Many recent advances in artificial intelligence are the result of representation learning: a machine learning model learns to represent data items as vectors in a multidimensional space, where geometric relationships between vectors correspond to semantic relationships between items.
The M5 team at Amazon strives to construct general-purpose semantic representations of data related to the Amazon Store — product descriptions, queries, reviews, and more — that can be employed by machine learning (ML) systems throughout Amazon. Our approach involves leveraging all accessible data for each entity, often spanning multiple modalities.
One of the most successful ways to produce general-purpose representations is through contrastive learning, in which a model is trained on pairs of inputs, which are either positive (similar inputs/products) or negative (dissimilar inputs/products). The model learns to pull positive examples together and push negative examples apart.
In a pair of recent papers, M5 researchers have made substantial contributions to the theory and practice of contrastive learning. In “Why do we need large batch sizes in contrastive learning? A gradient-bias perspective”, presented at the 2022 Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) conference, we propose a new contrastive-learning loss function that enables models to converge on useful representations with lower memory cost and less training data.
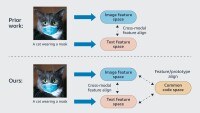
And in “Understanding and constructing latent modality structures in multi-modal representation learning”, presented at this year’s Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition conference (CVPR), we propose geometric constraints on the representations of different modes of the same data item — say, image and text — that are more useful for downstream tasks than simply trying to resolve both representations to the same point in the representational space.
Do we need large batch sizes in contrastive learning?
In contrast with standard ML methods, contrastive learning typically requires very large batch sizes to achieve good performance: several popular models, for instance, require tens of thousands of training examples, significantly increasing the memory overhead; reducing the batch size can impair performance. In our NeurIPS paper, we attempt to understand this phenomenon and to propose techniques for mitigating it.
Part of the appeal of contrastive learning is that it’s unsupervised, meaning it doesn’t require data annotation. Positive pairs can be generated by mathematically transforming an “anchor sample” and pairing the transformed version with the original; negative pairs can be generated by pairing an anchor sample with transformed versions of other anchor samples. With image data, a transformation might involve re-cropping, reversing, or distorting the colors of the anchor sample; with textual data, a transformation might involve substituting synonyms for the words in a sentence.
Given a measure of similarity between vectors in the representational space, the standard loss function for contrastive learning involves a ratio whose numerator includes the similarity between an anchor sample and one of its transformations; the denominator includes the sum of the similarities of the anchor sample and all possible negative samples. The goal of training is to maximize that ratio.
In principle, given the possibility of applying transformations to negative samples, “all possible negative samples” could describe an infinite set. In practice, contrastive learning typically just relies on the negative examples available in the training batch. Hence the need for large batch sizes — to approximate an infinite sum.
![contrastive_learning [Read-Only].png](https://assets.amazon.science/dims4/default/155752b/2147483647/strip/true/crop/2999x1687+0+0/resize/1200x675!/quality/90/?url=http%3A%2F%2Famazon-topics-brightspot.s3.amazonaws.com%2Fscience%2F79%2Fef%2F34a9ab3a466f88b64b3f3832e6b8%2Fcontrastive-learning-framework.png)
If the distribution of minibatch samples differs from the distribution of possible negatives, however, this approximation can bias the model. One difficulty in correcting the bias is that, because the loss function contrasts each positive pair with all possible negatives at once, in a ratio, it cannot be decomposed into a sum of sub-losses.
We address the decomposability problem using Bayesian augmentation. The general approach is that, for each anchor sample, we create a random auxiliary variable, which can be thought of as a weight applied to the anchor sample’s similarity scores. Using identity under the gamma function, we can show that the auxiliary variable follows a gamma distribution, which is easy to sample. As a consequence, we can rewrite the loss in an exponential rather than a fractional form, making it decomposable.
During training, we begin by sampling the auxiliary variables for the current batch of data from a gamma distribution, giving us the weight of the similarity scores for all the anchor samples. Conditioned on the sampled values, we then apply maximum likelihood estimation to optimize the parameters of the model, which will consider the sampled weights on the similarity scores from the first step. We then repeat this process for the entire dataset, summing a sequence of (weighted) sub-losses to produce a cumulative loss. In our paper, we show that this procedure will converge toward the expected loss for the original contrastive-loss function, with its infinite sum in the denominator.
