Recently, we published a paper showing that training a neural network to do language processing in English, then retraining it in German, drastically reduces the amount of German-language training data required to achieve a given level of performance.
This is an example of cross-lingual transfer learning, or adapting a machine learning model trained on abundant data in one language to a new linguistic context in which training data is sparse.
In a paper we’ll present in June, at the annual meeting of the North American chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, we expand the scope of cross-lingual transfer learning, reporting experiments in transferring an English-language model to Japanese.
Transfer learning between European languages and Japanese has been little explored because of the mismatch between character sets. We address this problem by taking as input to our Japanese system both Japanese characters and their Roman-alphabet transliterations.
We also perform extensive experiments to determine which aspects of the English-language model to transfer to Japanese, and our results are somewhat at odds with those reported in the literature on cross-lingual transfer learning. This is probably, again, because of the incompatibility of scripts.
In tests that involved two public data sets, we compared a transferred model, with Romanization of Japanese words, to a model trained from scratch on the same data. On the two data sets, the transferred model exhibited improvements of 5.9% and 7.4% in F1 score, a composite score that measures both false-positive and false-negative rates.
Our model — in both English and Japanese — is trained to do named-entity recognition, or to determine which words in an utterance are names and what categories the names fall into (song names, sports team names, city names, and so on).
Inputs to the model undergo two types of embedding, word embedding and character embedding. Embeddings are usually produced by neural networks, which are trained to represent data as vectors, or strings of coordinates. Those vectors define points in a multidimensional space, and the idea is that proximity in the space should indicate some sort of similarity between the underlying data items.
In natural-language-understanding systems, such as named-entity recognizers, that similarity is usually semantic: two words whose word embeddings are close to each other should have similar meanings.
The networks that produce character embeddings first split words into all of their component parts: two-letter components, three-letter components, and so on. Proximity in the character-embedding space indicates similarity between words’ subcomponents. Character embeddings are often a useful complement to word embeddings, because they enable machine learning systems to make educated guesses about the meanings of unfamiliar words on the basis of their roots, prefixes, and suffixes.
In our model, pairs of characters from each input word are embedded separately and then passed to a type of neural network called a bi-LSTM. An LSTM, or long short-term memory, processes sequenced inputs in order, so each output reflects the inputs and outputs that preceded it. A bi-LSTM processes the same input sequence — in this case, subword chunks of a single word — forward and backward.
We concatenate the output of the character-level bi-LSTM with the word-level embedding, and together they pass to another bi-LSTM. This bi-LSTM processes all the words of the input utterance in sequence, so its output is a rich representation that captures information about each input word’s roots and affixes, intrinsic meaning, and context within the sentence.
That representation passes to another network, which does the actual classifying of named entities.
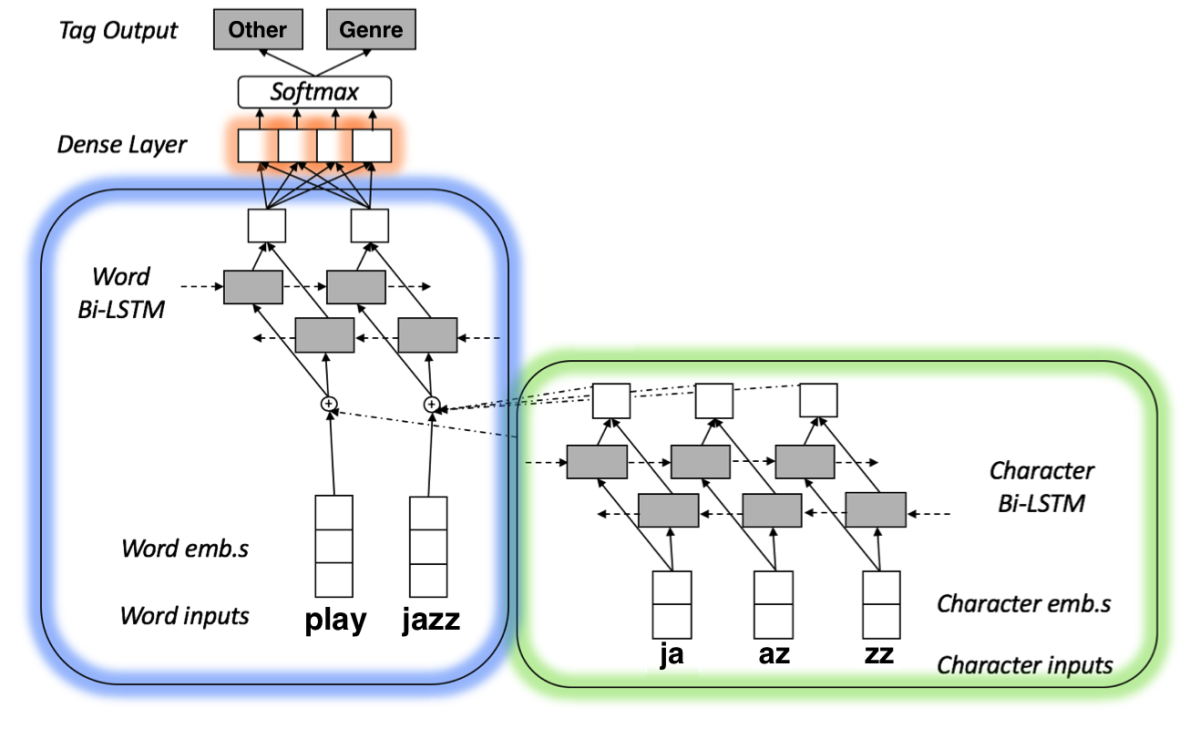
The whole network is trained end to end, so the embedding layers and bi-LSTMs learn to produce representations that are useful for named-entity recognition, and the classifier learns which characteristics of a representation indicate which entity types.
Our first experiment was to determine which of the three modules of our English-language network — the character representation module, the word representation module, and the classifier — should be transferred over to the Japanese context. We were experimenting with three different data sets — the two public data sets and our own proprietary data set — and a different combination of modules yielded the best results on each. Nonetheless, the combination with the best results across the board was of the classifier and the character-level representations.
This is at odds with results reported in the literature on cross-lingual transfer learning, where transfer of character representations alone often seems to be enough. The difference in our case may be the change of script between source and target languages.
After identifying the best-performing combination of transfer modules, we experimented with combinations of Japanese characters and their Romanized transliterations as inputs. We found that using Japanese characters as inputs to the word representation module, but Romanized characters as inputs to the character representation module, yielded mild increases in F1 score on all data sets.
The results of transfer learning were more dramatic on smaller data sets. On an in-house data set with 500,000 entries, the improvement in F1 score from transfer learning was only 0.6%. Nonetheless, the transferred model trained on 500,000 examples still outperformed a model trained from scratch on a million examples. So even at larger scales, transfer learning could still enable substantial reductions in data requirements.
Acknowledgments: Andrew Johnson, Penny Karanasou, Dietrich Klakow

















