AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies provide customers with fine-grained control over who has access to what resources in the Amazon Web Services (AWS) Cloud. This control helps customers enforce the principle of least privilege by granting only the permissions required to perform particular tasks. In practice, however, writing IAM policies that enforce least privilege requires customers to understand what permissions are necessary for their applications to function, which can become challenging when the scale of the applications grows.
To help customers understand what permissions are not necessary, we launched IAM Access Analyzer unused access findings at the 2023 re:Invent conference. IAM Access Analyzer analyzes your AWS accounts to identify unused access and creates a centralized dashboard to report its findings. The findings highlight unused roles and unused access keys and passwords for IAM users. For active IAM roles and users, the findings provide visibility into unused services and actions.
To take this service a step further, in June 2024 we launched recommendations to refine unused permissions in Access Analyzer. This feature recommends a refinement of the customer’s original IAM policies that retains the policy structure while removing the unused permissions. The recommendations not only simplify removal of unused permissions but also help customers enact the principle of least privilege for fine-grained permissions.
In this post, we discuss how Access Analyzer policy recommendations suggest policy refinements based on unused permissions, which completes the circle from monitoring overly permissive policies to refining them.
Policy recommendation in practice
Let's dive into an example to see how policy recommendation works. Suppose you have the following IAM policy attached to an IAM role named MyRole:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"lambda:AddPermission",
"lambda:GetFunctionConfiguration",
"lambda:UpdateFunctionConfiguration",
"lambda:UpdateFunctionCode",
"lambda:CreateFunction",
"lambda:DeleteFunction",
"lambda:ListVersionsByFunction",
"lambda:GetFunction",
"lambda:Invoke*"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:my-lambda"
},
{
"Effect" : "Allow",
"Action" : [
"s3:Get*",
"s3:List*"
],
"Resource" : "*"
}
]
}
The above policy has two policy statements:
- The first statement allows actions on a function in AWS Lambda, an AWS offering that provides function execution as a service. The allowed actions are specified by listing individual actions as well as via the wildcard string lambda:Invoke*, which permits all actions starting with Invoke in AWS Lambda, such as lambda:InvokeFunction.
- The second statement allows actions on any Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) bucket. Actions are specified by two wildcard strings, which indicate that the statement allows actions starting with Get or List in Amazon S3.
Enabling Access Analyzer for unused finding will provide you with a list of findings, each of which details the action-level unused permissions for specific roles. For example, for the role with the above policy attached, if Access Analyzer finds any AWS Lambda or Amazon S3 actions that are allowed but not used, it will display them as unused permissions.
The unused permissions define a list of actions that are allowed by the IAM policy but not used by the role. These actions are specific to a namespace, a set of resources that are clustered together and walled off from other namespaces, to improve security. Here is an example in Json format that shows unused permissions found for MyRole with the policy we attached earlier:
[
{
"serviceNamespace": "lambda",
"actions": [
"UpdateFunctionCode",
"GetFunction",
"ListVersionsByFunction",
"UpdateFunctionConfiguration",
"CreateFunction",
"DeleteFunction",
"GetFunctionConfiguration",
"AddPermission"
]
},
{
"serviceNamespace": "s3",
"actions": [
"GetBucketLocation",
"GetBucketWebsite",
"GetBucketPolicyStatus",
"GetAccelerateConfiguration",
"GetBucketPolicy",
"GetBucketRequestPayment",
"GetReplicationConfiguration",
"GetBucketLogging",
"GetBucketObjectLockConfiguration",
"GetBucketNotification",
"GetLifecycleConfiguration",
"GetAnalyticsConfiguration",
"GetBucketCORS",
"GetInventoryConfiguration",
"GetBucketPublicAccessBlock",
"GetEncryptionConfiguration",
"GetBucketAcl",
"GetBucketVersioning",
"GetBucketOwnershipControls",
"GetBucketTagging",
"GetIntelligentTieringConfiguration",
"GetMetricsConfiguration"
]
}
]
This example shows actions that are not used in AWS Lambda and Amazon S3 but are allowed by the policy we specified earlier.
How could you refine the original policy to remove the unused permissions and achieve least privilege? One option is manual analysis. You might imagine the following process:
- Find the statements that allow unused permissions;
- Remove individual actions from those statements by referencing unused permissions.
This process, however, can be error prone when dealing with large policies and long lists of unused permissions. Moreover, when there are wildcard strings in a policy, removing unused permissions from them requires careful investigation of which actions should replace the wildcard strings.
Policy recommendation does this refinement automatically for customers!
The policy below is one that Access Analyzer recommends after removing the unused actions from the policy above (the figure also shows the differences between the original and revised policies):
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement" : [
{
"Effect" : "Allow",
"Action" : [
- "lambda:AddPermission",
- "lambda:GetFunctionConfiguration",
- "lambda:UpdateFunctionConfiguration",
- "lambda:UpdateFunctionCode",
- "lambda:CreateFunction",
- "lambda:DeleteFunction",
- "lambda:ListVersionsByFunction",
- "lambda:GetFunction",
"lambda:Invoke*"
],
"Resource" : "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:my-lambda"
},
{
"Effect" : "Allow",
"Action" : [
- "s3:Get*",
+ "s3:GetAccess*",
+ "s3:GetAccountPublicAccessBlock",
+ "s3:GetDataAccess",
+ "s3:GetJobTagging",
+ "s3:GetMulti*",
+ "s3:GetObject*",
+ "s3:GetStorage*",
"s3:List*"
],
"Resource" : "*"
}
]
}
Let’s take a look at what’s changed for each policy statement.
For the first statement, policy recommendation removes all individually listed actions (e.g., lambda:AddPermission), since they appear in unused permissions. Because none of the unused permissions starts with lambda:Invoke, the recommendation leaves lambda:Invoke* untouched.