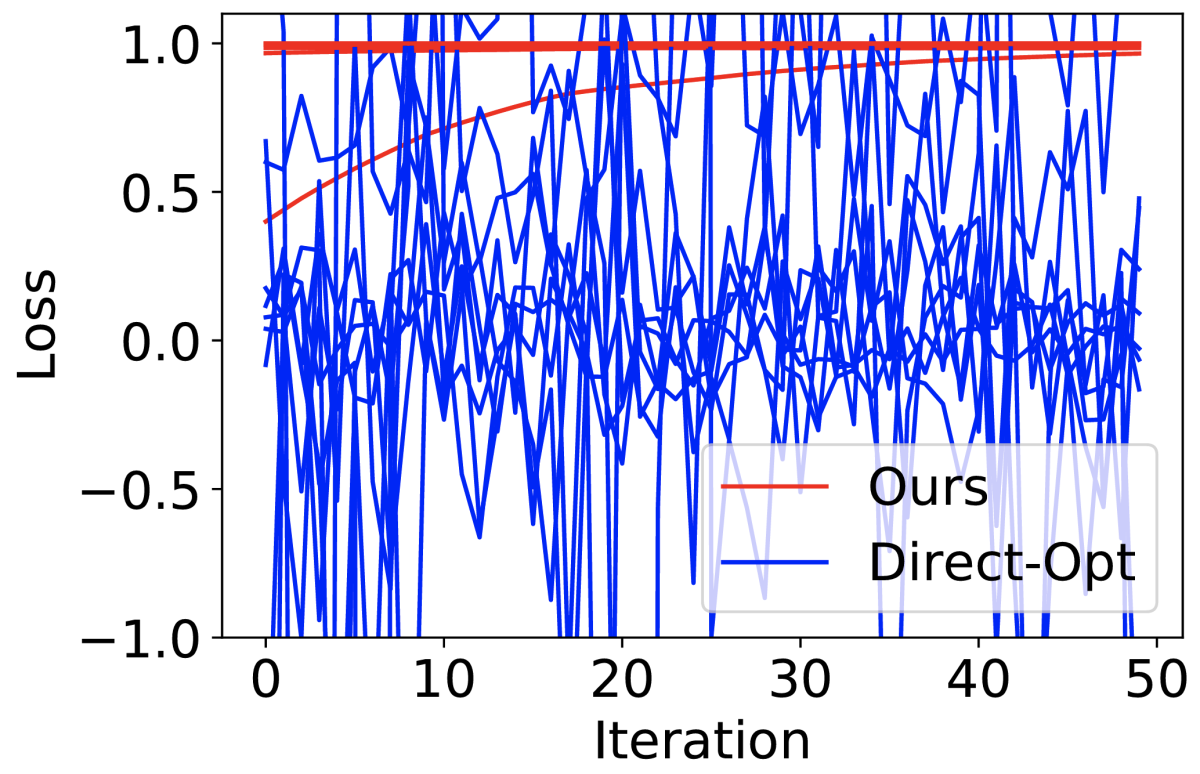
We evaluate our approach through a number of experiments. In one, we used simulated data, into which we injected noise to simulate bias. Then we used both our loss and the conventional loss function to train a model 10 times, with different initialization values. At heavy noise levels, the model trained with the conventional loss failed to converge, while ours consistently converged to the optimum.
We also evaluated the models on a variety of downstream tasks, including zero-/few-shot image classification and image/text retrieval. Our approach showed significant performance improvement over state-of-the-art baseline methods.
What geometries work best for multimodal representation matching?
At M5, we are building scalable models that can handle multimodal data — for instance, multilingual models that translate between product descriptions in different languages or multi-entity models that jointly model different images of the same product. Contrastive learning is a promising method for building such models: data in different modalities that are associated with the same products can be treated as positive pairs, and contrastive learning pulls them together in the representational space.
We theoretically investigated whether the standard contrastive-learning framework is optimal in terms of the prediction error rate on downstream tasks, and the surprising answer is no. In our CVPR paper, we prove that if the information gap between two modalities is large — that is, if you can’t infer much about one modality from the other — then the best prediction error we can hope to achieve using standard contrastive-learning representations is larger than that we can achieve if we simply train a machine learning model directly on data in a single modality.
This makes some intuitive sense. Ideally, contrastive learning would pull the different modalities so tightly together that they would essentially resolve to a single point in the representational space. But of course, the reason to use multimodal representations for downstream tasks is that each modality may capture useful information that the other does not. Collapsing the different modalities’ representations together neutralizes this advantage.
