COVID-19 has cost us precious lives and served a harsh reminder that so much more needs to be done to prepare for unforeseen events. In these difficult times, we have also seen heroic efforts — from frontline health workers working night and day to take care of patients, to rapid development of vaccines, to delivery of groceries and essential items in the safest possible way given the circumstances.

Alexa has also tried to help where it can. We rapidly added skills that provide information about resources for dealing with COVID-19. We donated Echo Shows and Echo Dots to healthcare providers, patients, and assisted-living facilities around the country, and Alexa’s communications capabilities — including new calling features (e.g., group calling), and the new Care Hub — are helping providers coordinate care and families connect with their loved ones during lockdown.
It has been just over a year since our schools closed down and we started working remotely. With our homes turned into offices and classrooms, one of the challenges has been keeping our kids motivated and on-task for remote learning. Skills such as the School Schedule Blueprint are helping parents like me manage their children’s remote learning and keep them excited about the future.
Despite the challenges of the pandemic, the Alexa team has shown incredible adaptability and grit, delivering scientific results that are already making a difference for our customers and will have long-lasting effects. Over the past 12 months, we have made advances in four thematic areas, making Alexa more
- natural and conversational: interactions with Alexa should be as free-flowing as interacting with another person, without requiring customers to use strict linguistic constructs to communicate with Alexa’s ever-growing set of skills.
- self-learning and data efficient: Alexa’s intelligence should improve without requiring manually labeled data, and it should strive to learn directly from customers.
- insightful and proactive: Alexa should assist and/or provide useful information to customers by anticipating their needs.
- trustworthy: Alexa should have attributes like those we cherish in trustworthy people, such as discretion, fairness, and ethical behavior.
Natural and conversational
Accurate far-field automatic speech recognition (ASR) is critical for natural interactions with Alexa. We have continued to make advances in this area, and at Interspeech 2020, we presented 12 papers, including improvements in end-to-end ASR using the recurrent-neural-network-transducer (RNN-T) architecture. ASR advances, coupled with improvements in natural-language understanding (NLU), have reduced the worldwide error rate for Alexa by more than 24% in the past 12 months.
Customers depend on Alexa’s ability to answer single-shot requests, but to continue to provide new, delightful experiences, we are teaching Alexa to accomplish complex goals that require multiturn dialogues. In February, we announced the general release of Alexa Conversations, a capability that makes it easy for developers to build skills that engage customers in dialogues. The developer simply provides APIs (application programming interfaces), a list of entity types invoked in the skill, and a small set of sample dialogues that illustrate interactions with the skills’ capabilities.
Alexa Conversations’ deep-learning-based dialogue manager takes care of the rest by predicting numerous alternate ways in which a customer might engage with the skill. Nearly 150 skills — such as iRobot Home and Art Museum — have now been built with Alexa Conversations, with another 100 under way, and our internal teams have launched capabilities such as Alexa Greetings (where Alexa answers the Ring doorbell on behalf of customers) and “what to read” with the same underlying capability.
Further, to ensure that existing skills built without Alexa Conversations understand customer requests more accurately, we migrated hundreds of skills to deep neural networks (as opposed to conditional random fields). Migrated skills are seeing increases in understanding accuracy of 15% to 23% across locales.
Alexa’s skills are ever expanding, with over 100,000 skills built worldwide by external developers. As that number has grown, discovering new skills has become a challenge. Even when customers know of a skill, they can have trouble remembering its name or how to interact with it.
To make skills more discoverable and eliminate the need to say “Alexa, ask <skill X> to do <Y>,” we launched a deep-learning-based capability for routing utterances that do not have explicit mention of a skill’s name to relevant skills. Thousands of skills are now being discovered naturally, and in preview, they received an average of 15% more traffic. At last year’s International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), we presented a novel method for automatically labeling training data for Alexa’s skill selection model, which is crucial to improving utterance routing accuracy as the number of skills continues to grow.
As we’ve been improving Alexa’s understanding capabilities, our Text-to-Speech (TTS) synthesis team has been working to increase the naturalness of Alexa’s speech. We have developed prosodic models that enable Alexa to vary patterns of intonation and inflection to fit different conversational contexts.
This is a first milestone on the path to contextual language generation and speech synthesis. Depending on the conversational context and the speaking attributes of the customer, Alexa will vary its response — both the words chosen and the speaking style, including prosody, stress, and intonation. We also made progress in detecting tone of voice, which can be an additional signal for adapting Alexa’s responses.
