Customer-obsessed science


Research areas
-
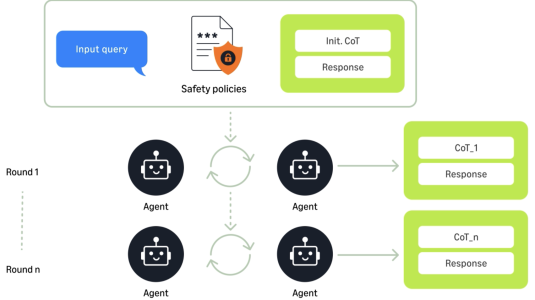
July 31, 2025Using ensembles of agents to generate and refine interactions annotated with chains of thought improves performance on a battery of benchmarks by an average of 29%.
Featured news
-
AISTATS 20252025Modeling and analysis for event series generated by users of heterogeneous behavioral patterns are closely involved in our daily lives, including credit card fraud detection, online platform user recommendation, and social network analysis. The most commonly adopted approach to this task is to assign users to behavior-based categories and analyze each of them separately. However, this requires extensive
-
M2AD: Multi-sensor multi-system anomaly detection through global scoring and calibrated thresholdingAISTATS 20252025With the widespread availability of sensor data across industrial and operational systems, we frequently encounter heterogeneous time series from multiple systems. Anomaly detection is crucial for such systems to facilitate predictive maintenance. However, most existing anomaly detection methods are designed for either univariate or single-system multivariate data, making them insufficient for these complex
-
2025In product search, negation is frequently used to articulate unwanted product features or components. Modern search engines often struggle to comprehend negations, resulting in suboptimal user experiences. While various methods have been proposed to tackle negations in search, none of them took the vocabulary gap between query keywords and product text into consideration. In this work, we introduced a query
-
2025Crafting effective features is a crucial yet labor-intensive and domain-specific task within machine learning pipelines. Fortunately, recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in automating various data science tasks, including feature engineering. But despite this potential, evaluations thus far are primarily based on the end performance of a complete ML pipeline, providing
-
2025In this paper, we tackle the novel computer vision problem of depth estimation through a translucent barrier. This is an important problem for robotics when manipulating objects through plastic wrapping, or when predicting the depth of items behind a translucent barrier for manipulation. We propose two approaches for providing depth prediction models the ability to see through translucent barriers: removing
Academia
View allWhether you're a faculty member or student, there are number of ways you can engage with Amazon.
View all