Marijn Heule, an Amazon Scholar and professor of computer science at Carnegie Mellon University, together with his colleague Manfred Scheucher of Technische Universität Berlin, have solved a geometry problem posed almost 100 years ago by the Hungarian-Australian mathematician Esther Szekeres.

Paul Erdős, the legendary Hungarian mathematician who gave his name to the Erdős number, dubbed it the “happy-ending problem”, because work on it led to the marriage of Esther, née Klein, and Erdős’s long-time collaborator George Szekeres.
The problem asks the minimum number of points in a plane, no three of which are collinear, required to guarantee that n of the points constitute a convex polygon that does not contain any of the other points. (“Convex” means that a line segment connecting any two points within the polygon itself lies entirely within the polygon.)
Esther Szekeres dispatched the case of n = 4 in the 1930s. It was almost 50 years before Heiko Harborth determined that 10 points are needed to guarantee an empty pentagon. Around the same time, Joseph Horton showed that the problem is insoluble for polygons with seven or more sides: no number of points will guarantee that a convex 7-gon can be found that contains no other points in the collection.
But the remaining case — the empty hexagon — was still outstanding. That’s the problem that Heule and Scheucher solved. They showed that 30 points is sufficient to guarantee a convex hexagon that doesn’t contain any of the other points.
To prove this result, Heule and Scheucher used a SAT solver, an automated-reasoning tool that determines whether long chains of logical constraints can be satisfied. The SAT solver generates a proof that particular assignments of values to variables are prohibited by the constraints. Verifying the correctness of the proof requires another automated-reasoning tool, a proof checker.
Proofs, however, can be hundreds of terabytes in size, and just managing input-output (I/O) and data retrieval during the proof-checking process can be hugely time consuming. “The cost of checking can be, say, 100% to 200% of the original solving time,” Heule says.
Heule, who is a member of Amazon Web Services’ (AWS’s) Automated Reasoning group, worked with his AWS colleagues to develop the infrastructure for a new streaming approach to proof checking, where a dedicated server core checks the proof as it is generated. This reduces the proof-checking overhead from 100% to 200% to somewhere around 10%.
This innovation, in turn, will be of use to the Automated Reasoning group in its future work on, say, software security, provably correct software, and hardware validation. Of course, those applications still require developers to create rigorous formal models of the systems they’re validating. But during the proof-checking phase, “if we can do things with say 10% overhead instead of 150%, that's a clear win,” Heule says.
Geometric constraints
SAT problems are NP-complete, meaning that SAT problems can be devised that would be insoluble by all the computers in the world in the lifetime of the universe.
But that doesn’t mean that all SAT problems, or even SAT problems with large numbers of variables, are insoluble, and part of the automated-reasoning researcher’s art is formulating problems in such a way that a SAT solver can solve them.
“Marijn is best-in-the-world at mapping complex problems to solvers,” says Robert Jones, a senior principal applied scientist in the AWS Automated Reasoning group.
The setup of the happy-ending problem can be described using binary (Boolean) variables each of which describes the orientations of three points. The variables all have the same general form: given three points in general position (i.e., not collinear), A, B, and C, C is above the line through A and B. (If the variable is false, C is necessarily below the line.) Chain enough of these together, and you can specify the 30 points of the 6-gon case (or 29 points, or any other number).
Within that framework, the difficulty is to describe the condition that there be at least one hexagon with no point inside it. Scheucher’s group had been batting that problem about for years without arriving at a formulation that a SAT solver could handle. That’s where Heule came in.
People mapping problems to SAT expressions often focus on concision, Heule explains; the more concise the expression, they reason, the fewer possibilities the solver will need to consider. That may be true in general, Heule says, but in his experience, long chains of simple constraints are often easier to reason about than short chains of more complex constraints.
