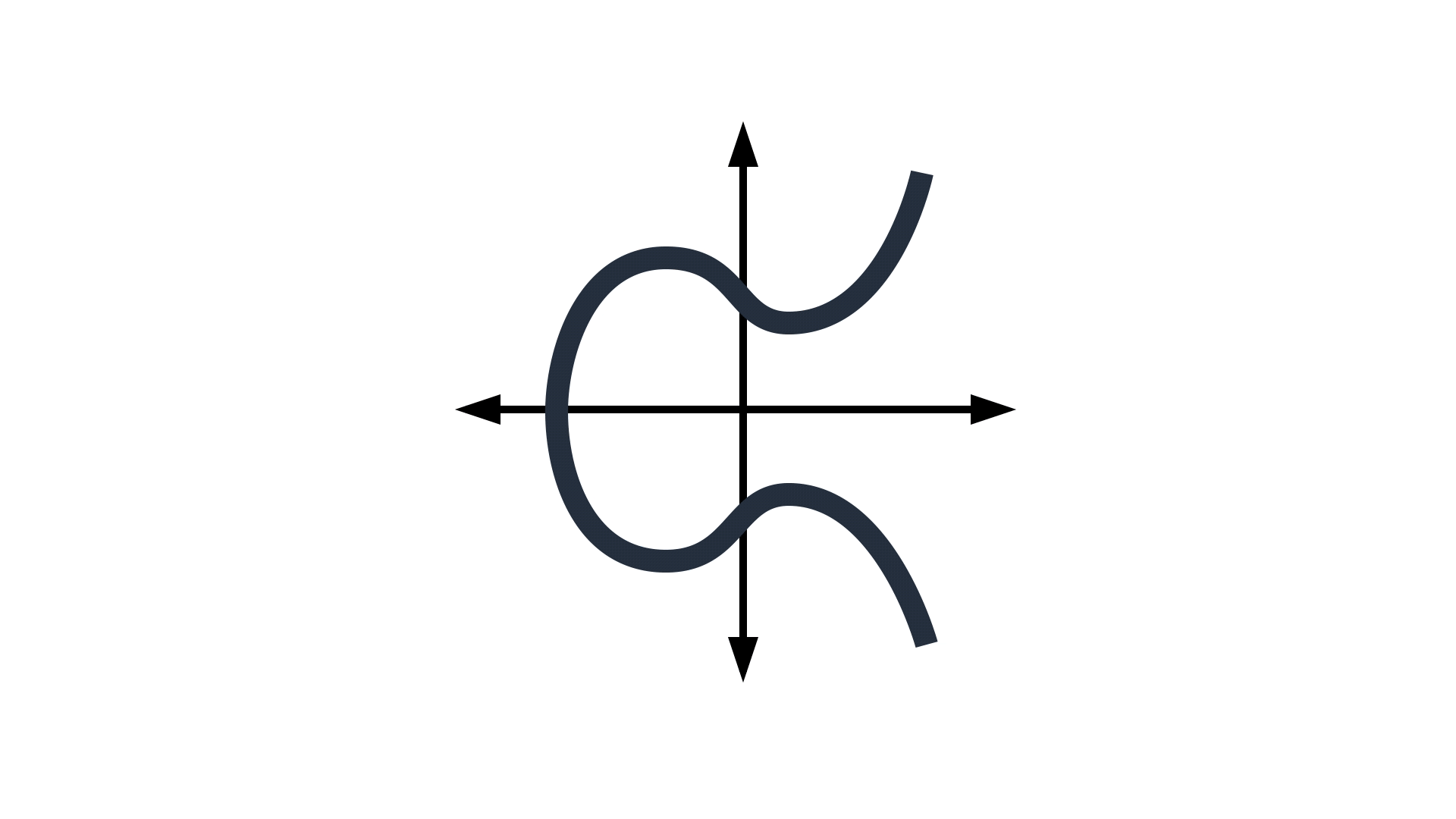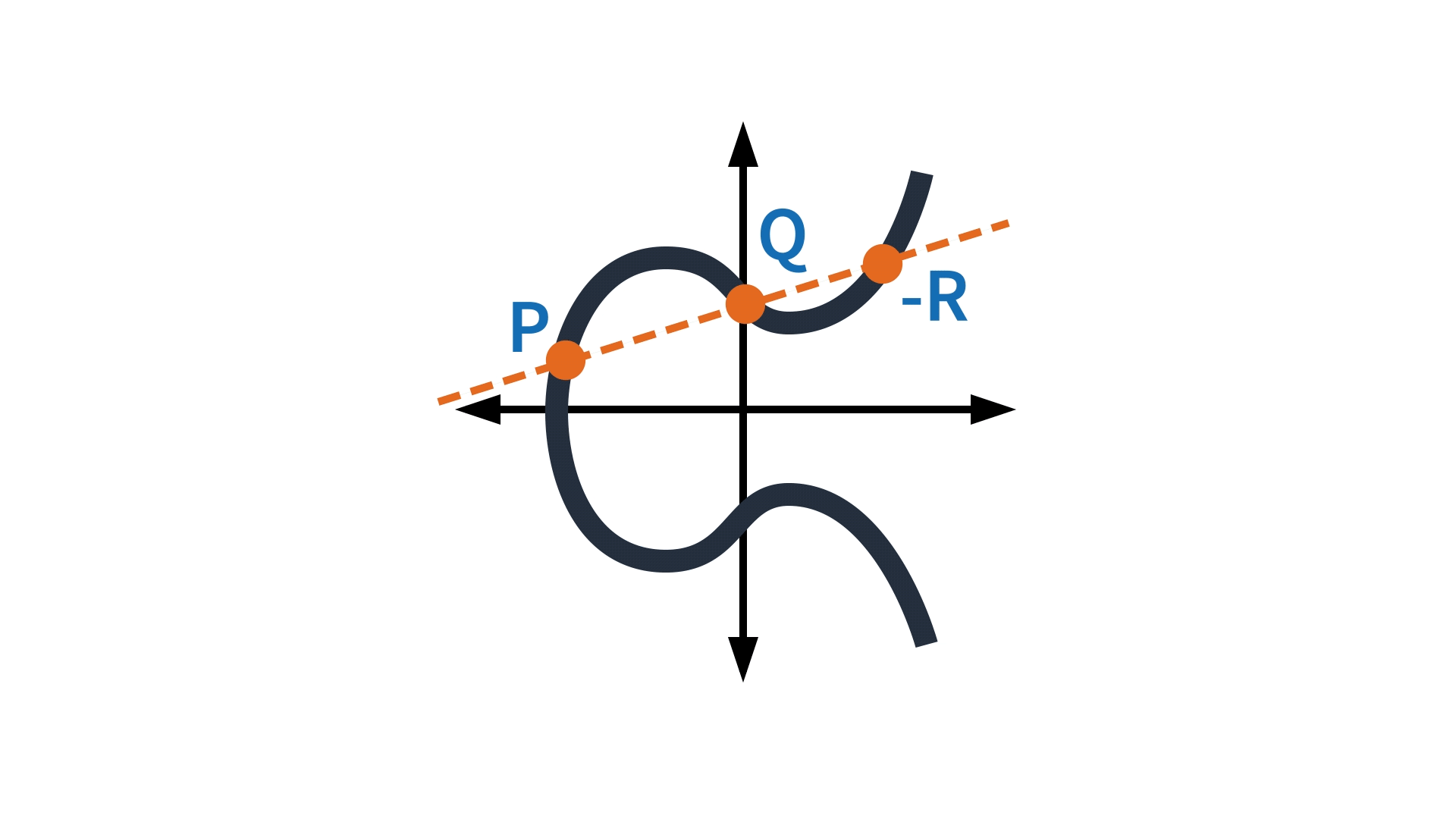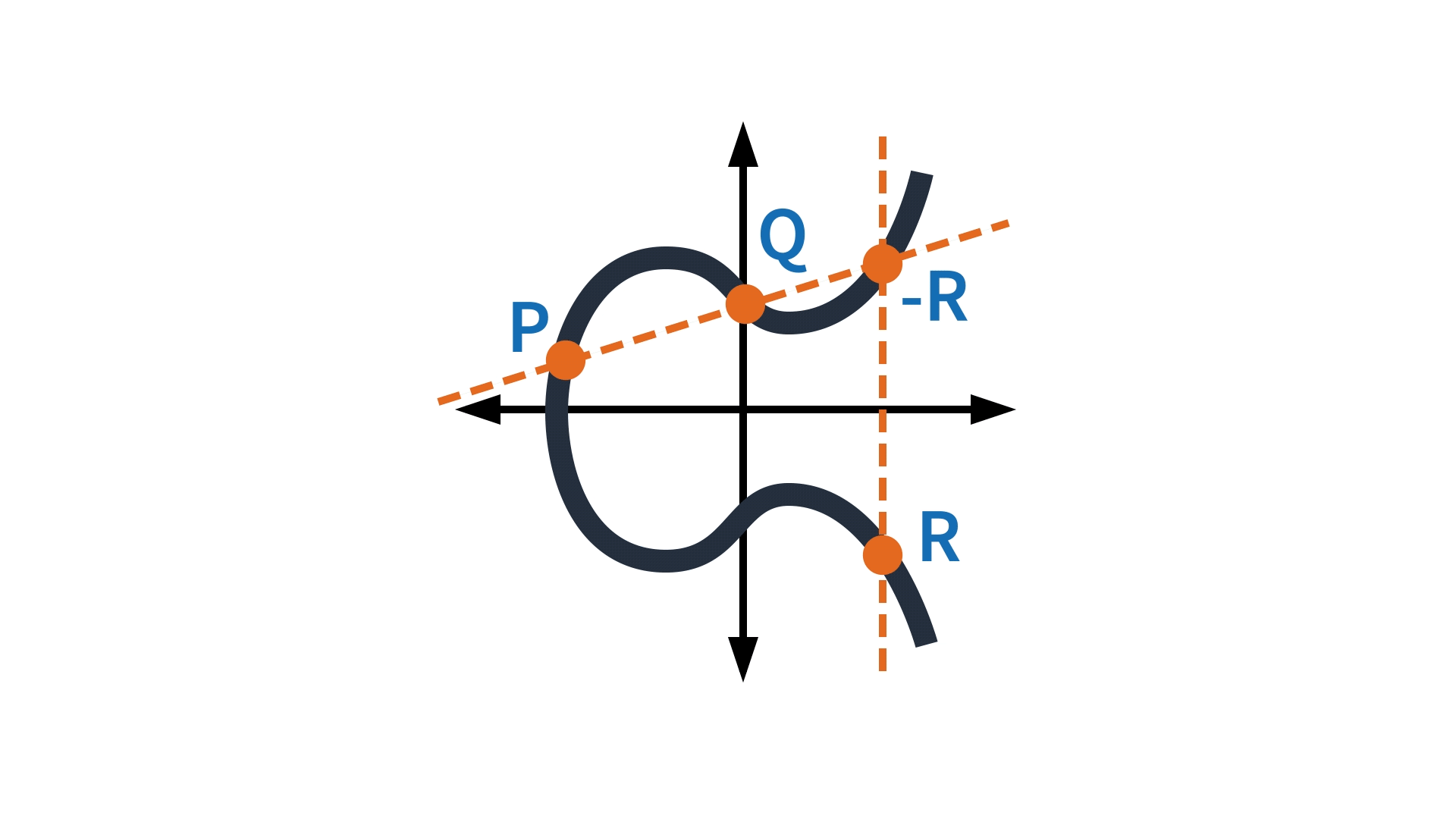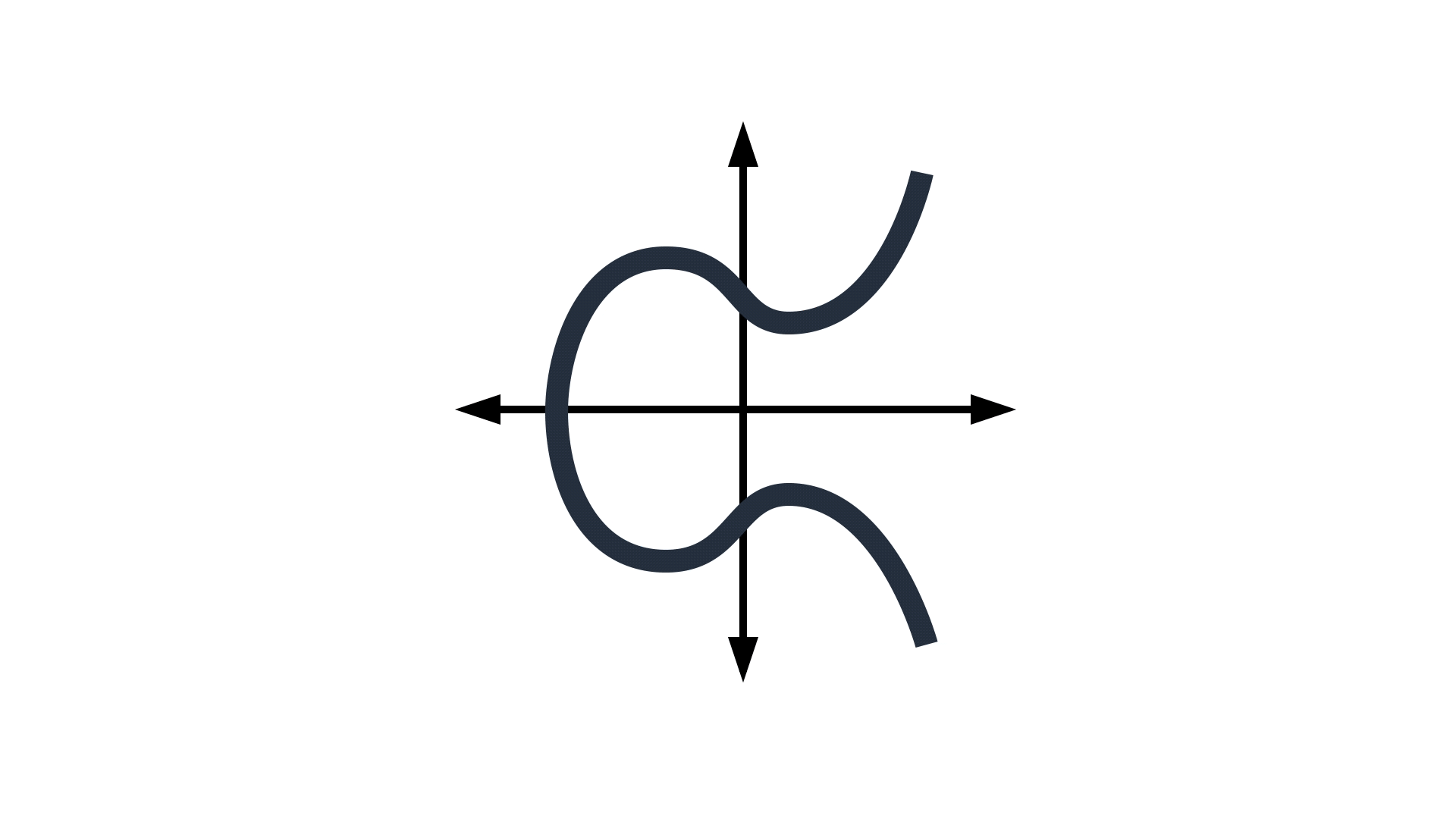
Now, if the coordinates of points on the curve are taken modulo some integer, the curve becomes a scatter of points in the plane, but a scatter that still exhibits symmetry, so the addition operation remains well defined. Curve25519 is named after a large prime integer — specifically, 2255 – 19. The set of numbers modulo the curve25519 prime, together with basic arithmetic operations such as multiplication of two numbers modulo the same prime, define the field in which our elliptic-curve operations take place.
Successive execution of elliptic-curve additions is called scalar multiplication, where the scalar is the number of additions. With