Last year, the first 2,000-2,500 publicly released tickets to the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, or NeurIPS, sold out in 12 minutes.
This year, the conference organizers moved to a lottery system, allowing aspiring attendees to register in advance and randomly selecting invitees from the pool of registrants. But they also bumped the number of public-release tickets up from around 2,000 to 3,500, testifying to the conference’s continued popularity.
At NeurIPS this year, there are 26 papers with Amazon coauthors. They cover a wide range of topics, but surveying their titles, Alex Smola, a vice president and distinguished scientist in the Amazon Web Services organization, discerns three prominent themes, all tied to Amazon’s efforts to deliver better value for its customers.
Those three themes are time series forecasting (and causality), bandit problems, and optimization.
1. Time series forecasting
Time series forecasting involves measuring some quantity over time — such as the number of deliveries in a particular region in the past six months, or the number of cloud servers required to support a particular site over the past two years — and attempting to project that quantity into the future.
“That’s something that is very dear to Amazon’s heart,” Smola says. “For anything that Amazon does, it’s really beneficial to have a good estimate of what our customers will expect from us ahead of time. Only by being able to do that will we be able to satisfy customers’ demands, be it for products or services.”
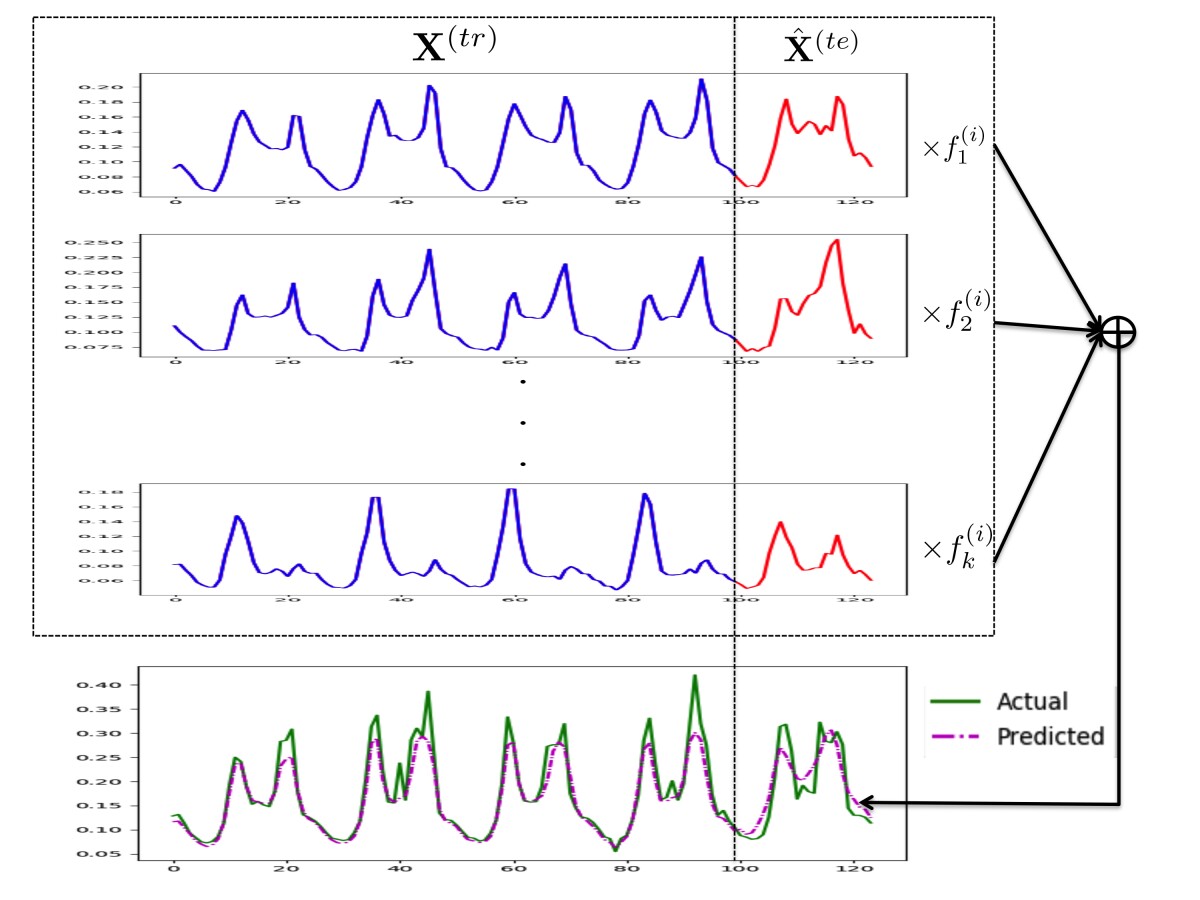
The basic mathematical framework for time series forecasting is a century old, but the scale of modern forecasting problems calls for new analytic techniques, Smola says.
