Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
July 22, 2025Generating diverse synthetic prior distributions leads to a tabular foundation model that outperforms task-specific baselines.
Featured news
-
2025Foundation models, such as large language models, have achieved remarkable success in natural language processing and are evolving into models capable of handling multiple modalities. Listening ability, in particular, is crucial for many applications, leading to research on building speech foundation models. However, the high computational cost of these large models presents a significant challenge for
-
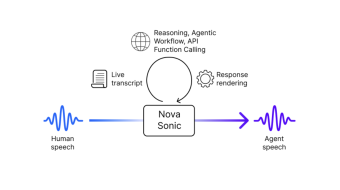
Amazon Technical Reports2025We present Amazon Nova Sonic, a new multimodal foundation model that unifies speech and text processing in a single architecture, delivering frontier voice intelligence and industry-leading price performance. Amazon Nova Sonic ("Nova Sonic") builds on the advances in large pre-trained text and speech models, while fusing the two modalities in a unified architecture to power downstream tasks requiring both
-
QID: Efficient query-informed ViTs in data-scarce regimes for OCR-free visual document understanding2025In Visual Document Understanding (VDU) tasks, fine-tuning a pre-trained Vision-Language Model (VLM) with new datasets often falls short in optimizing the vision en-coder to identify query-specific regions in text-rich document images. Existing methods that directly inject queries into model layers by modifying the network architecture often struggle to adapt to new datasets with limited annotations. To
-
2025Recent advances in Multi-Modal Large Language Models (M-LLMs) show promising results in video reasoning. Popular Multi-Modal Large Language Model (M-LLM) frameworks usually apply naive uniform sampling to reduce the number of video frames that are fed into an M-LLM, particularly for long context videos. However, it could lose crucial context in certain periods of a video, so that the downstream M-LLM may
-
2025While retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has been shown to enhance factuality of large language model (LLM) outputs, LLMs still suffer from hallucination, generating incorrect or irrelevant information. A common detection strategy involves prompting the LLM again to assess whether its response is grounded in the retrieved evidence, but this approach is costly. Alternatively, lightweight natural language
Academia
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all