Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
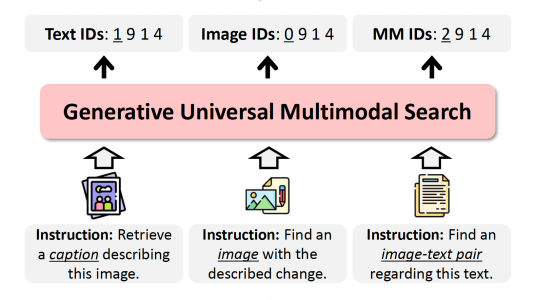
June 25, 2025With large datasets, directly generating data ID codes from query embeddings is much more efficient than performing pairwise comparisons between queries and candidate responses.
Featured news
-
2025Text chunking is fundamental to modern retrieval-augmented systems, yet existing methods often struggle with maintaining semantic coherence, both within and across chunks, while dealing with document structure and noise. We present AutoChunker, a bottom-up approach for text chunking that combines document structure awareness with noise elimination. AutoChunker leverages language models to identify and segregate
-
SIGMOD/PODS 2025 Workshop on Data Management on New Hardware2025We present insert-optimized implementations of three fundamental data sketching algorithms: Count Sketch (CS), SpaceSaving (SS), and Karnin-Lang-Liberty (KLL).While these sketches are widely used for approximate query processing and stream analytics, their practical insert performance often falls short of their full potential. Through careful engineering and novel implementation strategies, we achieve substantial
-
IEEE ICIP 20252025Copy Detection system aims to identify if a query image is an edited/manipulated copy of an image from a large reference database with millions of images. While global image descriptors can retrieve visually similar images, they struggle to differentiate near-duplicates from semantically similar instances. We propose a dual-triplet metric learning (DTML) technique to learn global image features that group
-
2025Vision Language Models (VLMs) have achieved significant advancements in complex visual understanding tasks. However, VLMs are prone to hallucinations—generating outputs that lack alignment with visual content. This paper addresses hallucination detection in VLMs by leveraging the visual grounding information encoded in transformer attention maps. We identify three primary challenges in this approach: the
-
2025In this paper, we present a novel algorithm for quantifying uncertainty and information gained within 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) through P-Optimality. While 3D-GS has proven to be a useful world model with high-quality rasterizations, it does not natively quantify uncertainty or information, posing a challenge for real-world applications such as 3D-GS SLAM. We propose to quantify information gain in
Academia
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all