Customer interactions with Alexa are constantly growing more complex, and on the Alexa science team, we strive to stay ahead of the curve by continuously improving Alexa’s speech recognition system.
Increasingly, keeping pace with Alexa’s expanding capabilities will require automating the learning process, through techniques such as semi-supervised learning, which leverages a small amount of annotated data to extract information from a much larger store of unannotated data.
At this year’s International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Alexa senior principal scientist Nikko Strom and I will report what amounts to a large-scale experiment in semi-supervised learning. We developed an acoustic model, a key component of a speech recognition system, using just 7,000 hours of annotated data and 1 million hours of unannotated data. To our knowledge, the largest data set previously used to train an acoustic model was 125,000 hours. In our paper, we describe a number of techniques that, in combination, made it computationally feasible to scale to a dataset eight times that size.
Compared to a model trained only on the annotated data, our semi-supervised model reduces the speech recognition error rate by 10% to 22%, with greater improvements coming on noisier data. We are currently working to integrate the new model into Alexa, with a projected release date of later this year.
As valuable as the model is in delivering better performance, it’s equally valuable for what it taught us about doing machine learning at scale.
Automatic speech recognition systems typically comprise three components: an acoustic model, which translates audio signals into phones, the smallest phonetic units of speech; a pronunciation model, which stitches phones into words; and a language model, which distinguishes between competing interpretations of the same phonetic sequences by evaluating the relative probabilities of different word sequences. Our new work concentrates on just the first stage in this process, acoustic modeling.
To build our model, we turned to a semi-supervised-learning technique called teacher-student training. Using our 7,000 hours of labeled data, we trained a powerful but impractically slow “teacher” network to convert frequency-level descriptions of audio data into sequences of phones. Then we used the teacher to automatically label unannotated data, which we used to train a leaner, more efficient “student” network.
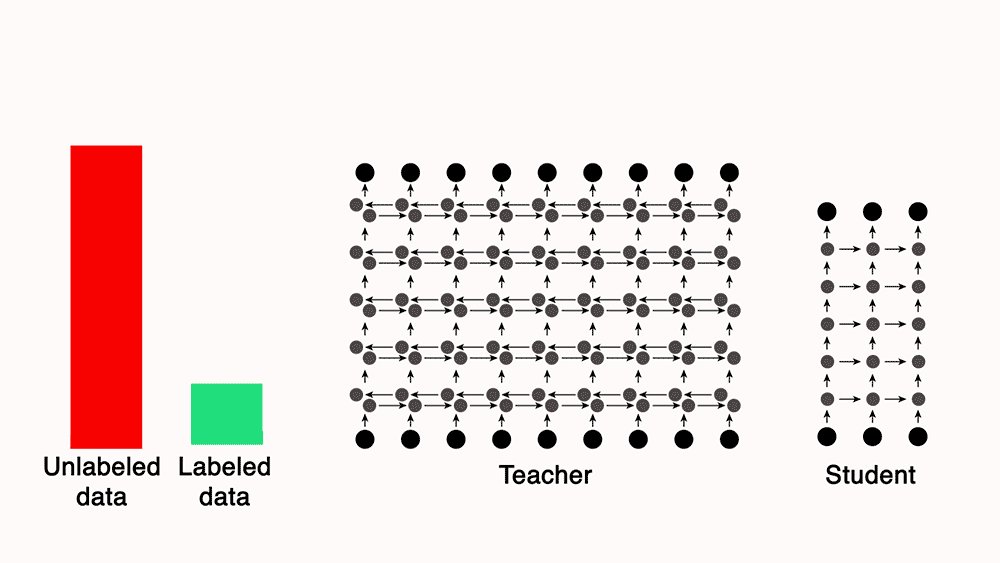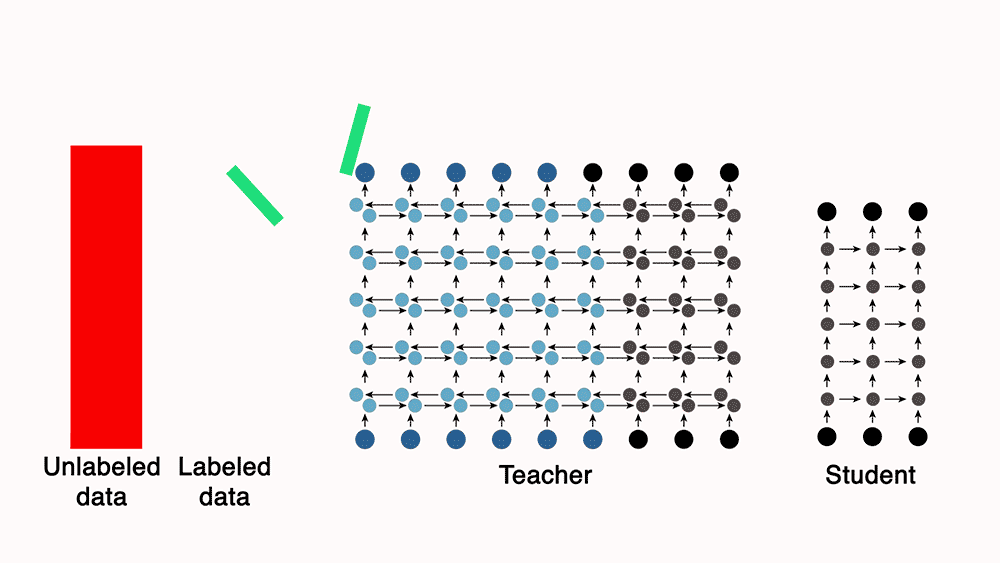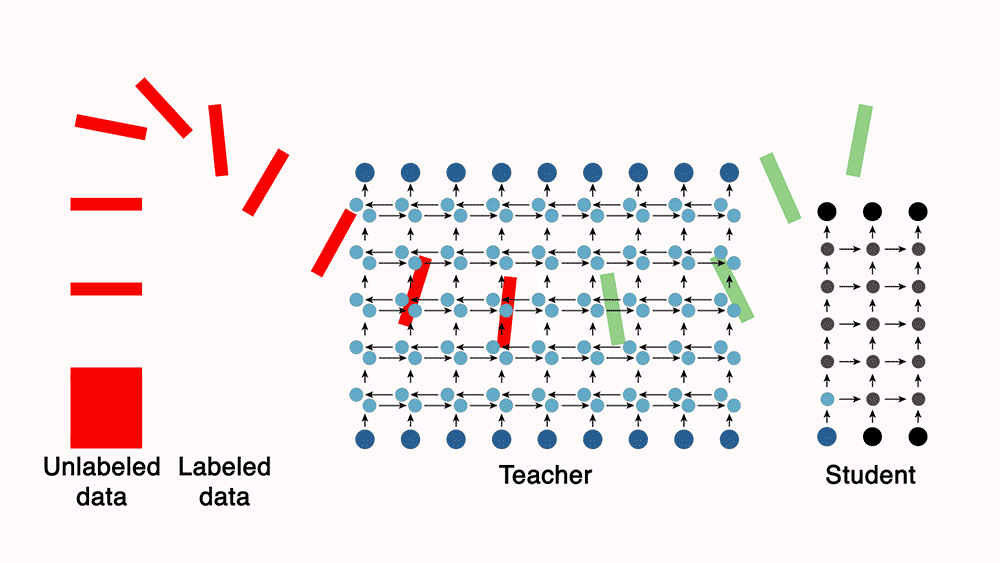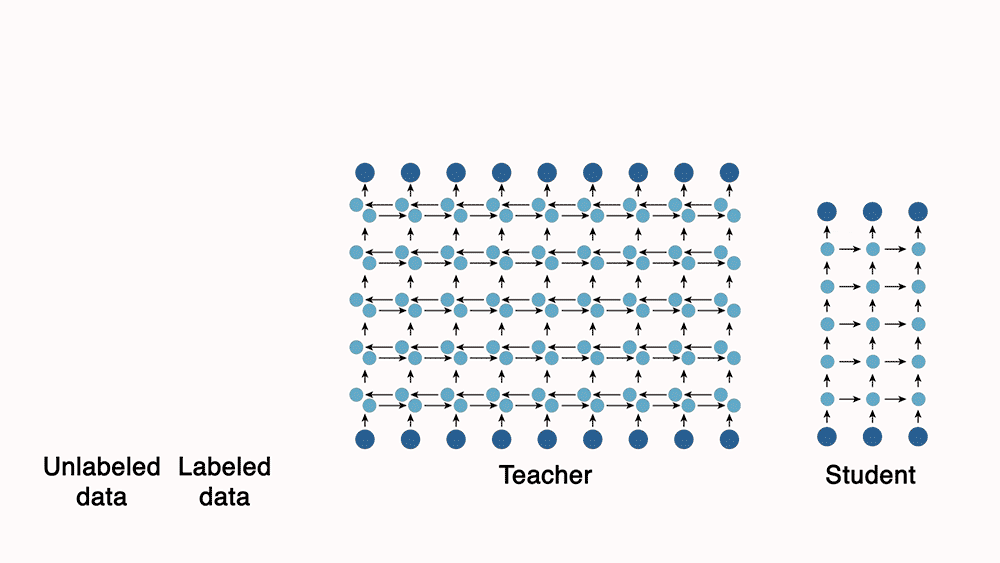
Both the teacher and the student were five-layer long-short-term-memory (LSTM) networks. LSTMs are common in speech and language applications because they process data in sequence, and the output corresponding to any given input factors in the inputs and outputs that preceded it.