the elliptic curves used in cryptography, if you know only the result of the scalar multiplication, it is intractable to recover the scalar, if the scalar is sufficiently large. The result of the scalar multiplication becomes the basis of a public key, the original scalar the basis of a private key.
The x25519 and Ed25519 cryptographic algorithms
The x/Ed25519 algorithms have distinct purposes. The x25519 algorithm is a key agreement algorithm, used to securely establish a shared secret between two peers; Ed25519 is a digital-signature algorithm, used to sign and verify data.
The x/Ed25519 algorithms have been adopted in transport layer protocols such as TLS and SSH. In 2023, NIST announced an update to its FIPS185-6 Digital Signature Standard that included the addition of Ed25519. The x25519 algorithm also plays a role in post-quantum safe cryptographic solutions, having been included as the classical algorithm in the TLS 1.3 and SSH hybrid scheme specifications for post-quantum key agreement.
Microarchitecture optimizations
When we write assembly code for a specific CPU architecture, we use its instruction set architecture (ISA). The ISA defines resources such as the available assembly instructions, their semantics, and the CPU registers accessible to the programmer. Importantly, the ISA defines the CPU in abstract terms; it doesn’t specify how the CPU should be realized in hardware.
The detailed implementation of the CPU is called the microarchitecture, and every μarch has unique characteristics. For example, while the AWS Graviton 2 CPU and AWS Graviton 3 CPU are both based on the Arm64 ISA, their μarch implementations are different. We hypothesized that if we could take advantage of the μarch differences, we could create x/Ed25519 implementations that were even faster than the existing implementations in AWS-LC. It turns out that this intuition was correct.
Let us look closer at how we took advantage of μarch differences. Different arithmetic operations can be defined on curve25519, and different combinations of those operations are used to construct the x/Ed25519 algorithms. Logically, the necessary arithmetic operations can be considered at three levels:
- Field operations: Operations within the field defined by the curve25519 prime 2255 – 19.
- Elliptic-curve group operations: Operations that apply to elements of the curve itself, such as the addition of two points, P1 and P2.