Simplifying the problem
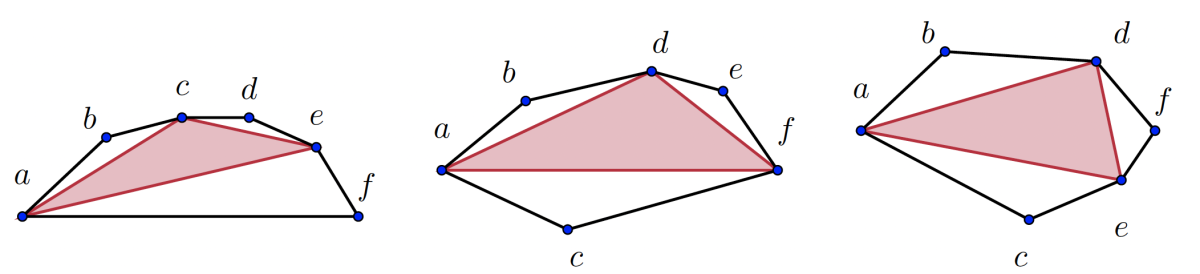
The natural way to approach the empty-hexagon problem is to break hexagons into triangles and reason about whether each triangle has a point in its interior. Prior attempts to map this problem to a SAT expression had taken a general approach, specifying a set of logical constraints that could be applied to any triangle in the collection and all hexagons that included that triangle. The resulting expression, Heule says, was easy to formulate but hard to reason about.
Heule suggested that he and Scheucher take the opposite tack, explicitly labeling every possible configuration of each hexagon, specifying the individual triangles using those labels, and checking each of the named triangles for points in its interior.