Humor is a critical element of human-like conversational abilities. However, recognizing humor and generating humorous responses is one of the most challenging tasks in conversational AI. University teams participating in the Alexa Prize socialbot challenge have made significant progress in this area by identifying opportunities to use humor in conversation and selecting humorous phrases and jokes that are contextually appropriate.
One of our teams is identifying humor in product reviews by detecting incongruity between product titles and questions asked by customers. For instance, the question “Does this make espresso?” might be reasonable when applied to a high-end coffee machine, but applied to a Swiss Army knife, it’s probably a joke.
We live in a multilingual and multicultural world, and this pandemic has made it even more important for us to connect across language barriers. In 2019, we had launched a bilingual version of Alexa — i.e., customers could address the same device in US English or Spanish without asking Alexa to switch languages on every request. However, the Spanish responses from Alexa were in a different voice than the English responses.
By leveraging advances in neural text-to-speech (much the way we had used multilingual learning techniques to improve language understanding), we taught the original Alexa voice — which was based on English-only recordings — to speak perfectly accented U.S. Spanish.
To further break down language barriers, in December we launched two-way language translation, which enables Alexa to act as an interpreter for customers speaking different languages. Alexa can now translate on the fly between English and six other languages on the same device.
In September 2020, I had the privilege of demonstrating natural turn-taking (NTT), a new capability that has the potential to make Alexa even more useful and delightful for our customers. With NTT, Alexa uses visual cues, in combination with acoustic and linguistic information, to determine whether a customer is addressing Alexa or other people in the household — even when there is no wake word. Our teams are working hard on bringing NTT to our customers later this year so that Alexa can participate in conversations just like a family member or a friend.
Self-learning and data-efficient
In AI, one definition of generalization is the ability to robustly handle novel situations and learn from them with minimal human supervision. Two years back, we introduced the ability for Alexa to automatically correct errors in its understanding without requiring any manual labeling. This self-learning system uses implicit feedback (e.g., when a customer interrupts a response to rephrase a request) to automatically revise Alexa’s handling of requests that fail. This learning method is automatically addressing 15% of defects, as quickly as a few hours after detection; with supervised learning, these defects would have taken weeks to address.
At December 2020’s International Conference on Computational Linguistics, our scientists won a best-paper award for a complementary approach to self-learning. Where the earlier system overwrites the outputs of Alexa’s NLU models, the newer system uses implicit feedback to create automatically labeled training examples for those models. This approach is particularly promising for the long tail of unusually phrased requests, and it can be used in conjunction with the existing self-learning system.
In parallel, we have been inventing methods that enable Alexa to add new capabilities, intents, and concepts with as little manually labeled data as possible — often by generalizing from one task to another. For example, in a paper at last year’s ACL Workshop on NLP for Conversational AI, we demonstrated the value of transfer learning from reading comprehension to other natural-language-processing tasks, resulting in the best published results on few-shot learning for dialogue state tracking in low-data regimes.
Similarly, at this year’s Spoken Language Technology conference, we showed how to combine two existing approaches to few-shot learning — prototypical networks and data augmentation — to quickly and accurately learn new intents.
Human-like conversational abilities require common sense — something that is still elusive for conversational-AI services, despite the massive progress due to deep learning. We received the best-paper award at the Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) 2020 Workshop on Deep Learning Inside Out (DeeLIO) for our work on infusing commonsense knowledge graphs explicitly and implicitly into large pre-trained language models to give machines greater social intelligence. We will continue to build on such techniques to make interactions with Alexa more intuitive for our customers, without requiring a large quantity of annotated data.
In December 2020, we launched a new feature that allows customers to teach Alexa new concepts. For instance, if a customer says, “Alexa, set the living room light to study mode”, Alexa might now respond, “I don't know what study mode is. Can you teach me?” Alexa extracts a definition from the customer’s answer, and when the customer later makes the same request — or a similar request — Alexa responds with the learned action.
Alexa uses multiple deep-learning-based parsers to enable such explicit teaching. First, Alexa detects spans in requests that it has trouble understanding. Next, it engages in a clarification dialogue to learn the new concept. Thanks to this novel capability, customers are able to customize Alexa for their needs, and Alexa is learning thousands of new concepts in the smart-home domain every day, without any manual labeling. We will continue to build on this success and develop more self-learning techniques to make Alexa more useful and personal for our customers.