- Top-level operations: Operations implemented by iterative application of elliptic-curve group operations, such as scalar multiplication.

Each level has its own avenues for optimization. We focused our μarch-dependent optimizations on the level-one operations, while for levels two and three our implementations employ known state-of-the-art techniques and are largely the same for different μarchs. Below, we give a summary of the different μarch-dependent choices we made in our implementations of x/Ed25519.
- For modern x86_64 μarchs, we use the instructions MULX, ADCX, and ADOX, which are variations of the standard assembly instructions MUL (multiply) and ADC (add with carry) found in the instruction set extensions commonly called BMI and ADX. These instructions are special because, when used in combination, they can maintain two carry chains in parallel, which has been observed to boost performance up to 30%. For older x86_64 μarchs that don’t support the instruction set extensions, we use more traditional single-carry chains.
- For Arm64 μarchs, such as AWS Graviton 3 with improved integer multipliers, we use relatively straightforward schoolbook multiplication, which turns out to give good performance. AWS Graviton 2 has smaller multipliers. For this Arm64 μarch, we use subtractive forms of Karatsuba multiplication, which breaks down multiplications recursively. The reason is that, on these μarchs, 64x64-bit multiplication producing a 128-bit result has substantially lower throughput relative to other operations, making the number size at which Karatsuba optimization becomes worthwhile much smaller.
We also optimized level-one operations that are the same for all μarchs. One example concerns the use of the binary greatest-common-divisor (GCD) algorithm to compute modular inverses. We use the “divstep” form of binary GCD, which lends itself to efficient implementation, but it also complicates the second goal we had: formally proving correctness.
