Today at the annual meeting of the ACM Special Interest Group on Information Retrieval (SIGIR), Ruhi Sarikaya, the director of applied science for Alexa AI, delivered a keynote address titled “Intelligent Conversational Agents for Ambient Computing”. This is an edited version of that talk.
.@Ruhi_Sarikaya (@amazon Alexa) is now giving the 3rd #SIGIR2022 keynote.
— SIGIR 2022 😷 (@SIGIRConf) July 14, 2022
First time Ruhi is attending SIGIR, surely not the last one! pic.twitter.com/KL0SnPq2CS
For decades, the paradigm of personal computing was a desktop machine. Then came the laptop, and finally mobile devices so small we can hold them in our hands and carry them in our pockets, which felt revolutionary.
All these devices, however, tether you to a screen. For the most part, you need to physically touch them to use them, which does not seem natural or convenient in a number of situations.
So what comes next?
The most likely answer is the Internet of things (IOT) and other intelligent, connected systems and services. What will the interface with the IOT be? Will you need a separate app on your phone for each connected device? Or when you walk into a room, will you simply speak to the device you want to reconfigure?
At Alexa, we’re betting that conversational AI will be the interface for the IOT. And this will mean a shift in our understanding of what conversational AI is.
In particular, the IOT creates new forms of context for conversational-AI models. By “context”, we mean the set of circumstances and facts that surround a particular event, situation, or entity, which an AI model can exploit to improve its performance.
For instance, context can help resolve ambiguities. Here are some examples of what we mean by context:
- Device state: If the oven is on, then the question “What is the temperature?” is more likely to refer to oven temperature than it is in other contexts.
- Device types: If the device has a screen, it’s more likely that “play Hunger Games” refers to the movie than if the device has no screen.
- Physical/digital activity: If a customer listens only to jazz, “Play music” should elicit a different response than if the customer listens only to hard rock; if the customer always makes coffee after the alarm goes off, that should influence the interpretation of a command like “start brewing”.
The same type of reasoning applies to other contextual signals, such as time of day, device and user location, environmental changes as measured by sensors, and so on.
Training a conversational agent to factor in so many contextual signals is much more complicated than training it to recognize, say, song titles. Ideally, we would have a substantial number of training examples for every combination of customer, device, and context, but that’s obviously not practical. So how do we scale the training of contextually aware conversational agents?
Self-learning
The answer is self-learning. By self-learning, we mean a framework that enables an autonomous agent to learn from customer-system interactions, system signals, and predictive models.
Customer-system interactions can provide both implicit feedback and explicit feedback. Alexa already handles both. If a customer interrupts Alexa’s response to a request — a “barge-in”, as we call it — or rephrases the request, that’s implicit feedback. Aggregated across multiple customers, barge-ins and rephrases indicate requests that aren’t being processed correctly.
Customers can also explicitly teach Alexa how to handle particular requests. This can be customer-initiated, as when customers use Alexa’s interactive-teaching capability, or Alexa-initiated, as when Alexa asks, “Did I answer your question?”
The great advantages of self-learning are that it doesn’t require data annotation, so it scales better while protecting customer privacy; it minimizes the time and cost of updating models; and it relies on high-value training data, because customers know best what they mean and want.
We have a few programs targeting different applications of self-learning, including automated generation of ground truth annotations, defect reduction, teachable AI, and determining root causes of failure.
Automated ground truth generation
At Alexa, we have launched a multiyear initiative to shift Alexa’s ML model development from manual-annotation-based to primarily self-learning-based. The challenge we face is to convert customer feedback, which is often binary or low dimensional (yes/no, defect/non-defect), into high-dimensional synthetic labels such as transcriptions and named-entity annotations.
