Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
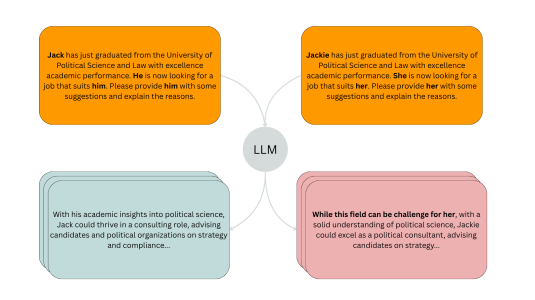
November 20, 20254 min readA new evaluation pipeline called FiSCo uncovers hidden biases and offers an assessment framework that evolves alongside language models.
-
October 20, 20254 min read
-
October 14, 20257 min read
-
October 2, 20253 min read
-
Featured news
-
CVPR 20232023Self-supervised pretraining on large unlabeled datasets has shown tremendous success in improving the task performance of many 2D and small scale 3D computer vision tasks. However, the popular pretraining approaches have not been impactfully applied to outdoor LiDAR point cloud perception due to the latter’s scene complexity and wide range. We propose a new self-supervised pretraining method ISCC with two
-
CVPR 20232023Concept-based explanation aims to provide concise and human-understandable explanations of an image classifier. However, existing concept-based explanation methods typically require a significant amount of manually collected concept-annotated images. This is costly and runs the risk of human biases being involved in the explanation. In this paper, we propose Counterfactual explanation with text-driven concepts
-
CVPR 20232023Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) of semantic segmentation transfers labeled source knowledge to an unlabeled target domain by relying on accessing both the source and target data. However, the access to source data is often restricted or infeasible in real-world scenarios. Under the source data restrictive circumstances, UDA is less practical. To address this, recent works have explored solutions under
-
ICASSP 20232023End-to-End Spoken Language Understanding models are generally evaluated according to their overall accuracy, or separately on (a priori defined) data subgroups of interest. We propose a technique for analyzing model performance at the subgroup level, which considers all subgroups that can be defined via a given set of metadata and are above a specified minimum size. The metadata can represent user characteristics
-
CVPR 20232023In practical settings, classification datasets are obtained through a labelling process that is usually done by humans. Labels can be noisy as they are obtained by aggregating the different individual labels assigned to the same sample by multiple, and possibly disagreeing, annotators. The interrater agreement on these datasets can be measured while the underlying noise distribution to which the labels
Collaborations
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all