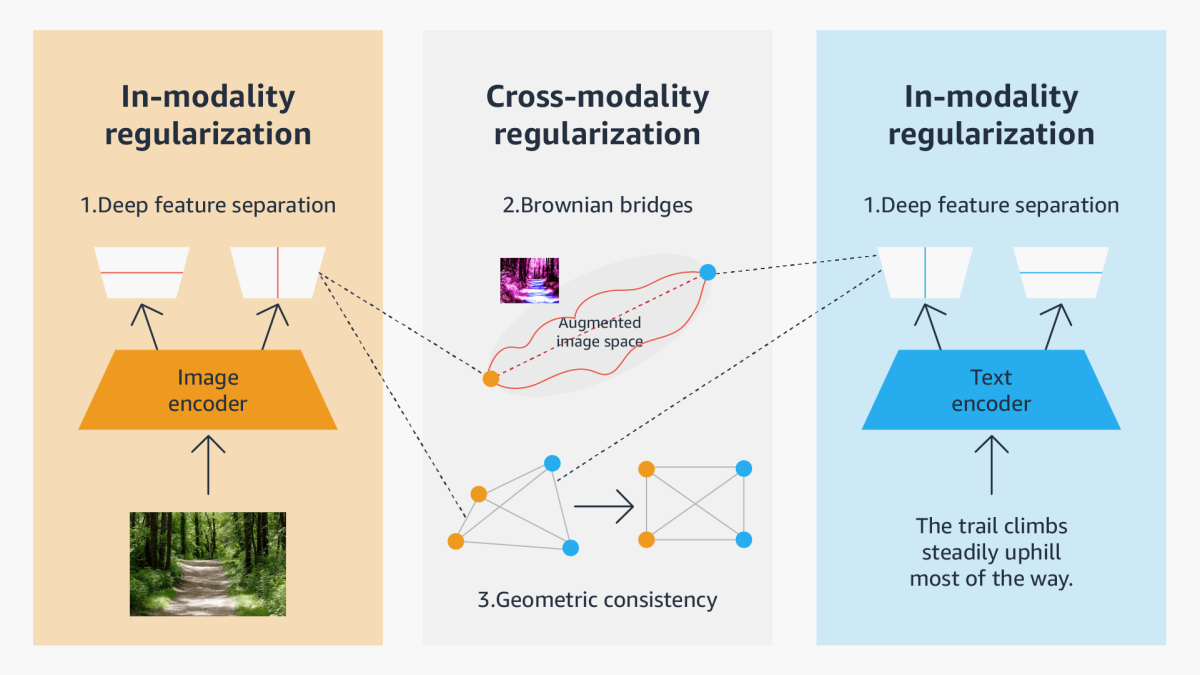
Consequently, in our CVPR paper, we explore different geometrical relationships in the representational space that can establish correlations between multimodal data without sacrificing information specific to each mode. We propose three general approaches to constructing modality structures in the representational space, suited to intramodal representation, intermodal representation, and a combination of the two:
- a deep feature separation loss for intramodality regularization, which uses two types of neural network components to separate different modality information: one component captures information that’s shared between modalities (tuned according to the standard contrastive-learning loss), and the other, which is orthogonal to the first, captures information unique to the modality;
- a “Brownian-bridge” loss for intermodality regularization, which uses Brownian motion to plot several trajectories/transitions between the representation of one modality (say, text) and the other (say, an image) and constrains representations of augmented data to lie along one of those paths; and
- a geometric-consistency loss for both intra- and intermodality regularization, which enforces symmetry in the geometric relationships between representations in one modality and the corresponding representations in the other modality, while simultaneously enforcing symmetries in cross-modal geometric relationships.
We have conducted extensive experiments on two popular multimodal representation-learning frameworks, the CLIP-based two-tower model and the ALBEF-based fusion model. We tested our model on a variety of tasks, including zero-/few-shot image classification, image-text retrieval, visual question answering, visual reasoning, and visual entailment. Our method achieves consistent improvements over existing methods, demonstrating the effectiveness and generalizability of our proposed approach on multimodal representation learning.
Going forward
Our NeurIPS and CVPR papers represent only two interesting projects from our M5 team. There is a lot more research on multimodal learning going on in M5. This includes generative models for images, videos, and text (e.g. Stable Diffusion, DreamBooth) to enable data synthesis and representation learning and training and applying large language models to enhance customer shopping experiences. We expect to report on more research highlights in the near future.