Binary GCD is an iterative algorithm with two arguments, whose initial values are the numbers whose greatest common divisor we seek. The arguments are successively reduced in a well-defined way, until the value of one of them reaches zero. With two n-bit numbers, the standard implementation of the algorithm removes at least one bit total per iteration, so 2n iterations suffice.
With divstep, however, determining the number of iterations needed to get down to the base case seems analytically difficult. The most tractable proof of the bound uses an elaborate inductive argument based on an intricate “stable hull” provably overapproximating the region in two-dimensional space containing the points corresponding to the argument values. Daniel Bernstein, one of the inventors of x25519 and Ed25519, proved the formal correctness of the bound using HOL Light, a proof assistant that one of us (John) created. (For more on HOL Light, see, again, our earlier RSA post.)
Performance results
In this section, we will highlight improvements in performance. For the sake of simplicity, we focus on only three μarchs: AWS Graviton 3, AWS Graviton 2, and Intel Ice Lake. To gather performance data, we used EC2 instances with matching CPU μarchs — c6g.4xlarge, c7g.4xlarge, and c6i.4xlarge, respectively; to measure each algorithm, we used the AWS-LC speed tool.
In the graphs below, all units are operations per second (ops/sec). The “before” columns represent the performance of the existing x/Ed25519 implementations in AWS-LC. The “after” columns represent the performance of the new implementations.
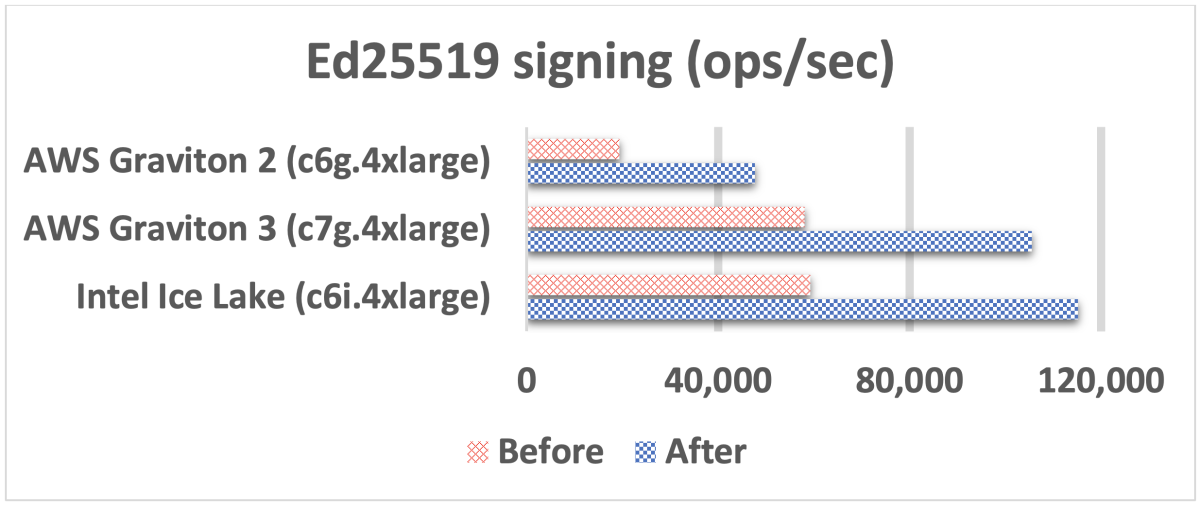
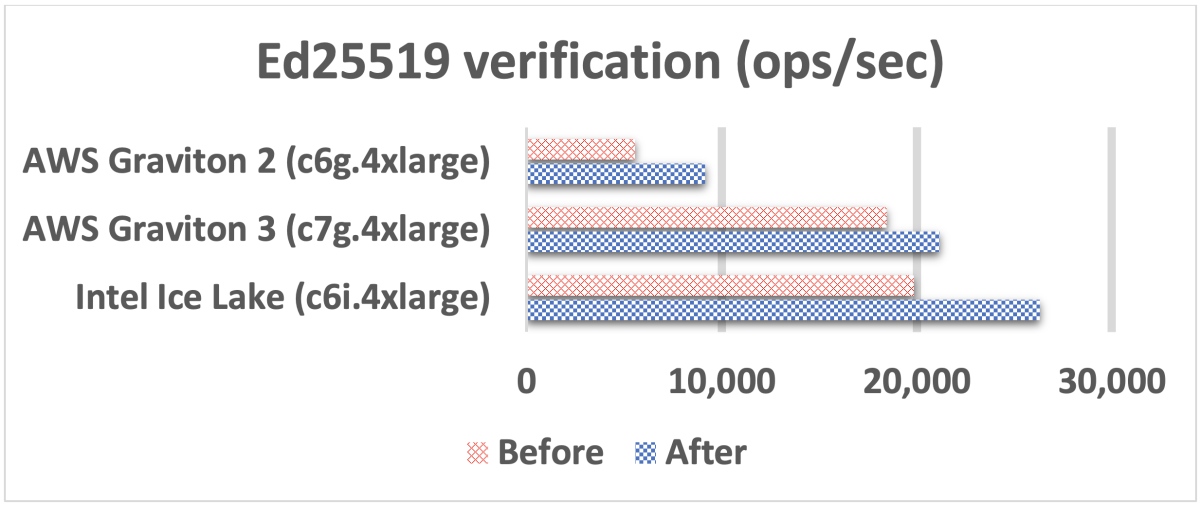
We observed the biggest improvement for the x25519 algorithm. Note that an x25519 operation in the graph below includes the two major operations needed for an x25519 key exchange agreement: base-point multiplication and variable-point multiplication.
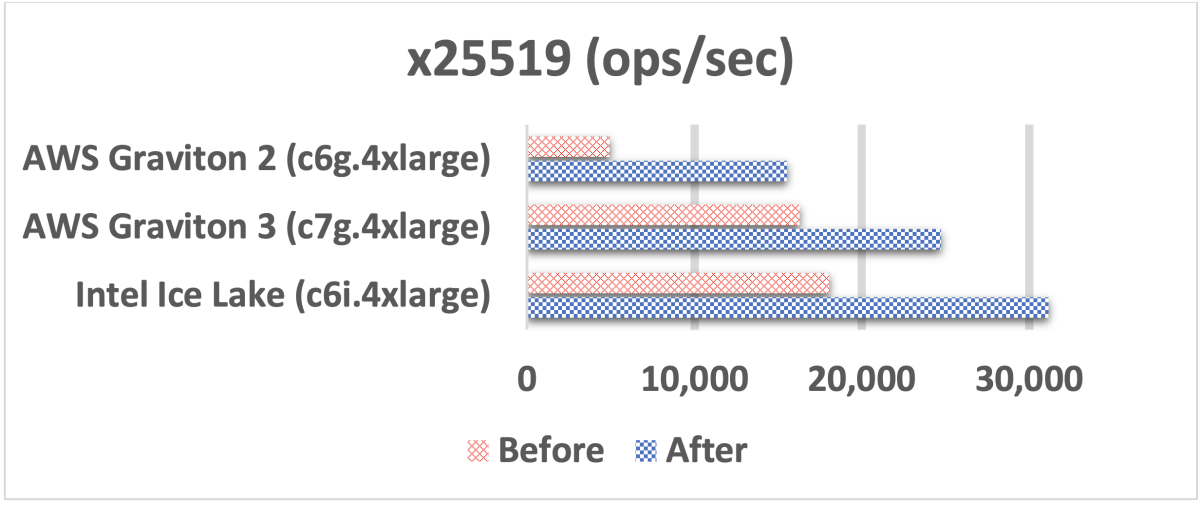
On average, over the AWS Graviton 2, AWS Graviton 3, and Intel Ice Lake microarchitectures, we saw an 86% improvement in performance.