Our approach has two major components: (1) an exploration module and (2) a feedback collection and label generation module. Here’s the architecture of the label generation model:
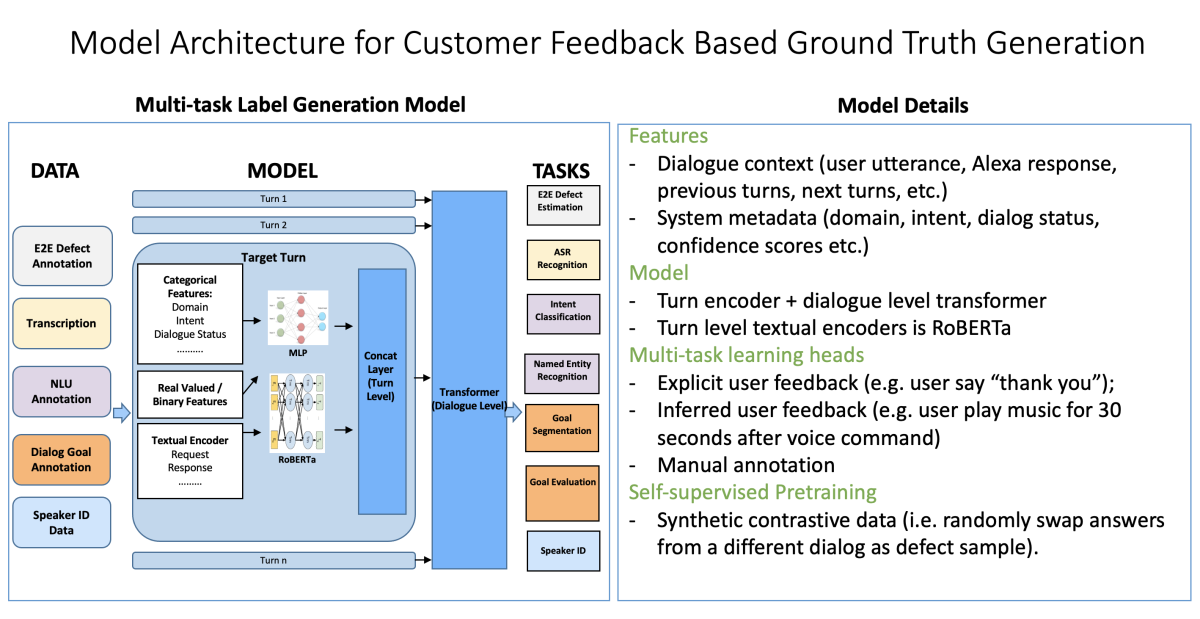
The input features include the dialogue context (user utterance, Alexa response, previous turns, next turns), categorical features (domain, intent, dialogue status), numerical features (number of tokens, speech recognition and natural-language-understanding confidence scores), and raw audio data. The model consists of a turn-level encoder and a dialogue-level Transformer-based encoder. The turn-level textual encoder is a pretrained RoBERTa model.
We pretrain the model in a self-supervised way, using synthetic contrastive data. For instance, we randomly swap answers from different dialogues as defect samples. After pretraining, the model is trained in a supervised fashion on multiple tasks, using explicit and implicit user feedback.
We evaluate the label generation model on several tasks. Two of these are goal segmentation, or determining which utterances in a dialogue are relevant to the accomplishment of a particular task, and goal evaluation, or determining whether the goal was successfully achieved.
As a baseline for these tasks, we used a set of annotations each of which was produced in a single pass by a single annotator. Our ground truth, for both the model and the baseline, was a set of annotations each of which had been corroborated by three different human annotators.
Our model’s outputs on both tasks were comparable to the human annotators’: our model was slightly more accurate but had a slightly lower F1 score. We can set a higher threshold, exceeding human performance significantly, and still achieve much larger annotation throughput than manual labeling does.
In addition to the goal-related labels, our model also labels utterances according to intent (the action the customer wants performed, such as playing music), slots (the data types the intent operates on, such as song names), and slot-values (the particular values of the slots, such as “Purple Haze”).
As a baseline for slot and intent labeling, we used a RoBERTa-based model that didn’t incorporate contextual information, and we found that our model outperformed it across the board.
Self-learning-based defect reduction
Three years ago, we deployed a self-learning mechanism that automatically corrects defects in Alexa’s interpretation of customer utterances based purely on implicit signals.
This mechanism — unlike the ground truth generation module — doesn’t involve retraining Alexa’s natural-language-understanding models. Instead, it overwrites those models’ outputs, to improve their accuracy.