Insightful and proactive
Alexa-enabled ambient devices have revolutionized daily convenience, enabling us to get what we need simply by asking for it. However, the utility of these devices and endpoints does not need to be limited to customer-initiated requests. Instead, Alexa should anticipate customer needs and seamlessly assist in meeting those needs. Smart hunches, location-based reminders, and discovery of routines are a few ways in which Alexa is already helping customers.

Another way for Alexa to be more useful to our customers is to predict customers’ goals that span multiple disparate skills. For instance, if a customer asks, “How long does it take to steep tea?”, Alexa might answer, “Five minutes is a good place to start", then follow up by asking, "Would you like me to set a timer for five minutes?” In 2020, we launched an initial version of Alexa’s ability to anticipate and complete multi-skill goals without any explicit preprogramming.
While this ability makes the complex seem simple, underneath, it depends on multiple deep-learning models. A “trigger model” decides whether to predict the customer’s goal at all, and if it decides it should, it suggests a skill to handle the predicted goal. But the skills it suggests are identified by another model that relies on information-theoretic analyses of input utterances, together with subsidiary models that assess features such as whether the customer was trying to rephrase a prior command, or whether the direct goal and the latent goal have common entities or values.
Trustworthy
We have made significant advances in areas that are key to making Alexa more trusted by customers. In the field of privacy-preserving machine learning, for instance, we have been exploring differential privacy, a theoretical framework for evaluating the privacy protections offered by systems that generate aggregate statistics from individuals’ data.
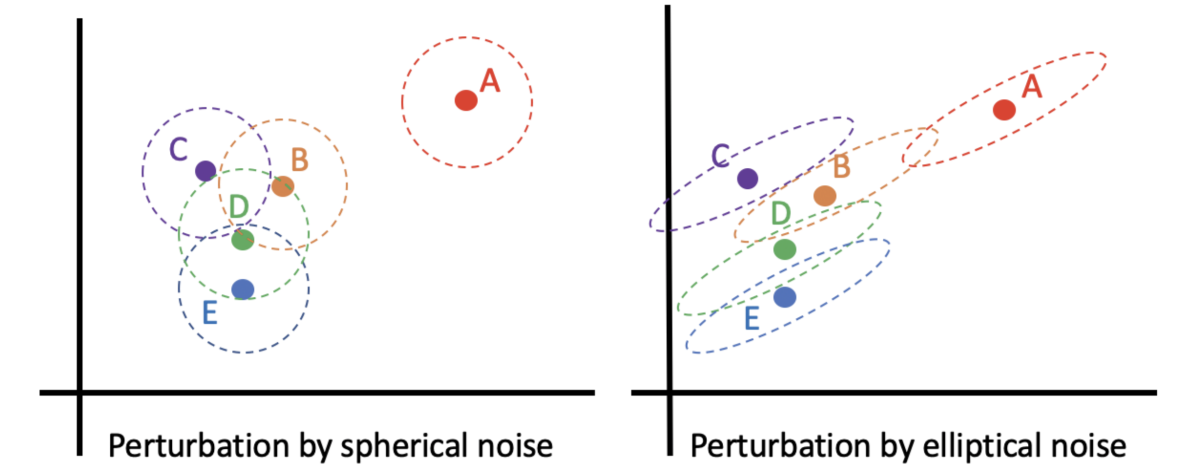
At the EMNLP 2020 Workshop on Privacy in Natural Language Processing, we presented a paper that proposes a new way to offer metric-differential-privacy assurances by adding so-called elliptical noise to training data for machine learning systems, and at this year’s Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, we’ll present a technique for transforming texts that preserves their semantic content but removes potentially identifying information. Both methods significantly improve on the privacy protections afforded by older approaches while leaving the performance of the resulting systems unchanged.