“Problems are nowadays highly multivariate,” Smola says. “If you look at the many millions of products that we offer, you want to be able to predict fairly well what will sell, where and to whom.
“You need to make reasonable assumptions on how this very large problem can be decomposed into smaller, more tractable pieces. You make structural approximations, and sometimes those structural approximations are what leads to very different algorithms.
“So you might, for instance, have a global model, and then you have local models that address the specific items or address the specific sales. If you look at ‘Think Globally, Act Locally’” — a NeurIPS paper whose first author is Rajat Sen, an applied scientist in the Amazon Search group — “it’s already in the title. Or look at ‘High-Dimensional Multivariate Forecasting with Low-Rank Gaussian Copula Processes’. In this case, you have a global structure, but it’s only in a small subspace where interesting things happen.”
An aspect of forecasting that has recently been drawing more attention, Smola says, is causality. Where traditional machine learning models merely infer statistical correlations between data points, “it is ultimately the causal relationship that matters,” Smola says.
“I think that causality is one of the most interesting conceptual developments affecting modern machine learning,” says Bernhard Schölkopf, like Smola a vice president and distinguished scientist in Amazon Web Services. “This is the main topic that I have been interested in for the last decade.”
Two of Schölkopf’s NeurIPS papers — “Perceiving the Arrow of Time in Autoregressive Motion” and “Selecting Causal Brain Features with a Single Conditional Independence Test per Feature” — address questions of causality, as does “Causal Regularization”, a paper by Dominik Janzing, a senior research scientist in Smola’s group.
“Normal machine learning builds on correlations of other statistical dependences,” Schölkopf explains. “This is fine as long as the source of the data doesn't change. For example, if in the training set of an image recognition system, all cows are standing on green pasture, then it is fine for an ML system to use the green as a useful feature in recognizing cows, as long as the test set looks the same. If in the test set, the cows are standing on the beach, then such a purely statistical system can fail.
“More generally: causal learning and inference attempts to understand how systems respond to interventions and other changes, and not just how to predict data that looks more or less the same as the training data.”
2. Bandit problems
The second major theme that Smola discerns in Amazon scientists’ NeurIPS papers is a concern with bandit problems, a phrase that shows up in the titles of Amazon papers such as “MaxGap Bandit: Adaptive Algorithms for Approximate Ranking” and “Low-Rank Bandit Methods for High-Dimensional Dynamic Pricing”. Bandit problems take their name from one-armed bandits, or slot machines.
“It used to be that those bandits were all mechanical, so there would be slight variations between them, and some would have maybe a slightly a higher return than others,” Smola explains. “I walk into a den of iniquity, and I want to find the one-armed bandit where I will lose the least money or maybe make some money. And the only feedback I have is that I pull arms, and I get money or lose money. These are very unreliable, noisy events.”
Bandit problems present what’s known as an explore-exploit trade-off. The gambler must simultaneously explore the environment — determine which machines pay out the most — and exploit the resulting knowledge — concentrate as much money as possible on the high-return machines. Early work on bandit problems concerned identifying the high-return machines with minimal outlays.
“That problem was solved about 20 years ago,” Smola says. “What hasn’t been solved — and this is where things get a lot more interesting — is once you start adding context. Imagine that I get to show you various results as you’re searching for your next ugly Christmas sweater. The unfortunate thing is that the creativity of sweater designers is larger than what you can fit on a page. Now the context is essentially, what time, where from, which user, all those things. We want to find and recommend the ugly Christmas sweater that works specifically for you. This is an example where context is immediately relevant.”
It’s really beneficial to have a good estimate of what our customers will expect from us ahead of time. Only by being able to do that will we be able to satisfy customers’ demands.
In the bandit-problem framework, in other words, the high-payout machines change with every new interaction. But there may be external signals that indicate how they’re changing.
Distributed computing, which is inescapable for today’s large websites, changes the structure of the bandit problem, too.
“Say you go to a restaurant, and the cook wants to improve the menu,” Smola says. “You can try out lots of new menu items, and that’s a good way to improve the menu overall. But if you start offering a lot of undercooked dishes because you’re experimenting, then at some point your loyal customers will stay away.