There are two ways to provide rewrites:
- Precomputed rewriting produces request-rewrite pairs offline and loads them at run time. This process has no latency constraints, so it can use complex models, and during training, it can take advantage of rich offline signals such as user follow-up turns, user rephrases, Alexa responses, and video click-through rate. Its drawback is that at run time, it can’t take advantage of contextual information.
- Online rewriting leverages contextual information (e.g., previous dialogue turns, dialogue location, times) at run time to produce rewrites. It enables rewriting of long-tail-defect queries, but it must meet latency constraints, and its training can’t take advantage of offline information.
Precomputed rewriting
We’ve experimented with two different approaches to precomputing rewrite pairs, one that uses pretrained BERT models and one that uses absorbing Markov chains.
This slide illustrates the BERT-based approach:
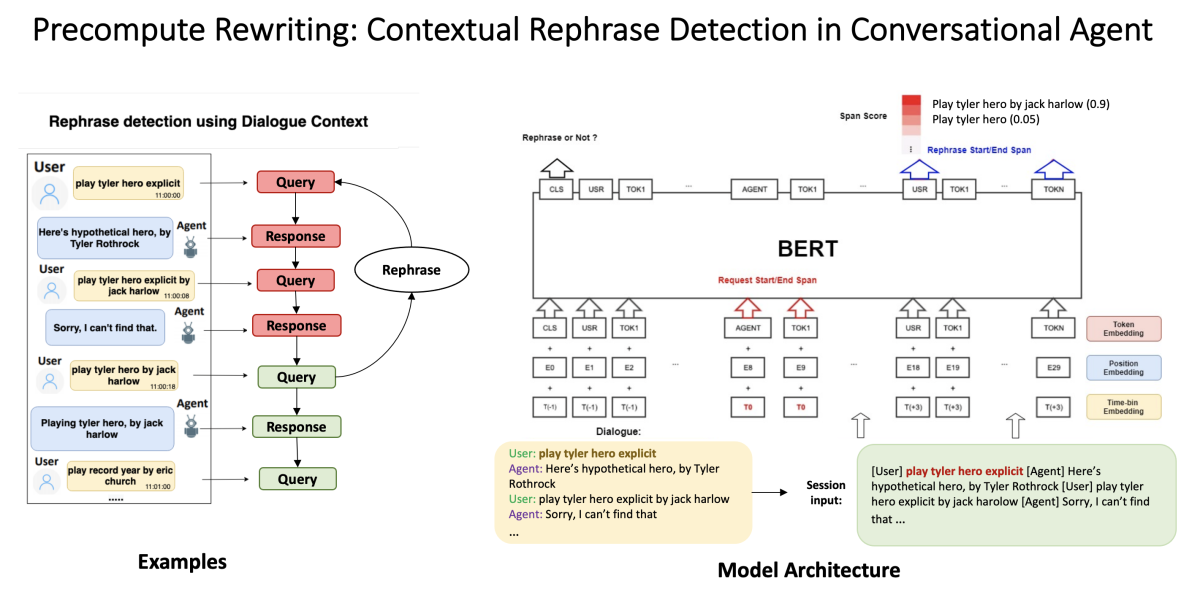
At left is a sample dialogue in which an Alexa customer rephrases a query twice. The second rephrase elicits the correct response, so it’s a good candidate for a rewrite of the initial query. The final query is not a rephrase, and the rephrase extraction model must learn to differentiate rephrases from unrelated queries.
We cast rephrase detection as a span prediction problem, where we predict the probability that each token is the start or end of a span, using the embedding output of the final BERT layer. We also use timestamping to threshold the number of subsequent customer requests that count as rephrase candidates.
We use absorbing Markov chains to extract rewrite pairs from rephrase candidates that recur across a wide range of interactions.