The teacher LSTM is more than three times the size of the student — 78 million parameters, versus 24 million — which makes it more than three times as slow. It’s also bidirectional, which means that it processes every input sequence both forward and backward. Bidirectional processing generally improves an LSTM’s accuracy, but it also requires that the input sequence be complete before it’s fed to the network. That’s impractical for a real-time, interactive system like Alexa, so the student network runs only in the forward direction.
The inputs to both networks are split into 30-millisecond chunks, or “frames”, which are small enough that any given frame could belong to multiple phones. Phones, in turn, can sound different depending on the phones that precede and follow them, so the acoustic model doesn’t just associate each frame with a range of possible phones; it associates it with a range of possible three-phone sequences, or triphones.
In the classification scheme we use, there are more than 4 million such triphones, but we group them into roughly 3,000 clusters. Still, for every frame, the output of the model is a 3,000-dimensional vector, representing the probabilities that the phone belongs to each of the clusters.
Because the teacher is so slow, we want to store its outputs for quick lookup while we’re training the more efficient student. Storing a 3,000-dimensional vector for every frame of audio in the training set is impractical, so we instead keep only the 20 highest probabilities. During training, the student’s goal is to match all 20 of those probabilities as accurately as it can.
The 7,000 hours of annotated data are more accurately labeled than the machine-labeled data, so while training the student, we interleave the two. Our intuition was that if the machine-labeled data began to steer the model in the wrong direction, the annotated data could provide a course correction.
As a corollary, we also increased the model’s learning rate when it was being trained on the annotated data. Essentially, that means that it could make more dramatic adjustments to its internal settings than it could when being trained on machine-labeled data.
Our experiments bore out our intuitions. Interleaving the annotated data and machine-labeled data during training led to a 23% improvement in error rate reduction versus a training regimen that segregated them.
We also experimented with different techniques for parallelizing the training procedure. Optimizing the settings of a neural network is like exploring a landscape with peaks and valleys, except in millions of dimensions. The elevations of the landscape represent the network’s error rates on the training data, so the goal is to find the bottom of one of the deepest valleys.
We were using so much training data that we had to split it up among processors. But the topography of the error landscape is a function of the data, so each processor sees a different landscape.
Historically, the Alexa team has solved this problem through a method called gradient threshold compression (GTC). After working through a batch of data, each processor sends a compressed representation of the gradients it measured — the slopes of the inclines in the error landscape — to all the other processors. Each processor aggregates all the gradients and updates its copy of the neural model accordingly.
We found, however, that with enough processors working in parallel, this approach required the exchange of so much data that transmission time started to eat up the time savings from parallelization. So we also experimented with a technique called blockwise model update filtering (BMUF). With this approach, each processor updates only its own, local copy of the neural model after working through each batch of data. Only rarely — every 50 batches or so — does a processor broadcast its local copy of the model to the other processors, saving a great deal of communication bandwidth.
Where GTC averages gradients, BMUF averages models. But averaging gradients provides an exact solution of the optimization problem, whereas averaging models provides only an approximate solution. We found that, on the same volume of training data, BMUF yielded slightly less accurate models than GTC. But it enabled distribution of the computation to four times as many processors, which means that in a given time frame, it could learn from four times as much data. Or, alternatively, it could deliver comparable performance improvements in one-fourth the time.
We believe that these techniques — and a few others we describe in greater detail in the paper — will generalize to other applications of large-scale semi-supervised learning, a possibility that we have begun to explore in the Alexa AI group.
Acknowledgments: Nikko Strom

