Proving correctness
We develop the core parts of the x/Ed25519 implementations in AWS-LC in s2n-bignum, an AWS-owned library of integer arithmetic routines designed for cryptographic applications. The s2n-bignum library is also where we prove the functional correctness of the implementations using HOL Light. HOL Light is an interactive theorem prover for higher-order logic (hence HOL), and it is designed to have a particularly simple (hence light) “correct by construction” approach to proof. This simplicity offers assurance that anything “proved” has really been proved rigorously and is not the artifact of a prover bug.
We follow the same principle of simplicity when we write our implementations in assembly. Writing in assembly is more challenging, but it offers a distinct advantage when proving correctness: our proofs become independent of any compiler.
The diagram below shows the process we use to prove x/Ed25519 correct. The process requires two different sets of inputs: first is the algorithm implementation we’re evaluating; second is a proof script that models both the correct mathematical behavior of the algorithm and the behavior of the CPU. The proof is a sequence of functions specific to HOL Light that represent proof strategies and the order in which they should be applied. Writing the proof is not automated and requires developer ingenuity.
From the algorithm implementation and the proof script, HOL Light either determines that the implementation is correct or, if unable to do so, fails. HOL Light views the algorithm implementation as a sequence of machine code bytes. Using the supplied specification of CPU instructions and the developer-written strategies in the proof script, HOL Light reasons about the correctness of the execution.
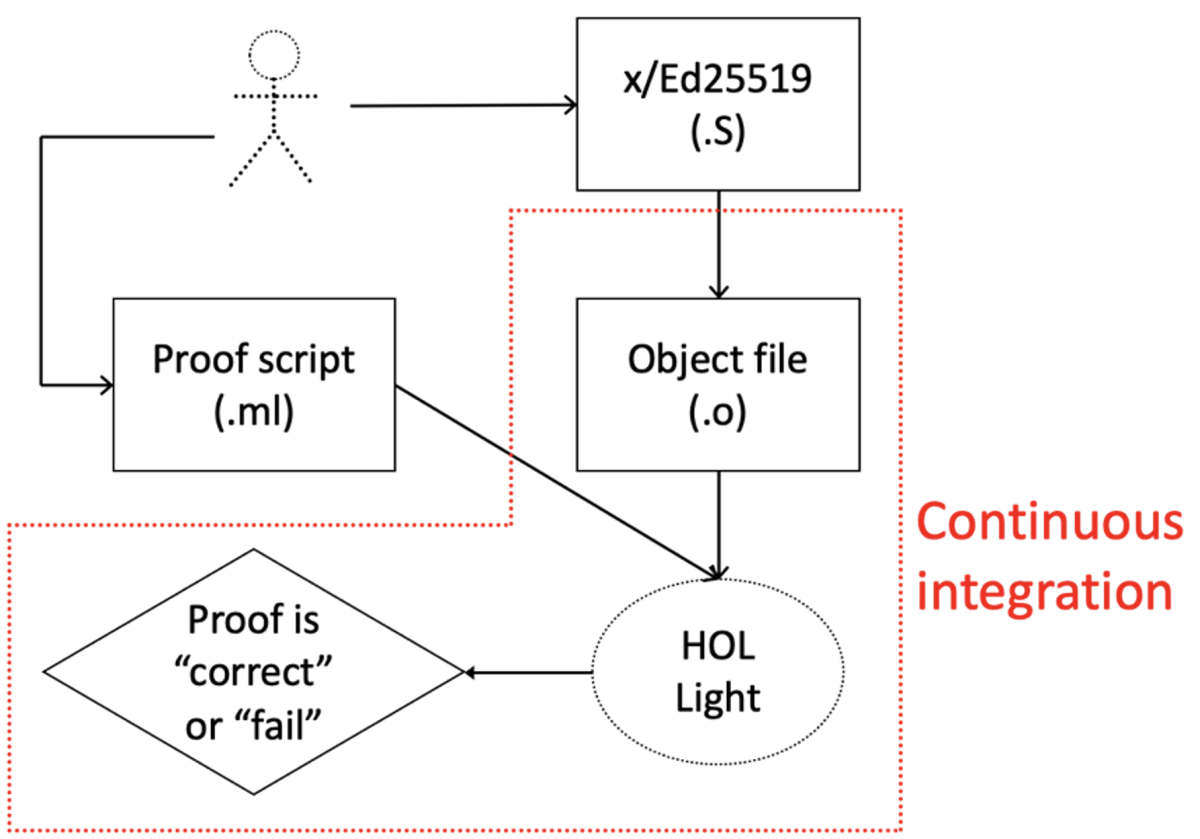
This part of the correctness proof is automated, and we even implement it inside s2n-bignum’s continuous-integration (CI) workflow. The workflow covered in the CI is highlighted by the red dotted line in the diagram below. CI integration provides assurance that no changes to the algorithm implementation code can be committed to s2n-bignum’s code repository without successfully passing a formal proof of correctness.