“In this case, you really need to blow it up in order to get much smaller later,” Heule explains. “I made it 10 times bigger and afterward realized that the new expression could be compressed substantially. This compression step is also possible with existing automated-reasoning tools.”
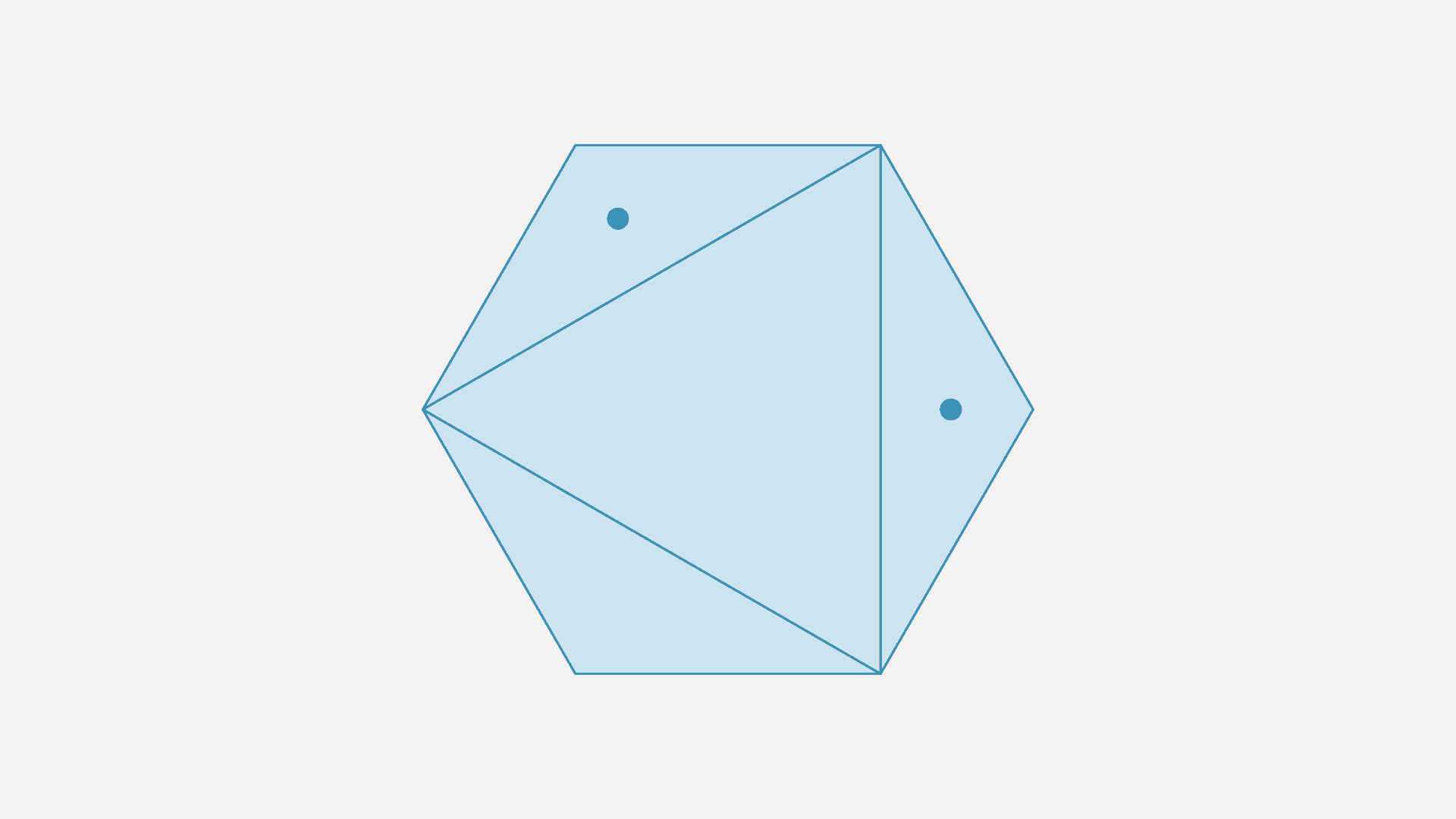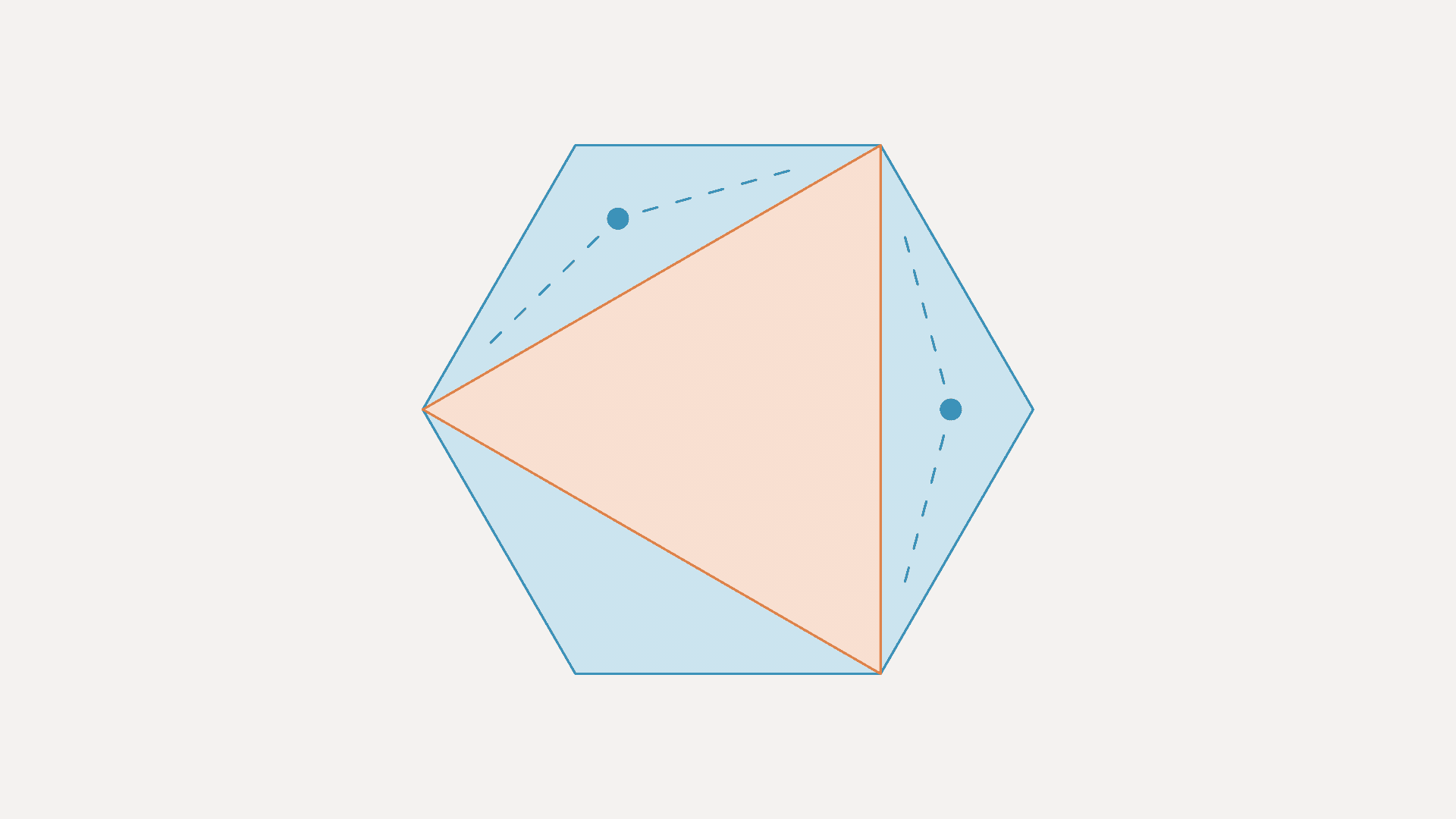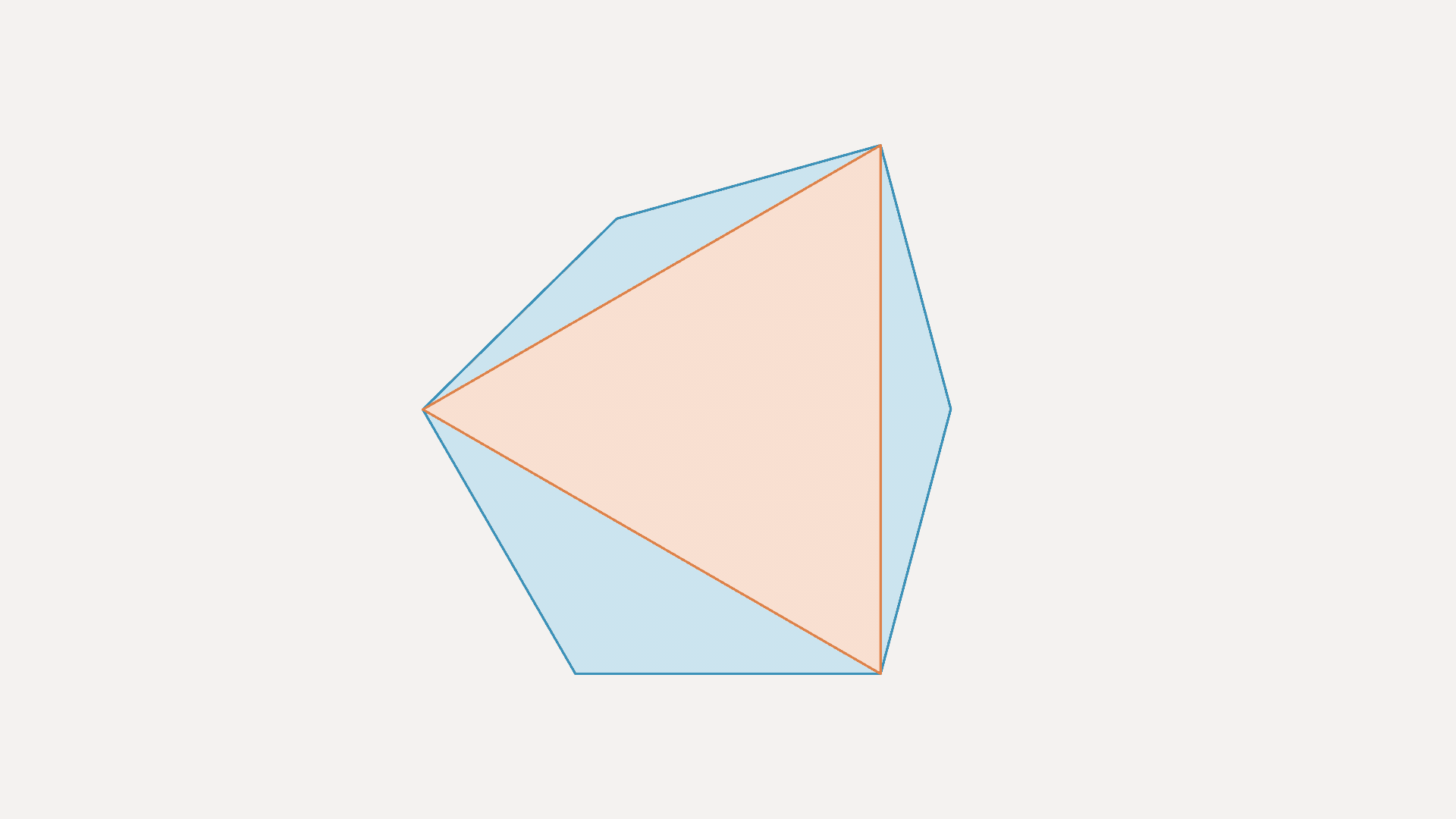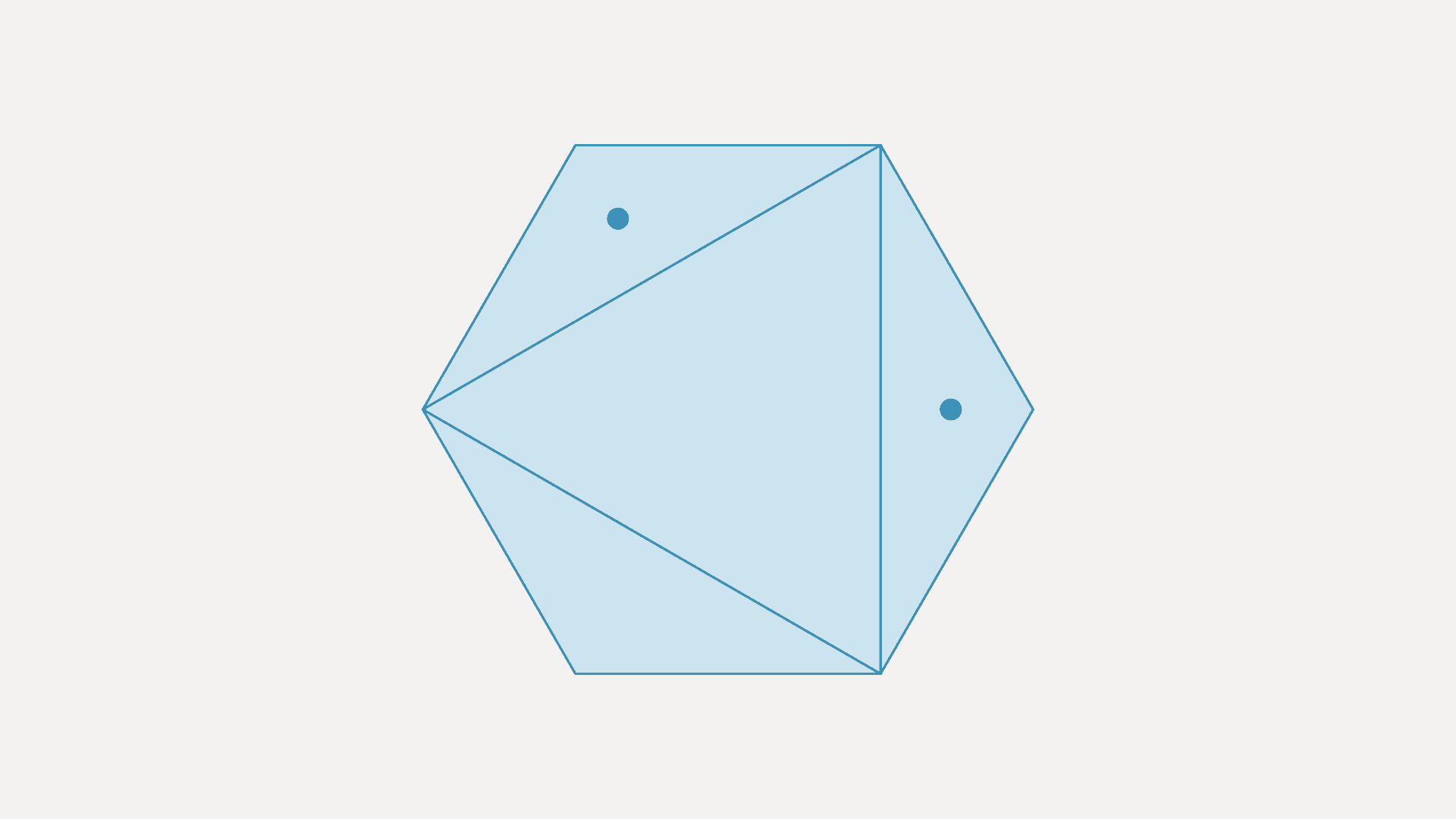
One of the ways that SAT solvers reduce the complexity of the problems they’re tackling is by looking for logical redundancies and removing them. In his initial specification of the empty-hexagon problem, Heule divided each hexagon in the point set into four triangles and checked each triangle for a point in its interior.
