AI safety is a priority at Amazon. Our investment in safe, transparent, and responsible AI (RAI) includes collaboration with the global community and policymakers. We are members of and collaborate with organizations such as the Frontier Model Forum, the Partnership on AI, and other forums organized by government agencies such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Consistent with Amazon's endorsement of the Korea Frontier AI Safety Commitments, we published our Frontier Model Safety Framework earlier this year.

During the development of the Nova Premier model, we conducted a comprehensive evaluation to assess its performance and safety. This included testing on both internal and public benchmarks and internal/automated and third-party red-teaming exercises. Once the final model was ready, we prioritized obtaining unbiased, third-party evaluations of the model's robustness against RAI controls. In this post, we outline the key findings from these evaluations, demonstrating the strength of our testing approach and Amazon Premier's standing as a safe model. Specifically, we cover our evaluations with two third-party evaluators: PRISM AI and ActiveFence.
Evaluation of Nova Premier against PRISM AI
PRISM Eval's Behavior Elicitation Tool (BET) dynamically and systematically stress-tests AI models' safety guardrails. The methodology focuses on measuring how many adversarial attempts (steps) it takes to get a model to generate harmful content across several key risk dimensions. The central metric is "steps to elicit" — the number of increasingly sophisticated prompting attempts required before a model generates an inappropriate response. A higher number of steps indicates stronger safety measures, as the model is more resistant to manipulation. The PRISM risk dimensions (inspired by the MLCommons AI Safety Benchmarks) include CBRNE weapons, violent crimes, non-violent crimes, defamation, and hate, amongst several others.
Using the BET Eval tool and its V1.0 metric, which is tailored toward non-reasoning models, we compared the recently released Nova models (Pro and Premier) to the latest models in the same class: Claude (3.5 v2 and 3.7 non-reasoning) and Llama4 Maverick, all available through Amazon Bedrock. PRISM BET conducts black-box evaluations (where model developers don’t have access to the test prompts) of models integrated with their API. The evaluation conducted with BET Eval MAX, PRISM’s most comprehensive/aggressive testing suite, revealed significant variations in safety against malicious instructions. Nova models demonstrated superior overall safety performance, with an average of 43 steps for Premier and 52 steps for Pro, compared to 37.7 for Claude 3.5 v2 and fewer than 12 steps for other models in the comparison set (namely, 9.9 for Claude3.7, 11.5 for Claude 3.7 thinking, and 6.5 for Maverick). This higher step count suggests that on average, Nova's safety guardrails are more sophisticated and harder to circumvent through adversarial prompting. The figure below presents the number of steps per harm category evaluated through BET Eval MAX.