“Now imagine you have 100 restaurants, and they all do the same thing at the same time. They can’t necessarily communicate at the per-second level; maybe every day or every week they chat with each other. Now this entire exploration problem becomes a little more challenging, because if two restaurants try out the same undercooked dish, you make the customer less happy than you could have.
“So how does this map back into Amazon land? Well, if you have many servers doing this recommendation, the explore-exploit trade-off might be too aggressive if every one of them works on their own.”
3. Optimization
Finally, Smola says, “There is a third category of results that has to do with making algorithms faster. If you look at ‘Primal-Dual Block Frank-Wolfe’, ‘Communication-Efficient Distributed SGD with Sketching’, ‘Qsparse-Local-SGD’ — those are the workhorses that run underneath all of this. Making them more efficient is obviously something that we care about, so we can respond to customer requests faster, train algorithms faster.”
Bird’s-eye view
NeurIPS is a huge conference, with more than 1,400 accepted papers that cover a bewildering variety of topics. Beyond the Amazon papers, Caltech professor and Amazon fellow Pietro Perona identifies three research areas as growing in popularity.
“One is understanding how deep networks work, so that we can better design architectures and optimization algorithms to train models,” Perona says. “Another is low-shot learning. Machines are still much less efficient than humans at learning, in that they need more training examples to achieve the same performance. And finally, AI and society — identifying opportunities for social good, sustainable development, and the like.”
NeurIPS is being held this year at the Vancouver Convention Center, and the main conference runs from Dec. 8 to Dec. 12. The Women in Machine Learning Workshop, for which Amazon is a gold-level sponsor, takes place on Dec. 9; the Third Conversational AI workshop, whose organizers include Alexa AI principal scientist Dilek Hakkani-Tür, will be held on Dec. 14.
Amazon's involvement at NeurIPS
Paper and presentation schedule
Tuesday, 12/10 | 10:45-12:45pm | East Exhibition Hall B&C
A Meta-MDP Approach to Exploration for Lifelong Reinforcement Learning | #192
Francisco Garcia (UMass Amherst/Amazon) · Philip Thomas (UMass Amherst)
Blocking Bandits | #17
Soumya Basu (UT Austin) · Rajat Sen (UT Austin/Amazon) · Sujay Sanghavi (UT Austin/Amazon) · Sanjay Shakkottai (UT Austin)
Causal Regularization | #180
Dominik Janzing (Amazon)
Communication-Efficient Distributed SGD with Sketching | #81
Nikita Ivkin (Amazon) · Daniel Rothchild (University of California, Berkeley) · Md Enayat Ullah (Johns Hopkins University) · Vladimir Braverman (Johns Hopkins University) · Ion Stoica (UC Berkeley) · Raman Arora (Johns Hopkins University)
Learning Distributions Generated by One-Layer ReLU Networks | #49
Shanshan Wu (UT Austin) ·Alexandros G. Dimakis (UT Austin) · Sujay Sanghavi (UT Austin/Amazon)
Tuesday, 12/10 | 5:30-7:30pm | East Exhibition Hall B&C
Efficient Communication in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning via Variance Based Control | #195
Sai Qian Zhang (Harvard University) · Qi Zhang (Amazon) · Jieyu Lin (University of Toronto)
Extreme Classification in Log Memory using Count-Min Sketch: A Case Study of Amazon Search with 50M Products | #37
Tharun Kumar Reddy Medini (Rice University) · Qixuan Huang (Rice University) · Yiqiu Wang (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) · Vijai Mohan (Amazon) · Anshumali Shrivastava (Rice University/Amazon)
Iterative Least Trimmed Squares for Mixed Linear Regression | #50
Yanyao Shen (UT Austin) · Sujay Sanghavi (UT Austin/Amazon)