The CPU instruction specification is one of the most critical ingredients in our correctness proofs. For the proofs to be true in practice, the specification must capture the real-world semantics of each instruction. To improve assurance on this point, we apply randomized testing against the instruction specifications on real hardware, “fuzzing out” inaccuracies.
Constant time
We designed our implementations and optimizations with security as priority number one. Cryptographic code must strive to be free of side channels that could allow an unauthorized user to extract private information. For example, if the execution time of cryptographic code depends on secret values, then it might be possible to infer those values from execution times. Similarly, if CPU cache behavior depends on secret values, an unauthorized user who shares the cache could infer those values.
Our implementations of x/Ed25519 are designed with constant time in mind. They perform exactly the same sequence of basic CPU instructions regardless of the input values, and they avoid any CPU instructions that might have data-dependent timing.
Using x/Ed25519 optimizations in applications
AWS uses AWS-LC extensively to power cryptographic operations in a diverse set of AWS service subsystems. You can take advantage of the x/Ed25519 optimizations presented in this blog by using AWS-LC in your application(s). Visit AWS-LC on Github to learn more about how you can integrate AWS-LC into your application.
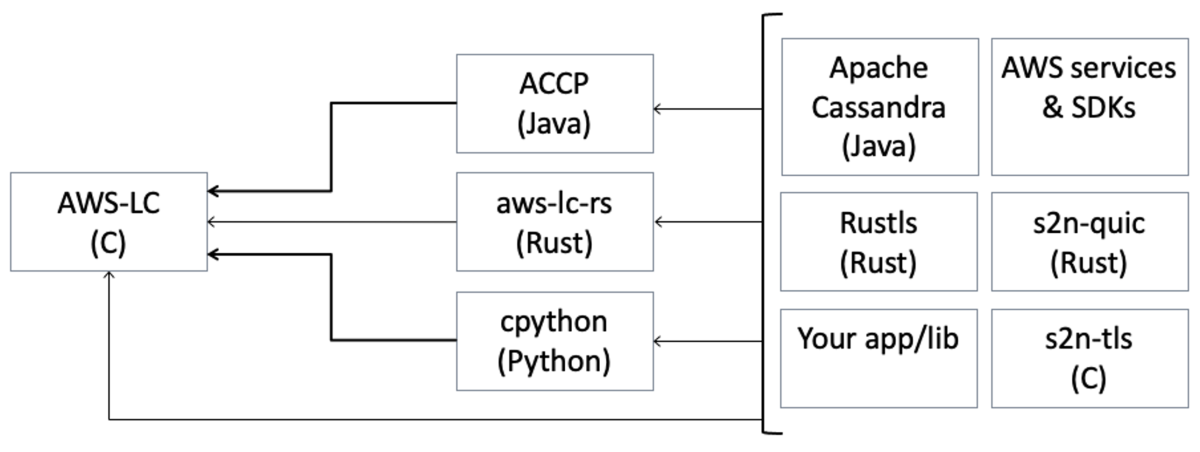
To allow easier integration for developers, AWS has created bindings from AWS-LC to multiple programming languages. These bindings expose cryptographic functionality from AWS-LC through well-defined APIs, removing the need to reimplement cryptographic algorithms in higher-level programming languages. At present, AWS has open-sourced bindings for Java and Rust — the Amazon Corretto Cryptographic Provider (ACCP) for Java, and AWS-LC for Rust (aws-lc-rs). Furthermore, we have contributed patches allowing CPython to build against AWS-LC and use it for all cryptography in the Python standard library. Below we highlight some of the open-source projects that are already using AWS-LC to meet their cryptographic needs.
We are not done yet. We continue our efforts to improve x/Ed25519 performance as well as pursuing optimizations for other cryptographic algorithms supported by s2n-bignum and AWS-LC. Follow the s2n-bignum and AWS-LC repositories for updates.