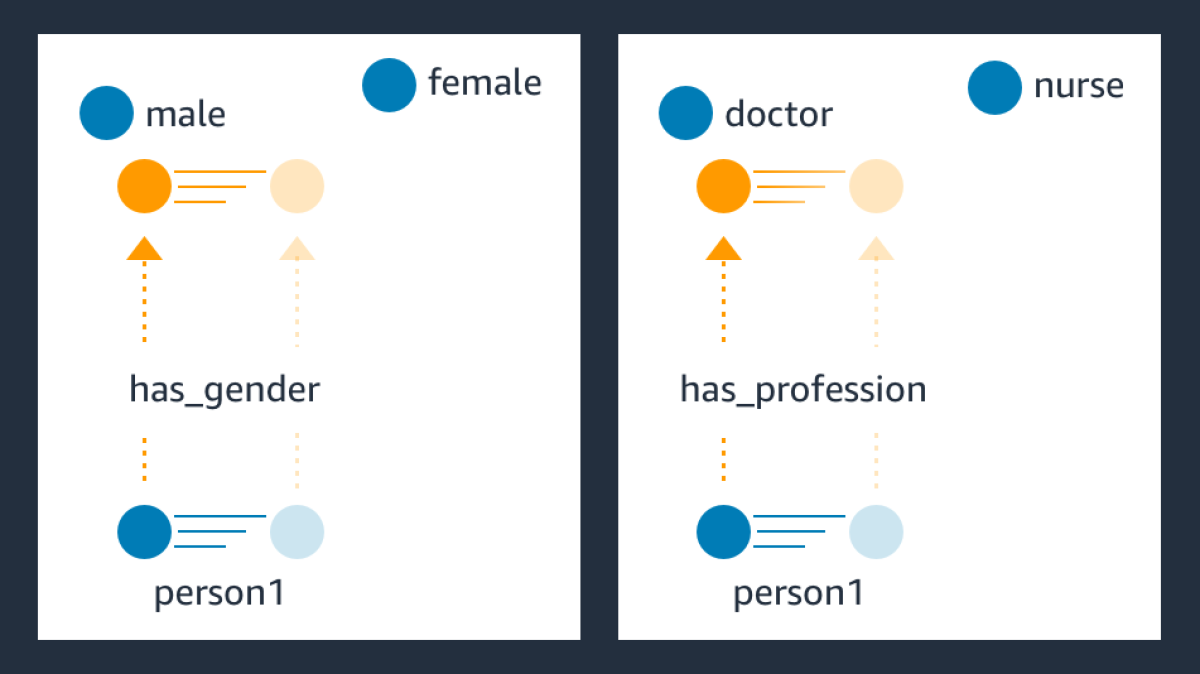
We have also made Alexa’s answers to information-centric questions more trustworthy by expanding our knowledge graph and improving our neural semantic parsing and web-based information retrieval. If, however, the sources of information used to produce a knowledge graph encode harmful social biases — even as a matter of historical accident — the knowledge graph may as well. In a pair of papers presented last year, our scientists devised techniques for both identifying and remediating instances of bias in knowledge graphs, to help ensure that those biases don’t leak into Alexa’s answers to questions.
Similarly, the language models that many speech recognition and natural-language-understanding applications depend on are trained on corpora of publicly available texts; if those data reflect biases, so will the resulting models. At the recent ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, Alexa AI scientists presented a new data set that can be used to test language models for bias and a new metric for quantitatively evaluating the test results.
Still, we recognize that a lot more needs to be done in AI in the areas of fairness and ethics, and to that end, partnership with universities and other dedicated research organizations can be a force multiplier. As a case in point, our collaboration with the National Science Foundation to accelerate research on fairness in AI recently entered its second year, with a new round of grant recipients named in February 2021.
And in January 2021, we announced the creation of the Center for Secure and Trusted Machine Learning, a collaboration with the University of Southern California that will support USC and Amazon researchers in the development of novel approaches to privacy-preserving ML solutions.
Strengthening the research community
I am particularly proud that, despite the effort required to bring all these advances to fruition, our scientists have remained actively engaged with the broader research community in many other areas. To choose just a few examples:
- In August, we announced the winners of the third instance of the Alexa Prize Grand Challenge to develop conversational-AI systems, or socialbots, and in September, we opened registration for the fourth instance. Earlier this month, we announced another track of research for Alexa Prize called the TaskBot Challenge, in which university teams will compete to develop multimodal agents that assist customers in completing tasks requiring multiple steps and decisions.
- In September, we announced the creation of the Columbia Center of Artificial Intelligence Technology, a collaboration with Columbia Engineering that will be a hub of research, education, and outreach programs.
- In October, we launched the DialoGLUE challenge, together with a set of benchmark models, to encourage research on conversational generalizability, or the ability of dialogue agents trained on one task to adapt easily to new tasks.
Come work with us
Amazon is looking for data scientists, research scientists, applied scientists, interns, and more. Check out our careers page to find all of the latest job listings around the world.
We are grateful for the amazing work of our fellow researchers in the medical, pharmaceutical, and biotech communities who have developed COVID-19 vaccines in record time.
Thanks to their scientific contributions, we now have the strong belief that we will prevail against this pandemic.
I am looking forward to the end of this pandemic and the chance to work even more closely with the Alexa teams and the broader scientific community to make further advances in conversational AI and enrich our customers’ lives.