He noticed, however, that the SAT solver reduced this step to checking only one triangle per hexagon. After thinking it through, Heule and Scheucher realized that in each hexagon, there was a single triangle — call it the inner triangle — that shared all its sides with the hexagon’s other three triangles — call them the outer triangles. If that inner triangle was empty, then it was possible to deduce the existence of an empty hexagon from the points in the point set.
Suppose that one of the outer triangles contains a point. Then it’s possible to draw a new triangle that contains that point and shares a side with the inner triangle. Repeating this process as needed is guaranteed to yield a convex hexagon with no points in its interior.
Heule and Scheucher extracted this line of reasoning from the SAT solver itself. “I have frequently seen that the solver provides useful feedback, although it's feedback for an expert,” Heule says. “I think it's really important that this feedback becomes available for nonexperts. For example, you implement something, and the solver says, ‘Okay, you're trying to do this, but that part of the expression is not needed.’ This feedback can be used to reformulate the expression in such a way that that it is much easier to solve.”
Once Heule and Scheucher understood what the solver was telling them, they were able to devise a more practical specification of the SAT problem. The solver was able to reason through all the possibilities for a 30-point point set and prove that, within that set, there must exist at least one hexagon whose inner triangle contained no other points.
It was still an extremely long proof, but Heule and his AWS colleagues’ new proof-checking mechanism was able to confirm its validity relatively quickly.
“One of the issues here is that many users of these tools don't know how to get the most out of them,” Heule says. “And that's not only for this specific problem but for many other problems as well. Within Amazon, there are a lot of applications where SAT solvers could verify developers’ work or find better solutions. I can help by writing an effective encoding, but ideally, everything would be done automatically. I would love to see myself being taken out of the equation.”