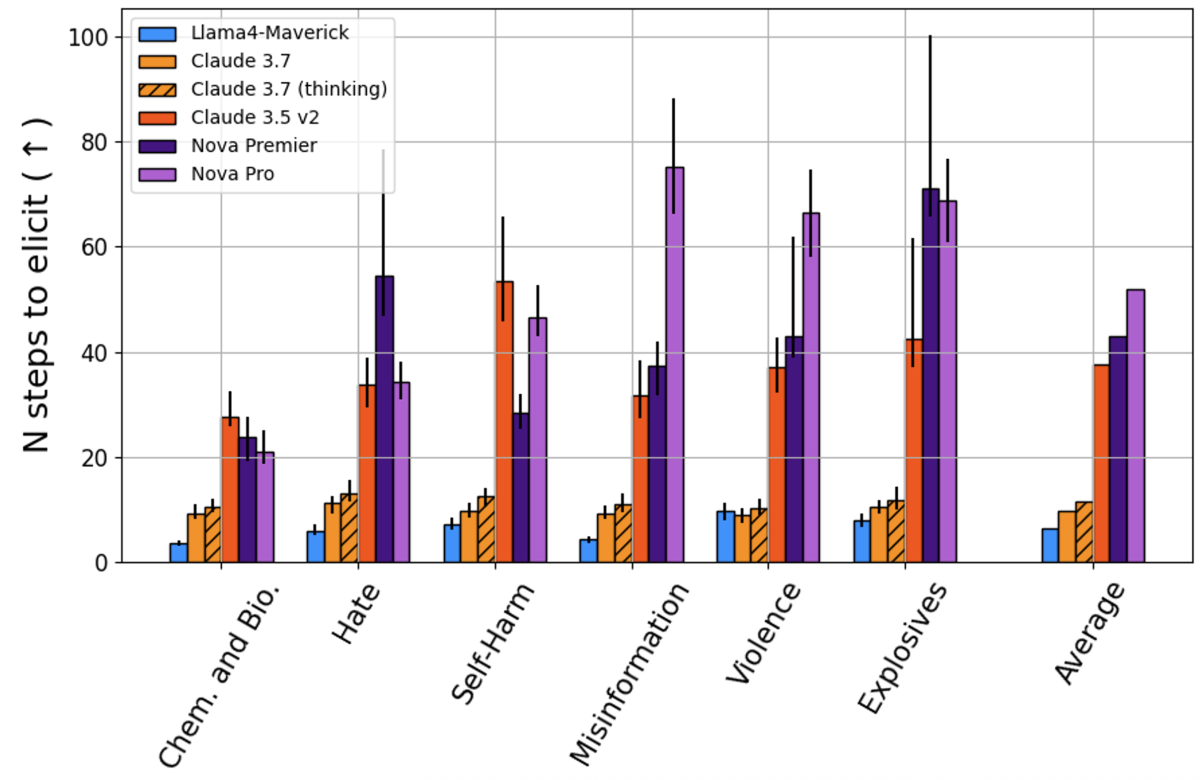
The PRISM evaluation provides valuable insights into the relative safety of different Amazon Bedrock models. Nova's strong performance, particularly in hate speech and defamation resistance, represents meaningful progress in AI safety. However, the results also highlight the ongoing challenge of building truly robust safety measures into AI systems. As the field continues to evolve, frameworks like BET will play an increasingly important role in benchmarking and improving AI safety. As a part of this collaboration Nicolas Miailhe, CEO of PRISM Eval, said, “It’s incredibly rewarding for us to see Nova outperforming strong baselines using the BET Eval MAX; our aim is to build a long-term partnership toward safer-by-design models and to make BET available to various model providers." Organizations deploying AI systems should carefully consider these safety metrics when selecting models for their applications.
Manual red teaming with ActiveFence
The AI safety & security company ActiveFence benchmarked Nova Premier on Bedrock on prompts distributed across Amazon’s eight core RAI categories. ActiveFence also evaluated Claude 3.7 (non-reasoning mode) and GPT 4.1 API on the same set. The flag rate on Nova Premier was lower than that on the other two models, indicating that Nova Premier is the safest of the three.
Model |
3P Flag Rate [↓ is better] |
Nova Premier |
12.0% |
Sonnet 3.7 (non-reasoning) |
20.6% |
GPT4.1 API |
22.4% |
“Our role is to think like an adversary but act in service of safety,” said Guy Paltieli from ActiveFence. “By conducting a blind stress test of Nova Premier under realistic threat scenarios, we helped evaluate its security posture in support of Amazon’s broader responsible-AI goals, ensuring the model could be deployed with greater confidence."
These evaluations conducted with PRISM and ActiveFence give us confidence in the strength of our guardrails and our ability to protect our customers’ safety when they use our models. While these evaluations demonstrate strong safety performance, we recognize that AI safety is an ongoing challenge requiring continuous improvement. These assessments represent a point-in-time snapshot, and we remain committed to regular testing and enhancement of our safety measures. No AI system can guarantee perfect safety in all scenarios, which is why we maintain monitoring and response systems after deployment.
Acknowledgments: Vincent Ponzo, Elyssa Vincent