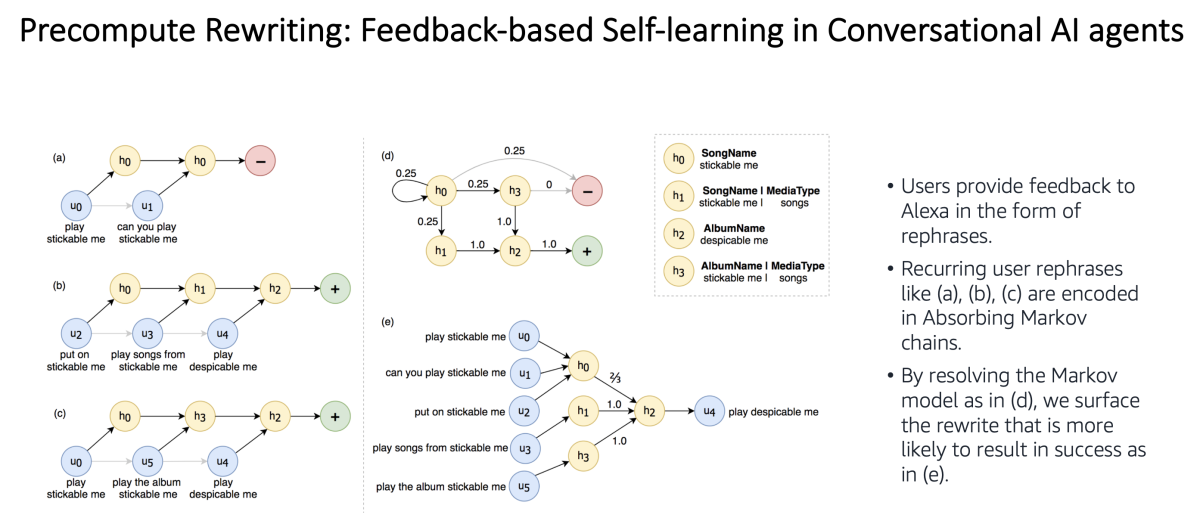
A Markov chain models a dynamic system as a sequence of states, each of which has a certain probability of transitioning to any of several other states. An absorbing Markov chain is one that has a final state, with zero probability of transitioning to any other, which is accessible from any other system state.
We use absorbing Markov chains to encode the probabilities that any given rephrase of the same query will follow any other across a range of interactions. Solving the Markov chain gives us the rewrite for any given request that is most likely to be successful.
Online rewriting
Instead of relying on customers’ own rephrasings, the online rewriting mechanism uses retrieval and ranking models to generate rewrites.
Rewrites are based on customers’ habitual usage patterns with the agent. In the example below, for instance, based on the customer’s interaction history, we rewrite the query “What’s the weather in Wilkerson?” as “What’s the weather in Wilkerson, California?” — even though “What’s the weather in Wilkerson, Washington?” is the more common query across interactions.
The model does, however, include a global layer as well as a personal layer, to prevent overindexing on personalized cases (for instance, inferring that a customer who likes the Selena Gomez song “We Don’t Talk Anymore” will also like the song from Encanto “We Don’t Talk about Bruno”) and to enable the model to provide rewrites when the customer’s interaction history provides little or no guidance.
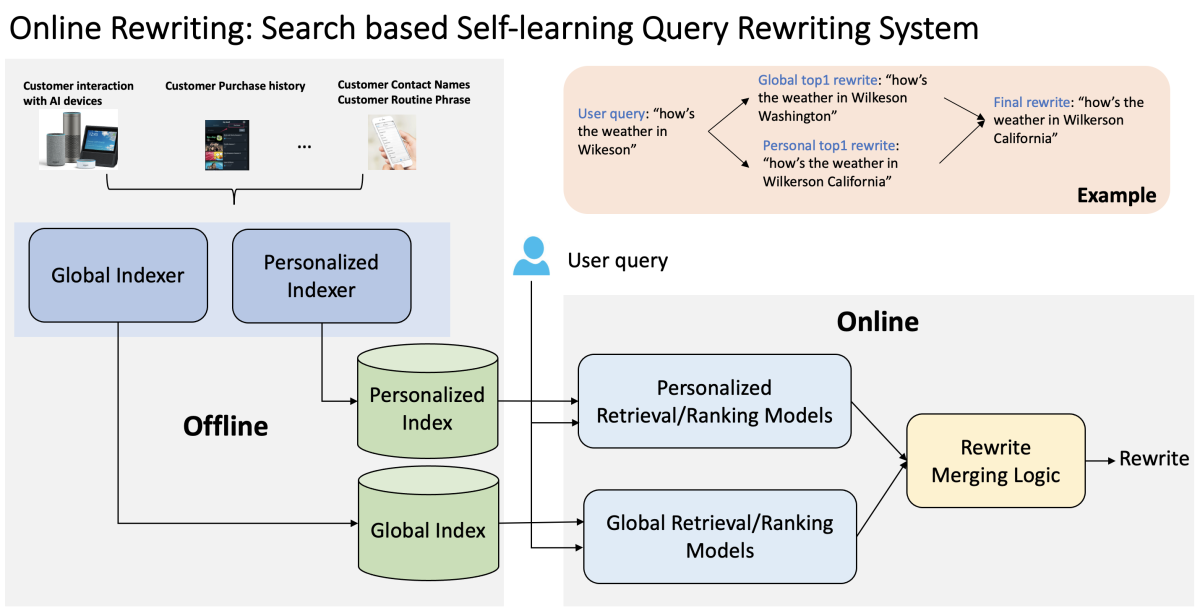
The personalized workstream and the global workstream include both retrieval and ranking models:
- The retrieval model uses a dense-passage-retrieval (DPR) model, which maps texts into a low-dimensional, continuous space, to extract embeddings for both the index and the query. Then it uses some similarity measurement to decide the rewrite score.
- The ranking model combines fuzzy match (e.g., through a single-encoder structure) with various metadata to make a reranking decision.
We’ve deployed all three of these self-learning approaches — BERT- and Markov-chain-based offline rewriting and online rewriting — and all have made a significant difference in the quality of Alexa customers’ experience.
In experiments, we compared the BERT-based offline approach to four baseline models on six machine-annotated and two human-annotated datasets, and it outperformed all baselines across the board, with improvements of as much as 16% to 17% on some of the machine-annotated datasets, while almost doubling the improvement on the human-annotated ones.