For the second statement, let’s focus on what happens to the wildcard s3:Get*, which appears in the original policy. There are many actions that can start with s3:Get, but only some of them are shown in the unused permissions. Therefore, s3:Get* cannot just be removed from the policy. Instead, the recommended policy replaces s3:Get* with seven actions that can start with s3:Get but are not reported as unused.
Some of these actions (e.g., s3:GetJobTagging) are individual ones, whereas others contain wildcards (e.g., s3:GetAccess* and s3:GetObject*). One way to manually replace s3:Get* in the revised policy would be to list all the actions that start with s3:Get except for the unused ones. However, this would result in an unwieldy policy, given that there are more than 50 actions starting with s3:Get.
Instead, policy recommendation identifies ways to use wildcards to collapse multiple actions, outputting actions such as s3:GetAccess* or s3:GetMulti*. Thanks to these wildcards, the recommended policy is succinct but still permits all the actions starting with s3:Get that are not reported as unused.
How do we decide where to place a wildcard in the newly generated wildcard actions? In the next section, we will dive deep on how policy recommendation generalizes actions with wildcards to allow only those actions that do not appear in unused permissions.
A deep dive into how actions are generalized
Policy recommendation is guided by the mathematical principle of “least general generalization” — i.e., finding the least permissive modification of the recommended policy that still allows all the actions allowed by the original policy. This theorem-backed approach guarantees that the modified policy still allows all and only the permissions granted by the original policy that are not reported as unused.
To implement the least-general generalization for unused permissions, we construct a data structure known as a trie, which is a tree each of whose nodes extends a sequence of tokens corresponding to a path through the tree. In our case, the nodes represent prefixes shared among actions, with a special marker for actions reported in unused permissions. By traversing the trie, we find the shortest string of prefixes that does not contain unused actions.
The diagram below shows a simplified trie delineating actions that replace the S3 Get* wildcard from the original policy (we have omitted some actions for clarity):
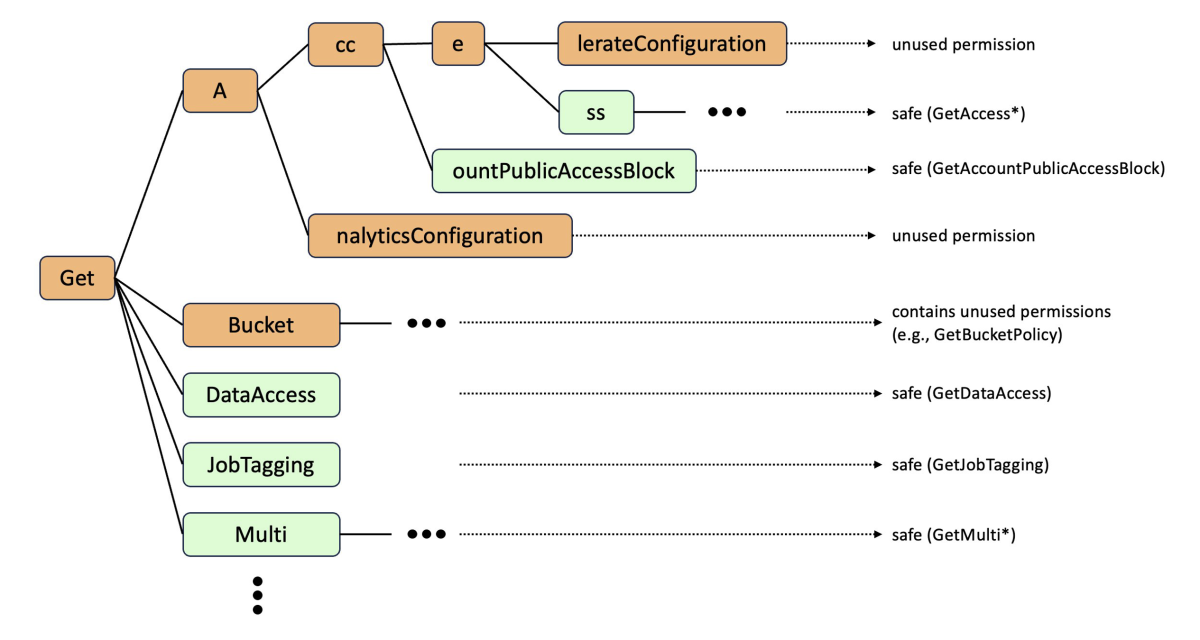
At a high level, the trie represents prefixes that are shared by some of the possible actions starting with s3:Get. Its root node represents the prefix Get; child nodes of the root append their prefixes to Get. For example, the node named Multi represents all actions that start with GetMulti.
We say that a node is safe (denoted in green in the diagram) if none of the unused actions start with the prefix corresponding to that node; otherwise, it is unsafe (denoted in orange). For example, the node s3:GetBucket is unsafe because the action s3:GetBucketPolicy is unused. Similarly, the node ss is safe since there are no unused permissions that start with GetAccess.
We want our final policies to contain wildcard actions that correspond only to safe nodes, and we want to include enough safe nodes to permit all used actions. We achieve this by selecting the nodes that correspond to the shortest safe prefixes—i.e., nodes that are themselves safe but whose parents are not. As a result, the recommended policy replaces s3:Get* with the shortest prefixes that do not contain unused permissions, such as s3:GetAccess*, s3:GetMulti* and s3:GetJobTagging.
Together, the shortest safe prefixes form a new policy that, while syntactically similar to the original policy, is the least-general generalization to result from removing the unused actions. In other words, we have not removed more actions than necessary.
You can find how to start using policy recommendation with unused access in Access Analyzer. To learn more about the theoretical foundations powering policy recommendation, be sure to check out our science paper.