Meta-Surrogate Benchmarking for Hyperparameter Optimization | #6
Aaron Klein (Amazon) · Zhenwen Dai (Spotify) · Frank Hutter (University of Freiburg) · Neil Lawrence (University of Cambridge) · Javier Gonzalez (Amazon)
Qsparse-local-SGD: Distributed SGD with Quantization, Sparsification and Local Computations | #32
Debraj Basu (Adobe) · Deepesh Data (UCLA) · Can Karakus (Amazon) · Suhas Diggavi (UCLA)
Selecting Causal Brain Features with a Single Conditional Independence Test per Feature | #139
Atalanti Mastakouri (Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems) · Bernhard Schölkopf (MPI for Intelligent Systems/Amazon) · Dominik Janzing (Amazon)
Wednesday, 12/11 | 10:45-12:45pm | East Exhibition Hall B&C
On Single Source Robustness in Deep Fusion Models | #93
Taewan Kim (Amazon) · Joydeep Ghosh (UT Austin)
Perceiving the Arrow of Time in Autoregressive Motion | #155
Kristof Meding (University Tübingen) · Dominik Janzing (Amazon) · Bernhard Schölkopf (MPI for Intelligent Systems/Amazon) · Felix A. Wichmann (University of Tübingen)
Wednesday, 12/11 | 5:00-7:00pm | East Exhibition Hall B&C
Compositional De-Attention Networks | #127
Yi Tay (Nanyang Technological University) · Anh Tuan Luu (MIT) · Aston Zhang (Amazon) · Shuohang Wang (Singapore Management University) · Siu Cheung Hui (Nanyang Technological University)
Low-Rank Bandit Methods for High-Dimensional Dynamic Pricing | #3
Jonas Mueller (Amazon) · Vasilis Syrgkanis (Microsoft Research) · Matt Taddy (Amazon)
MaxGap Bandit: Adaptive Algorithms for Approximate Ranking | #4
Sumeet Katariya (Amazon/University of Wisconsin-Madison) · Ardhendu Tripathy (UW Madison) · Robert Nowak (UW Madison)
Primal-Dual Block Generalized Frank-Wolfe | #165
Qi Lei (UT Austin) · Jiacheng Zhuo (UT Austin) · Constantine Caramanis (UT Austin) · Inderjit S Dhillon (Amazon/UT Austin) · Alexandros Dimakis (UT Austin)
Towards Optimal Off-Policy Evaluation for Reinforcement Learning with Marginalized Importance Sampling | #208
Tengyang Xie (University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign) · Yifei Ma (Amazon) · Yu-Xiang Wang (UC Santa Barbara)
Thursday, 12/12 | 10:45-12:45pm | East Exhibition Hall B&C
AutoAssist: A Framework to Accelerate Training of Deep Neural Networks | #155
Jiong Zhang (UT Austin) · Hsiang-Fu Yu (Amazon) · Inderjit S Dhillon (UT Austin/Amazon)
Exponentially Convergent Stochastic k-PCA without Variance Reduction | #200 (oral, 10:05-10:20 W Ballroom C)
Cheng Tang (Amazon)
Failing Loudly: An Empirical Study of Methods for Detecting Dataset Shift | #54
Stephan Rabanser (Technical University of Munich/Amazon) · Stephan Günnemann (Technical University of Munich) · Zachary Lipton (Carnegie Mellon University/Amazon)
High-Dimensional Multivariate Forecasting with Low-Rank Gaussian Copula Processes | #107
David Salinas (Naverlabs) · Michael Bohlke-Schneider (Amazon) · Laurent Callot (Amazon) · Jan Gasthaus (Amazon) · Roberto Medico (Ghent University)
Learning Search Spaces for Bayesian Optimization: Another View of Hyperparameter Transfer Learning | #30
Valerio Perrone (Amazon) · Huibin Shen (Amazon) · Matthias Seeger (Amazon) · Cedric Archambeau (Amazon) · Rodolphe Jenatton (Amazon)
Mo’States Mo’Problems: Emergency Stop Mechanisms from Observation | #227
Samuel Ainsworth (University of Washington) · Matt Barnes (University of Washington) · Siddhartha Srinivasa (University of Washington/Amazon)
Think Globally, Act Locally: A Deep Neural Network Approach to High-Dimensional Time Series Forecasting | #113
Rajat Sen (Amazon) · Hsiang-Fu Yu (Amazon) · Inderjit S Dhillon (UT Austin/Amazon)
Thursday, 12/12 | 5:00-7:00pm | East Exhibition Hall B&C
Dynamic Local Regret for Non-Convex Online Forecasting | #20