The offline approach that uses absorbing Markov chains has rewritten tens of millions of outputs from Alexa’s automatic-speech-recognition models, and it has a win-loss ratio of 8.5:1, meaning that for every one incorrect rewrite, it has 8.5 correct ones.
And finally, in a series of A/B tests of the online rewrite engine, we found that the global rewrite alone reduced the defect rate by 13%, while the addition of the personal rewrite model reduced defects by a further 4%.
Teachable AI
Query rewrites depend on implicit signals from customers, but customers can also explicitly teach Alexa their personal preferences, such as “I’m a Warriors fan” or “I like Italian restaurants.”
Alexa’s teachable-AI mechanism can be either customer-initiated or Alexa-initiated. Alexa proactively senses teachable moments — as when, for instance, a customer repeats the same request multiple times or declares Alexa’s response unsatisfactory. And a customer can initiate a guided Q&A with Alexa with a simple cue like “Alexa, learn my preferences.”
In either case, Alexa can use the customer’s preferences to guide the very next customer interaction.
Failure point isolation
Besides recovering from defects through query rewriting, we also want to understand the root cause of failures for defects.
Dialogue assistants like Alexa depend on multiple models that process customer requests in stages. First, a voice trigger (or “wake word”) model determines whether the user is speaking to the assistant. Then an automatic-speech-recognition (ASR) module converts the audio stream into text. This text passes to a natural-language-understanding (NLU) component that determines the user request. An entity recognition model recognizes and resolves entities, and the assistant generates the best possible response using several subsystems. Finally, the text-to-speech (TTS) model renders the response into human-like speech.
For Alexa, part of self-learning is automatically determining, when a failure occurs, which component has failed. An error in an upstream component can propagate through the pipeline, in which case multiple components may fail. Thus, we focus on the first component that fails in a way that is irrecoverable, which we call the “failure point”.
In our initial work on failure point isolation, we recognize five error points as well as a “correct” class (meaning no component failed). The possible failure points are false wake (errors in voice trigger); ASR errors; NLU errors (for example, incorrectly routing “play Harry Potter” to video instead of audiobook); entity resolution and recognition errors; and result errors (for example, playing the wrong Harry Potter movie).