Sergul Aydore (Stevens Institute of Technology) · Tianhao Zhu (Stevens Institute of Technology) · Dean Foster (Amazon)
Interaction Hard Thresholding: Consistent Sparse Quadratic Regression in Sub-quadratic Time and Space | #47
Suo Yang (UT Austin), Yanyao Shen (UT Austin), Sujay Sanghavi (UT Austin/Amazon)
Inverting Deep Generative Models, One Layer at a Time |#48
Qi Lei (University of Texas at Austin) · Ajil Jalal (UT Austin) · Inderjit S Dhillon (UT Austin/Amazon) · Alexandros Dimakis (UT Austin)
Provable Non-linear Inductive Matrix Completion| #215
Kai Zhong (Amazon) · Zhao Song (UT Austin) · Prateek Jain (Microsoft Research) · Inderjit S Dhillon (UT Austin/Amazon)
Amazon researchers on NeurIPS committees and boards
- Bernhard Schölkopf – Advisory Board
- Michael I. Jordan – Advisory Board
- Thorsten Joachims – senior area chair
- Anshumali Shrivastava – area chair
- Cedric Archambeau – area chair
- Peter Gehler – area chair
- Sujay Sanghavi – committee member
Workshops
Learning with Rich Experience: Integration of Learning Paradigms
Paper: "Meta-Q-Learning" | Rasool Fakoor, Pratik Chaudhari, Stefano Soatto, Alexander J. Smola
Human-Centric Machine Learning
Paper: "Learning Fair and Transferable Representations" | Luco Oneto, Michele Donini, Andreas Maurer, Massimiliano Pontil
Paper: "Online Bayesian Learning for E-Commerce Query Reformulation" | Gaurush Hiranandani, Sumeet Katariya, Nikhil Rao, Karthik Subbian
Paper: "Constrained Bayesian Optimization with Max-Value Entropy Search" | Valerio Perrone, Iaroslav Shcherbatyi, Rodolphe Jenatton, Cedric Archambeau, Matthias Seeger
Paper: "A Quantile-Based Approach to Hyperparameter Transfer Learning" | David Salinas, Huibin Shen, Valerio Perrone
Paper: "A Baseline for Few-Shot Image Classification" | Guneet Singh Dhillon, Pratik Chaudhari, Avinash Ravichandran, Stefano Soatto
Organizer: Dilek Hakkani-Tür
Paper: "The Eighth Dialog System Technology Challenge" | Seokhwan Kim, Michel Galley, Chulaka Gunasekara, Sungjin Lee, Adam Atkinson, Baolin Peng, Hannes Schulz, Jianfeng Gao, Jinchao Li, Mahmoud Adada, Minlie Huang, Luis Lastras, Jonathan K. Kummerfeld, Walter S. Lasecki, Chiori Hori, Anoop Cherian, Tim K. Marks, Abhinav Rastogi, Xiaoxue Zang, Srinivas Sunkara, Raghav Gupta
Paper: “Just Ask: An Interactive Learning Framework for Vision and Language Navigation” | Ta-Chung Chi, Minmin Shen, Mihail Eric, Seokhwan Kim, Dilek Hakkani-Tur
Paper: “MA-DST: Multi-Attention-Based Scalable Dialog State Tracking” | Adarsh Kumar, Peter Ku, Anuj Kumar Goyal, Angeliki Metallinou, Dilek Hakkani-Tür
Paper: “Investigation of Error Simulation Techniques for Learning Dialog Policies for Conversational Error Recovery” | Maryam Fazel-Zarandi, Longshaokan Wang, Aditya Tiwari, Spyros Matsoukas
Paper: “Towards Personalized Dialog Policies for Conversational Skill Discovery”| Maryam Fazel-Zarandi, Sampat Biswas, Ryan Summers, Ahmed Elmalt, Andy McCraw, Michael McPhillips, John Peach
Paper: “Conversation Quality Evaluation via User Satisfaction Estimation” | Praveen Kumar Bodigutla, Spyros Matsoukas, Lazaros Polymenakos
Paper: “Multi-domain Dialogue State Tracking as Dynamic Knowledge Graph Enhanced Question Answering” | Li Zhou, Kevin Small
Science Meets Engineering of Deep Learning
Paper: "X-BERT: eXtreme Multi-label Text Classification using Bidirectional Encoder from Transformers" Wei-Cheng Chang, Hsiang-Fu Yu, Kai Zhong, Yiming Yang, Inderjit S. Dhillon
Machine Learning with Guarantees
Organizers: Ben London, Thorsten Joachims
Program Committee: Kevin Small, Shiva Kasiviswanathan, Ted Sandler
MLSys: Workshop on Systems for ML
Paper: "Block-Distributed Gradient Boosted Trees" | Theodore Vasiloudis, Hyunsu Cho, Henrik Boström
Gold sponsor: Amazon


