To better illustrate failure point problem, let's examine a multiturn dialogue:
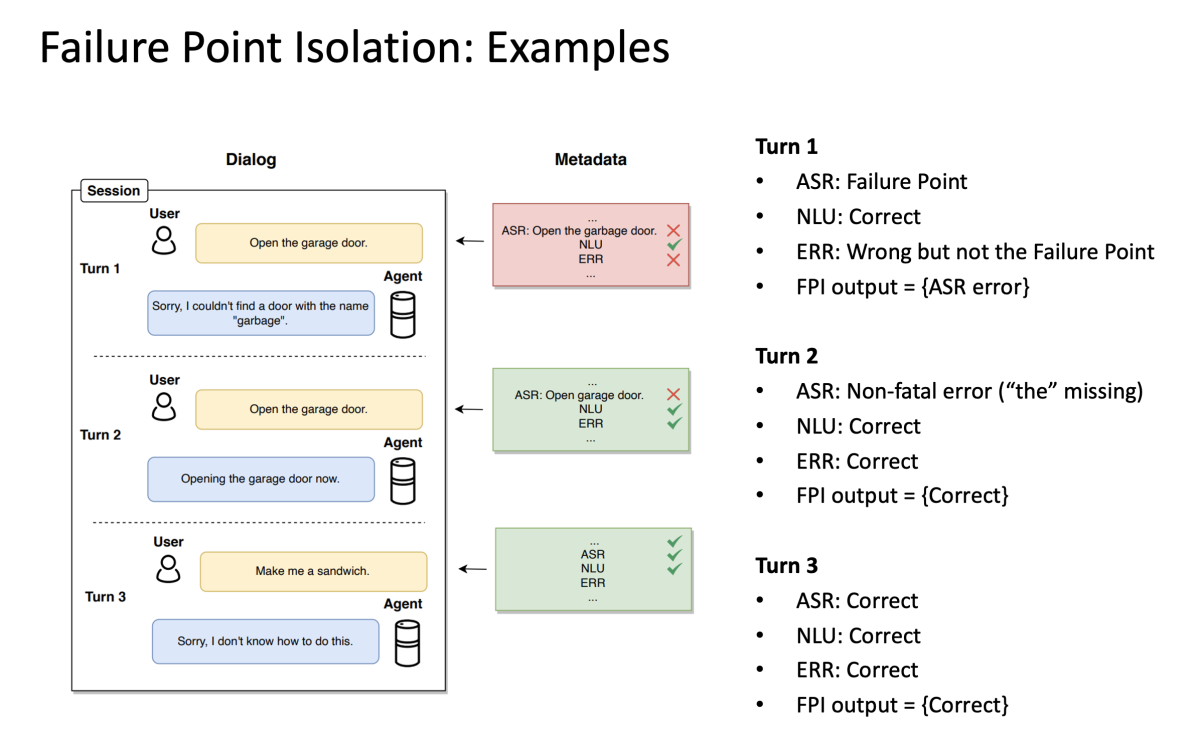
In the first turn, the customer is trying to open a garage door, and the conversational assistant recognizes the speech incorrectly. The entity resolution model doesn't recover from this error and also fails. Finally, the dialogue assistant fails to perform the correct action. In this case, ASR is the failure point, despite the other models’ subsequent failure.
On the second turn, the customer repeats the request. ASR makes a small error by not recognizing the article "the" in the speech, but the dialogue assistant takes the correct action. We would mark this turn as correct, as the ASR error didn't lead to downstream failure.
The last turn highlights one of the limitations of our method. The user is asking the dialogue assistant to make a sandwich, which dialogue assistants cannot do — yet. All models have worked correctly, but the user is not satisfied. In our work, we do not consider such turns defective.
On average, our best failure point isolation model achieves close to human performance across different categories (>92% vs human). This model uses extended dialogue context, features derived from logs of the assistants (e.g., ASR confidence), and traces of decision-making components (e.g., NLU modules). We outperform humans in result and correct-class detection. ASR, entity resolution, and NLU are in the 90-95% range.
The day when computing fades into the environment, and we walk from room to room casually instructing embedded computing devices how we want them to behave, may still lie in the future. But at Alexa AI, we’re already a long way down that path. And we’re moving farther forward every day.